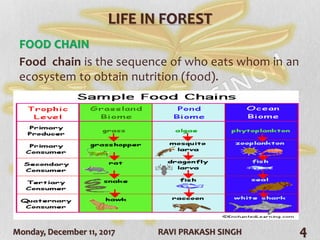
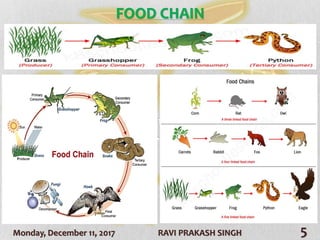
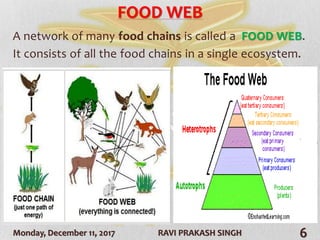
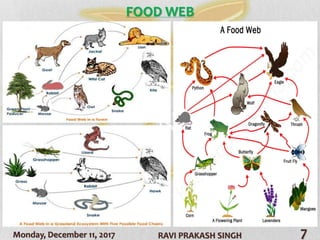
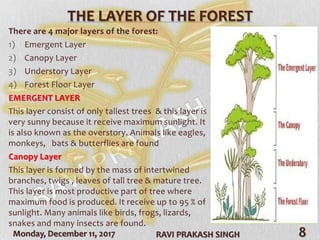
The document discusses forest ecosystems, covering their components (biotic and abiotic), food chains, and layers of the forest. It highlights the importance of forests for biodiversity, climate regulation, and human livelihoods, while addressing deforestation causes and consequences. Additionally, it lists common trees in India and their uses.