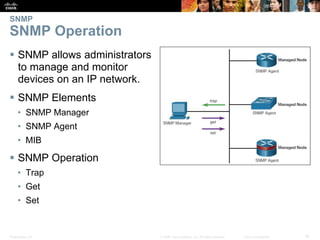
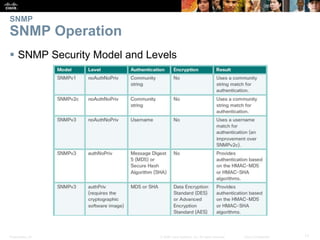
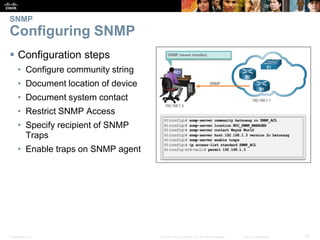
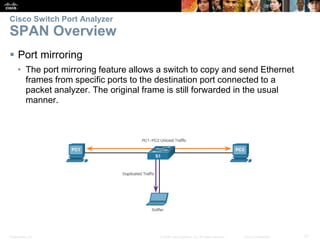
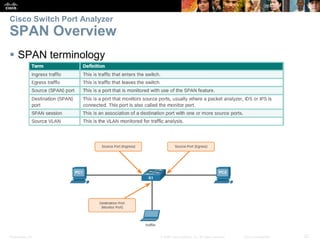
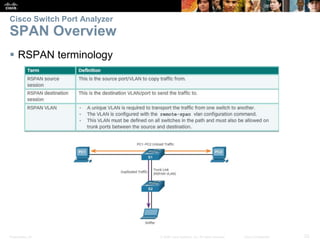
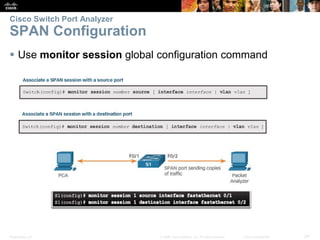
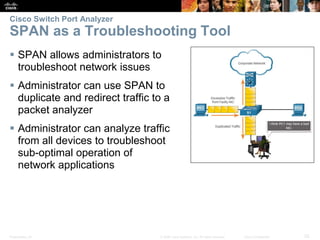
This document discusses network security and monitoring techniques in three sections. Section 5.1 covers LAN security best practices like port security and DHCP snooping to mitigate common attacks. Section 5.2 explains how SNMP allows network monitoring and configuration, including the elements of SNMP and securing SNMPv3. Section 5.3 introduces SPAN as a tool for troubleshooting network issues by duplicating and redirecting traffic to a packet analyzer.