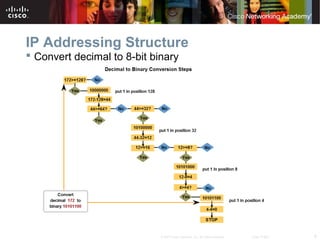
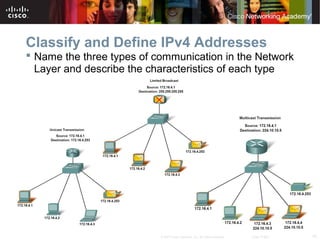
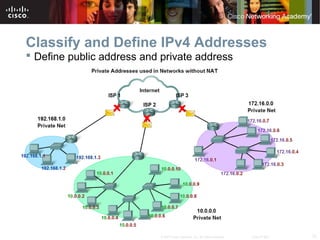
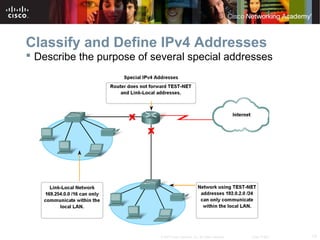
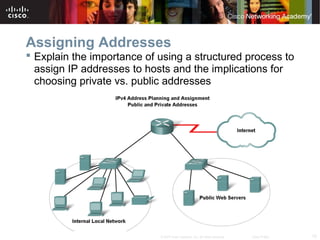
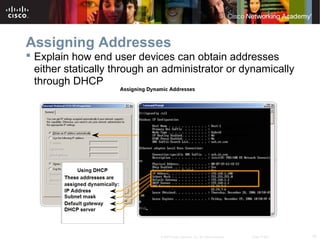
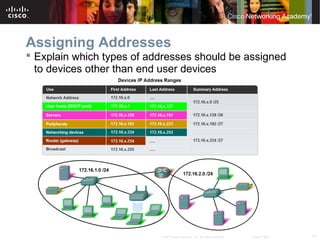
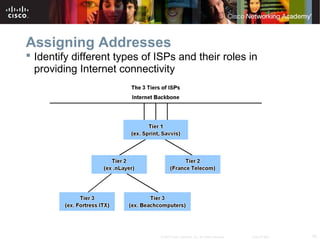
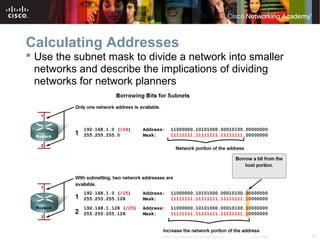
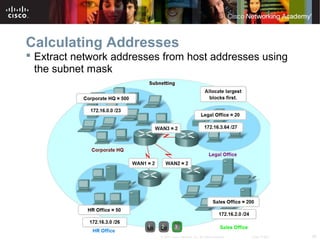
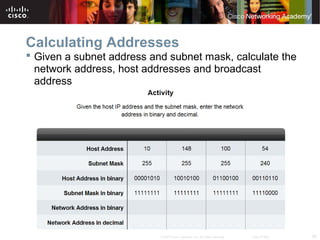
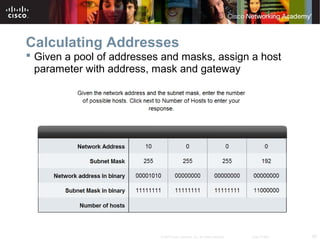
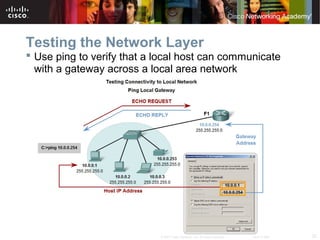
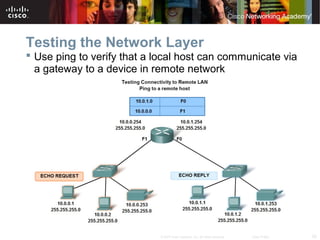
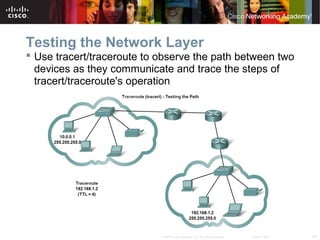
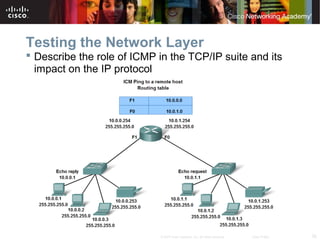
This document outlines objectives for learning about IPv4 addressing and network fundamentals. It will cover IP address structure and notation, address classification, public and private addresses, address assignment methods, subnetting using subnet masks, network address calculation, and testing network connectivity using tools like ping and traceroute. The overall goal is to teach students how to work with IP addresses and design effective IP networks.