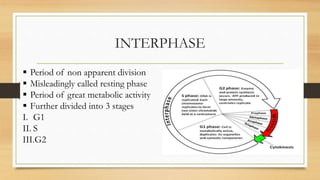
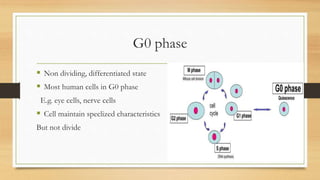
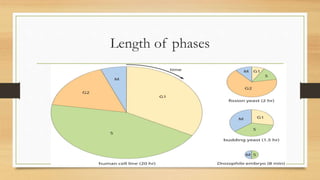
The document summarizes the cell cycle process. It discusses that the cell cycle involves a period of growth, DNA replication, and cell division. It is comprised of two main phases: interphase and mitosis. Interphase includes the G1, S, and G2 phases where the cell grows in size, DNA is replicated, and prepares for division. Mitosis is the phase where the cell undergoes division and separates the duplicated DNA between the two new daughter cells. The length of the cell cycle phases can vary depending on the type of cell.