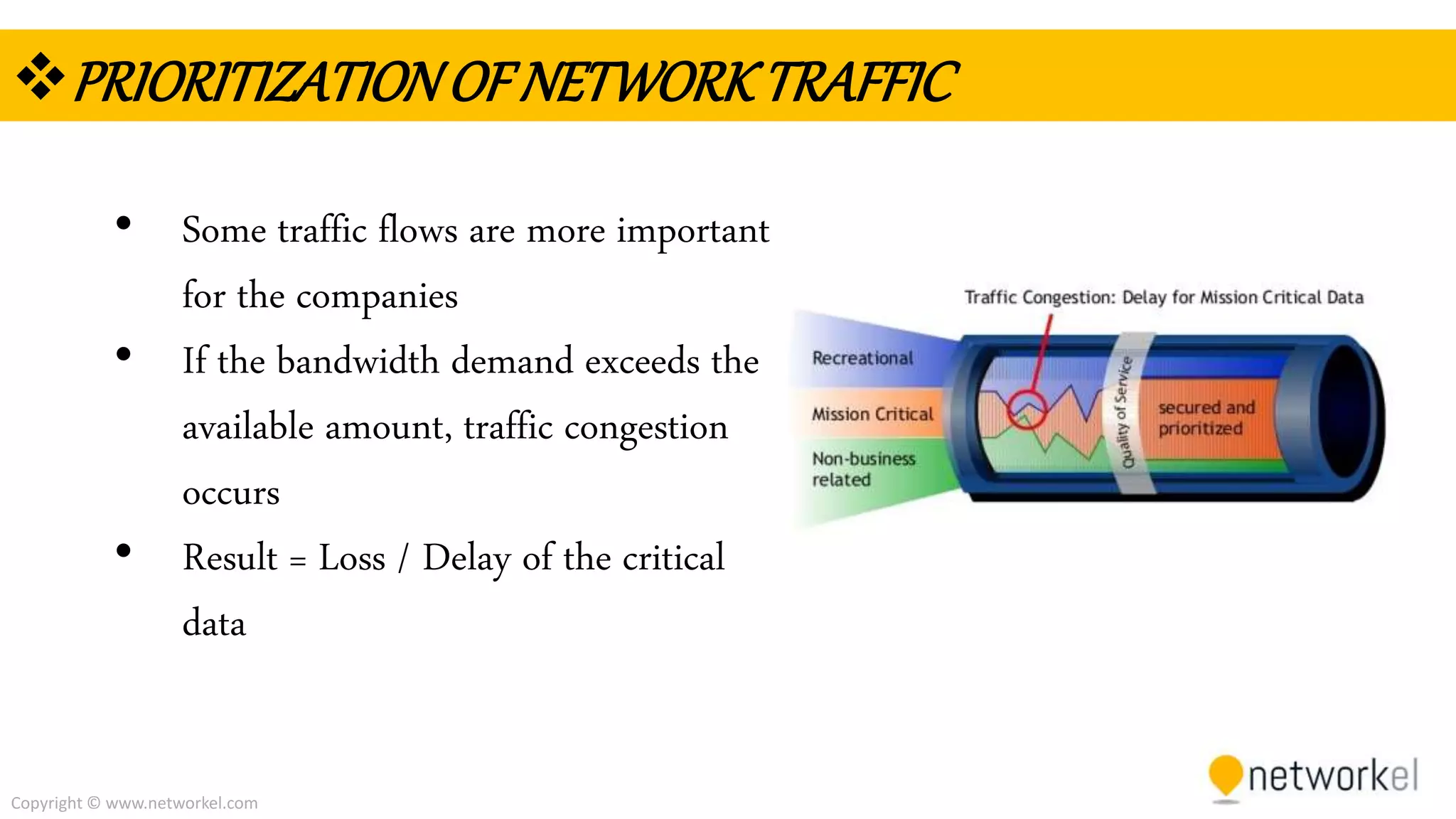
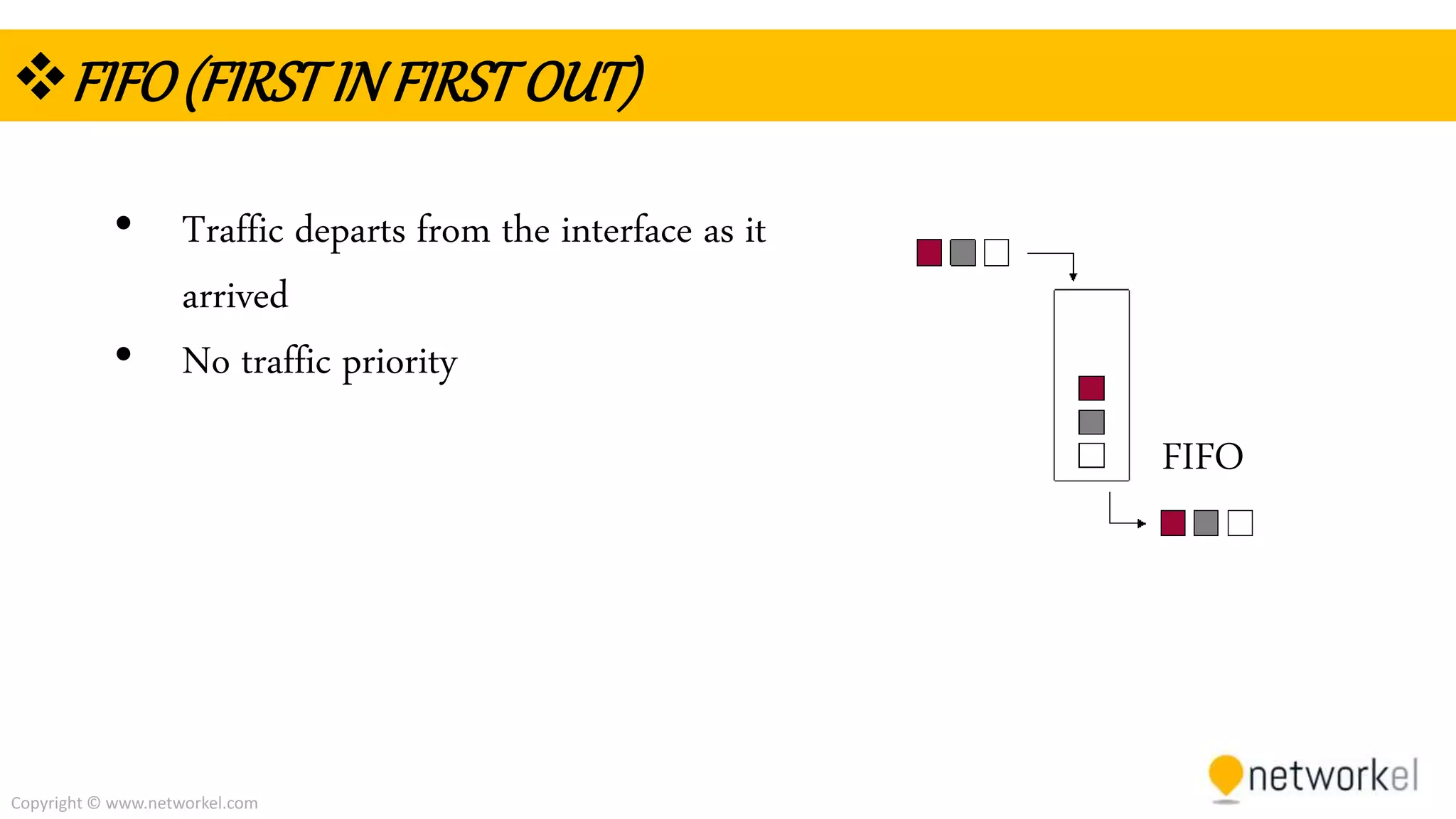
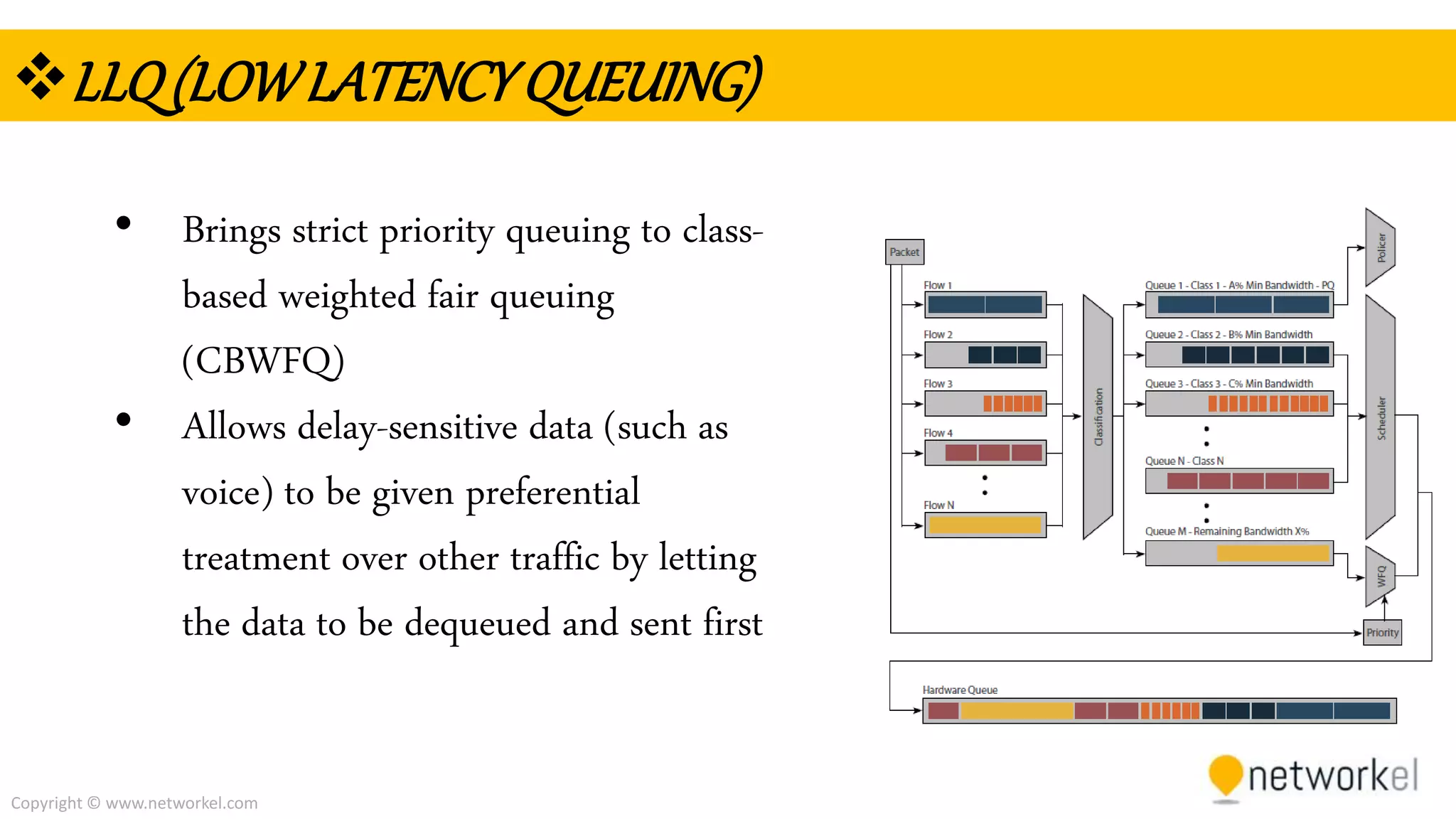
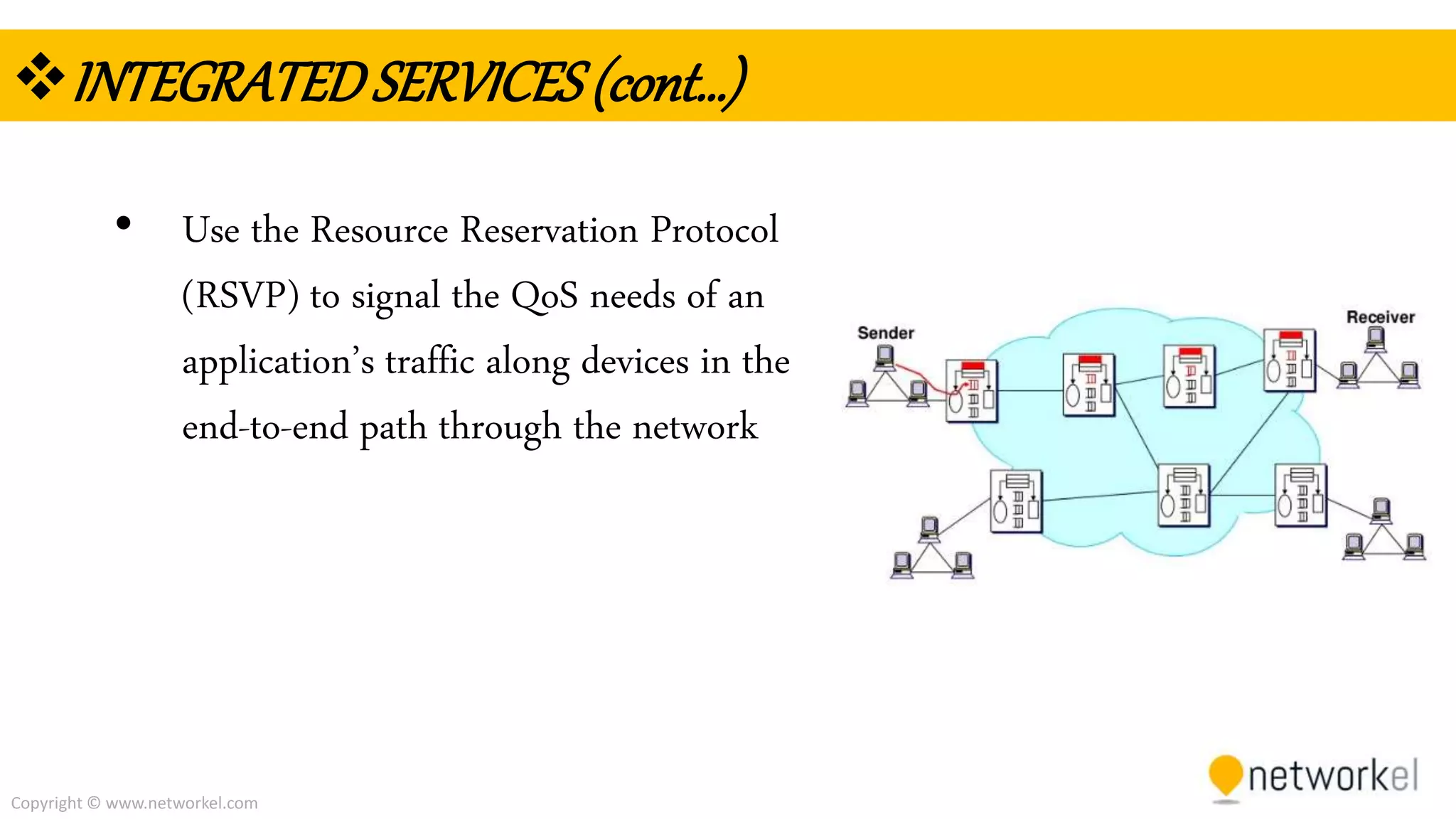
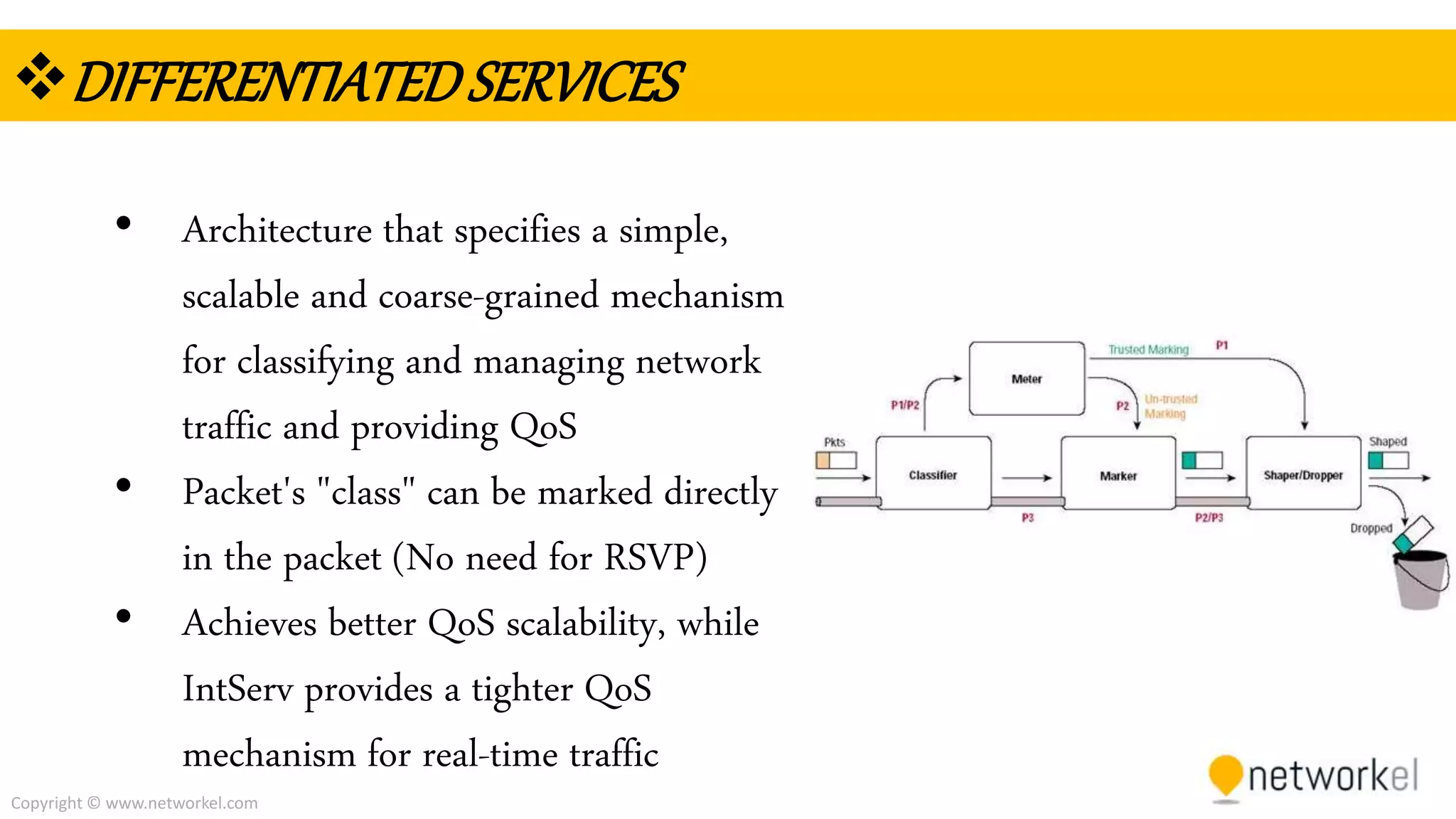
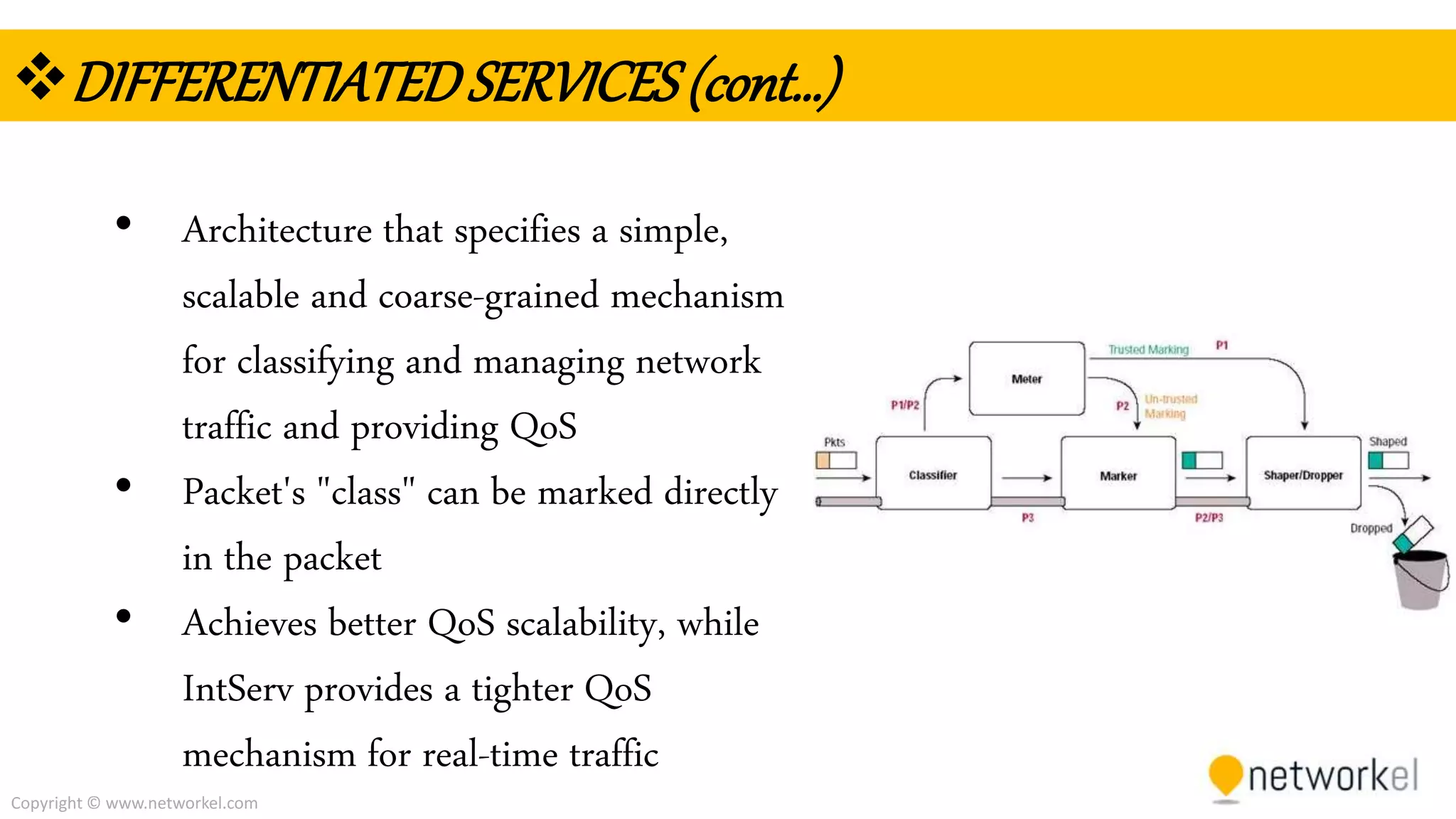
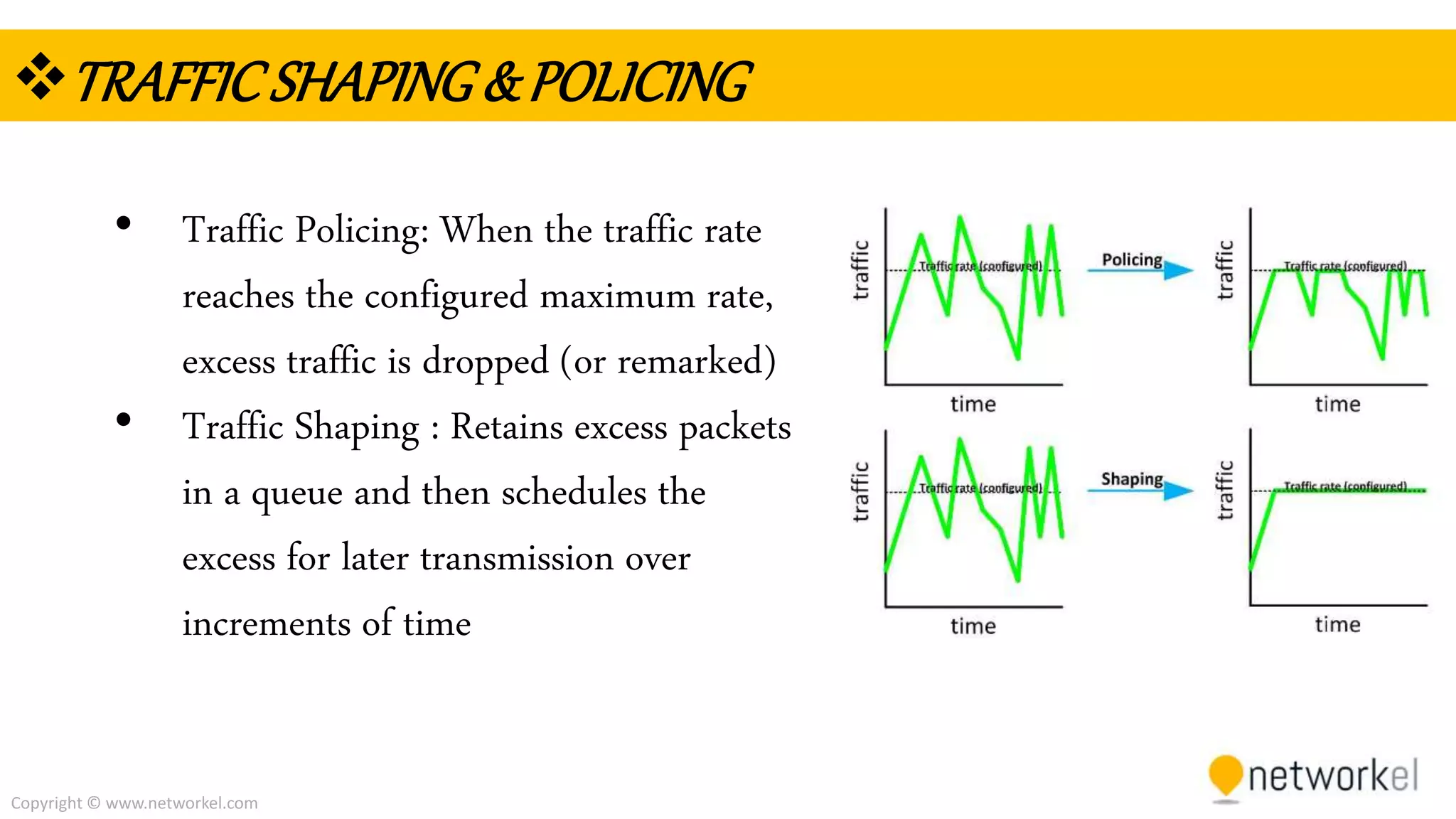
The document discusses quality of service (QoS) in computer networks. It provides an overview of QoS, including its goal of ensuring high-quality performance for critical applications by prioritizing certain network traffic over others. The document also outlines several QoS mechanisms like Integrated Services, Differentiated Services, and tools for classifying, marking, shaping, and policing network traffic to implement QoS. Common queuing algorithms used by network devices to prioritize traffic, such as FIFO, WFQ, CBWFQ, and LLQ are also summarized.