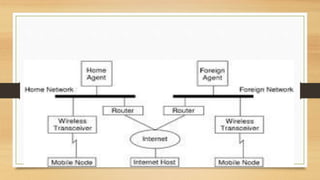
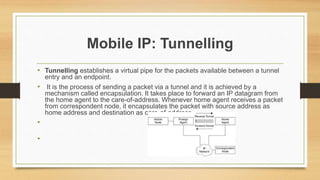
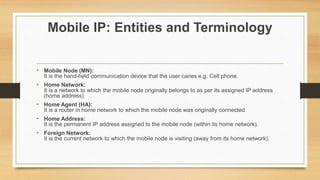
Mobile IP is an Internet protocol that allows mobile devices to stay connected to the Internet as they move between different networks. It enables a mobile device to use a temporary IP address in a foreign network while keeping its permanent IP address. When a packet needs to be sent to the mobile device, the home agent intercepts it and tunnels it to the device's current location using its care-of address. This allows the mobile device to maintain ongoing connections despite changing networks.