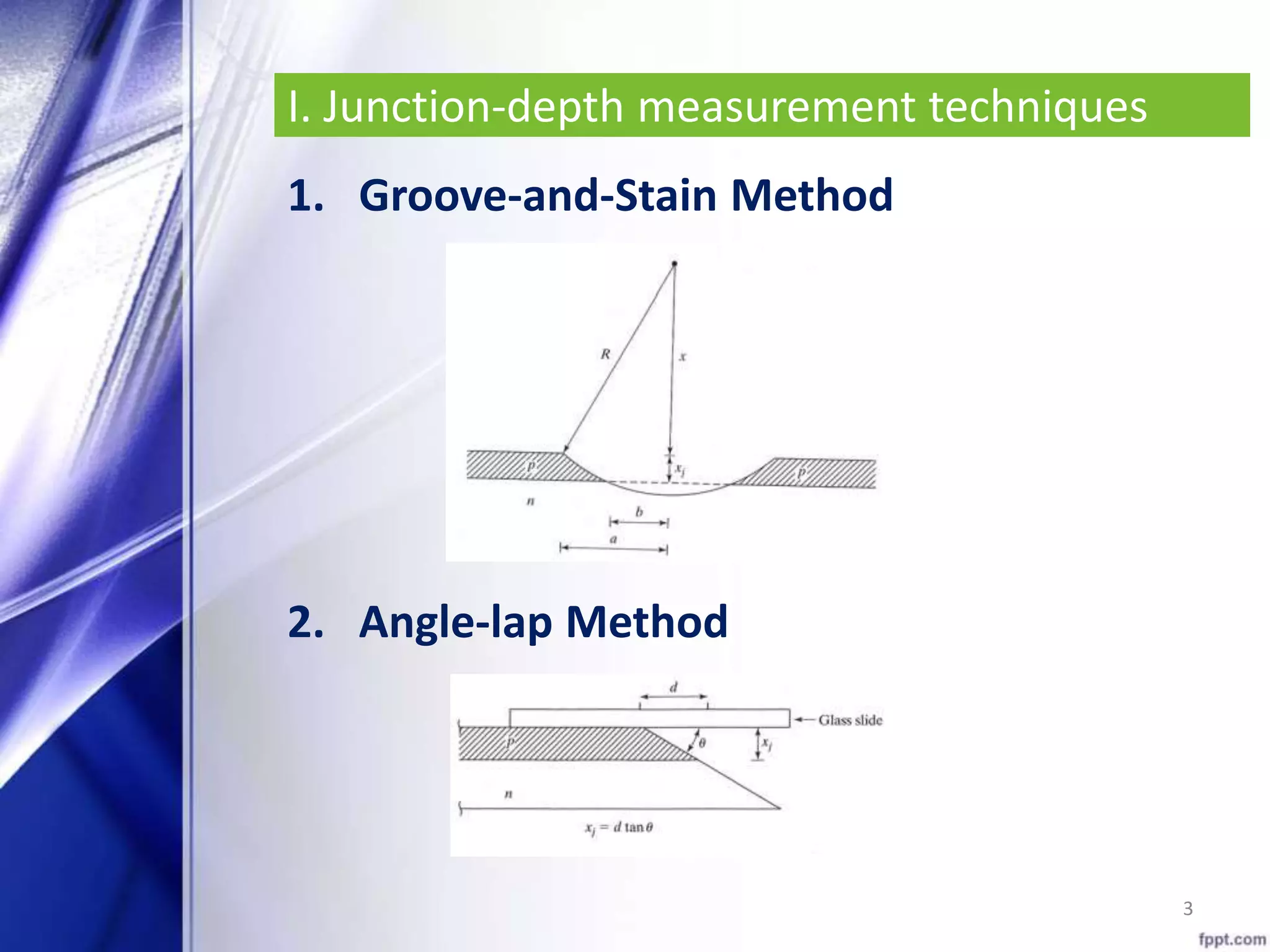
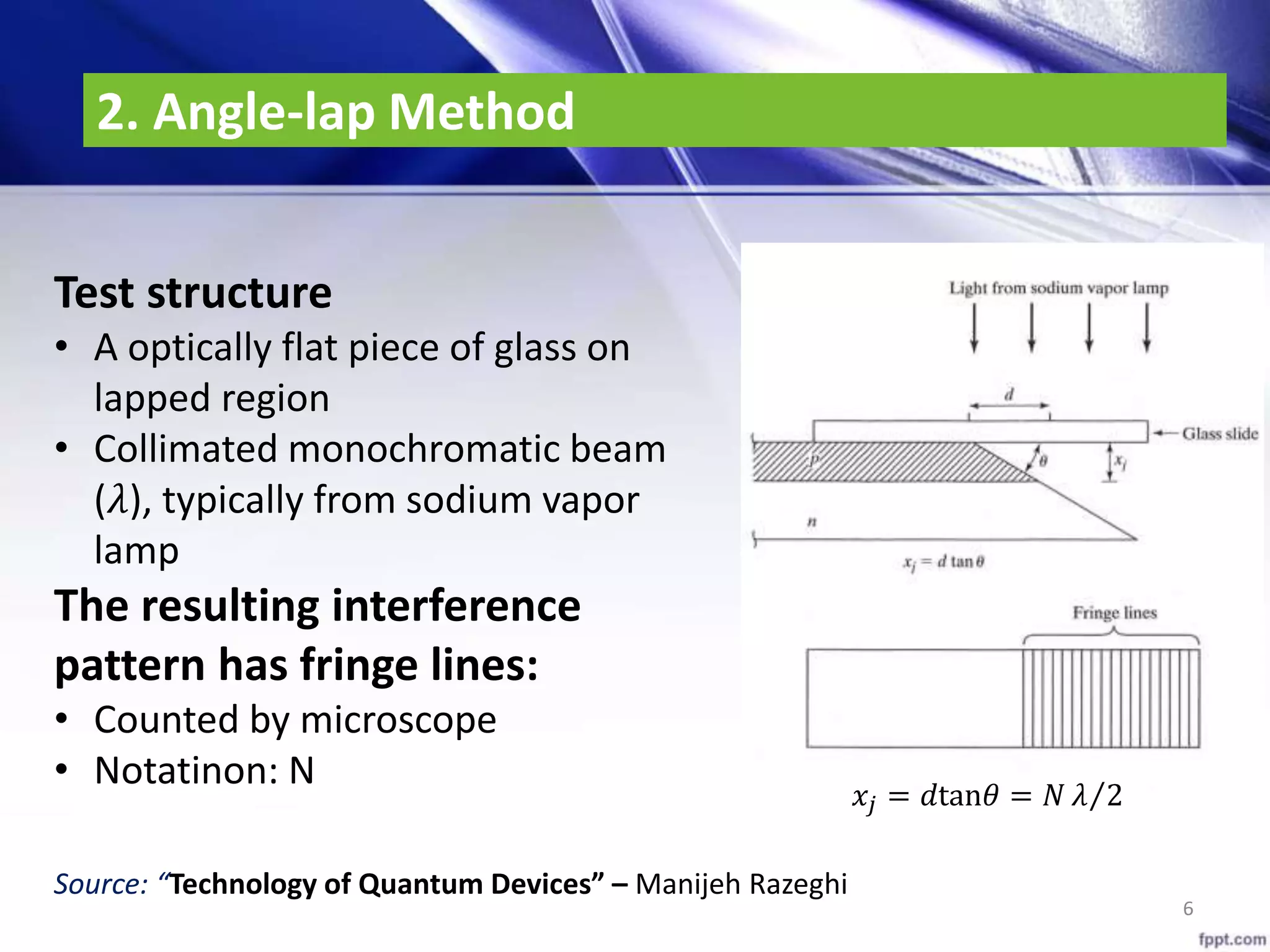
This document discusses techniques for measuring junction depth and sheet resistance of diffused layers. It describes two common junction depth measurement methods: the groove-and-stain method which uses etching and staining to measure junction depth, and the angle-lap method which mounts and laps the wafer edge to create an interference pattern for measurement. The document also outlines two sheet resistance measurement techniques: the four-point probe method for infinite sheets, and Van der Pauw's method which applies a correction factor to resistance measurements taken from multiple contacts.


![II. Sheet-resitance measurement techniques
7
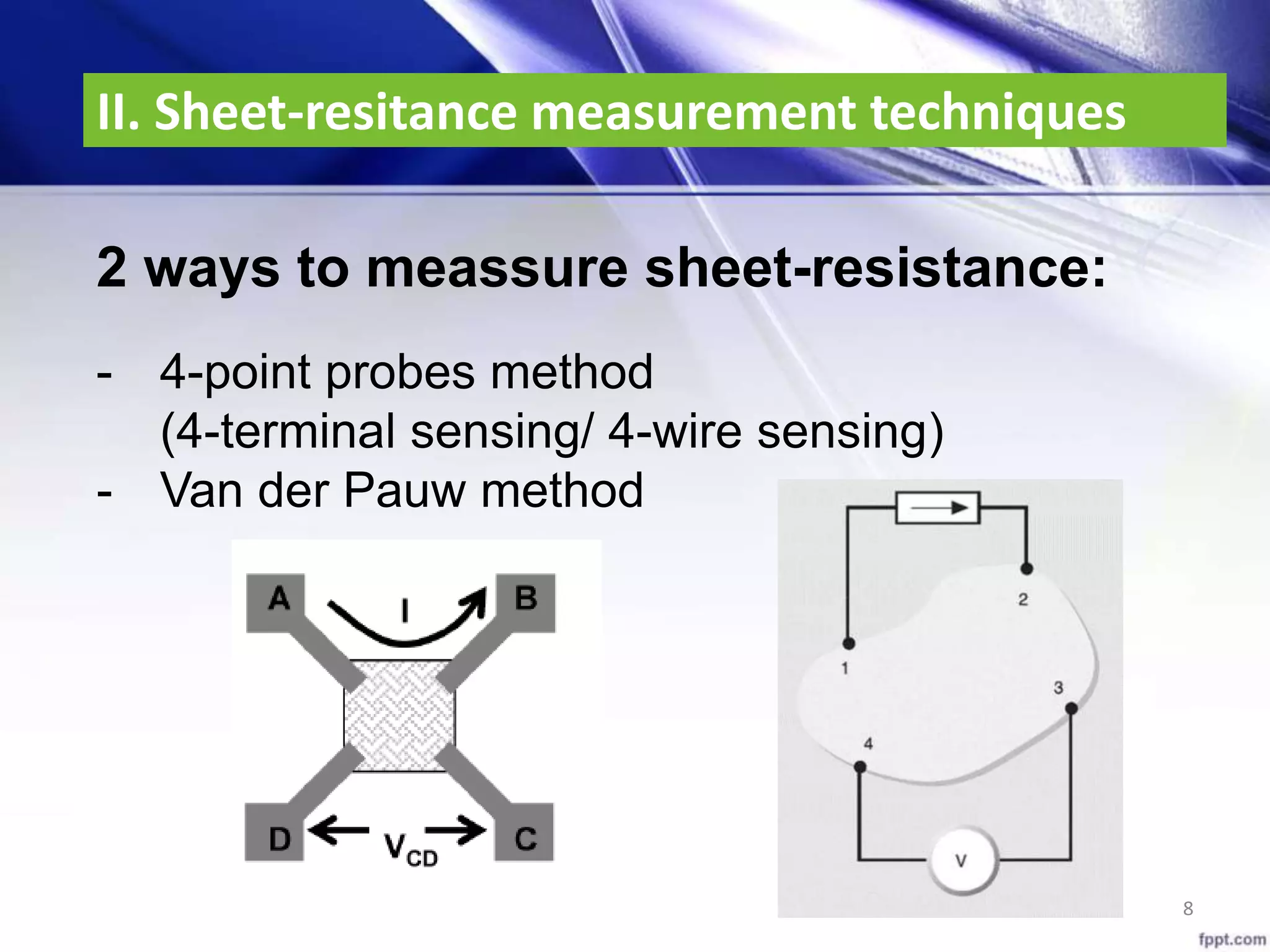
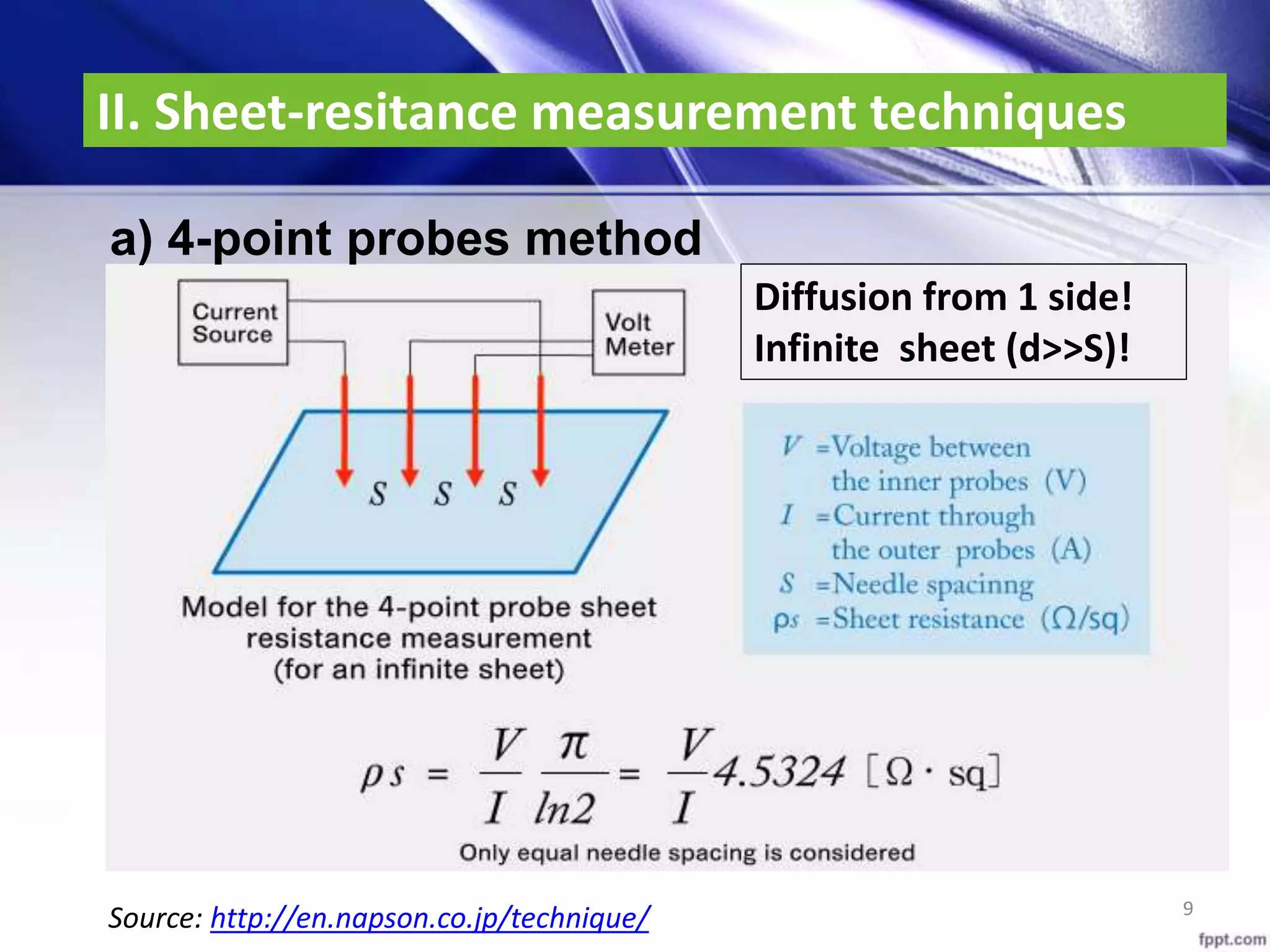
Sheet-resitance = Ω/□ (ohm per square) (*)
𝑹 𝑺 = [𝒒 𝝁 𝑪 𝑪 𝒆 𝒙 𝒅𝒙]−𝟏
[𝜴 /□]
𝐶𝑒 𝑥 : dopant concentration; 𝜇 𝐶 : mobility depend on concentration
𝑅 𝑆: square-resistance
When it expresses the electrical
resistance of a sheet (such as a thin
film or a film-like substance), this
sheet-resitance is used. R = ρ × L/A = L/W ×ρs
ρ 𝑺 = ρ/t (t: thickness)
For semiconductors:
(*) Source: http://en.napson.co.jp/technique/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/junction-depthsheet-resitancemeassurement-161207065345/75/Junction-depth-Sheet-resitance-meassurement-7-2048.jpg)
![II. Sheet-resitance measurement techniques
11
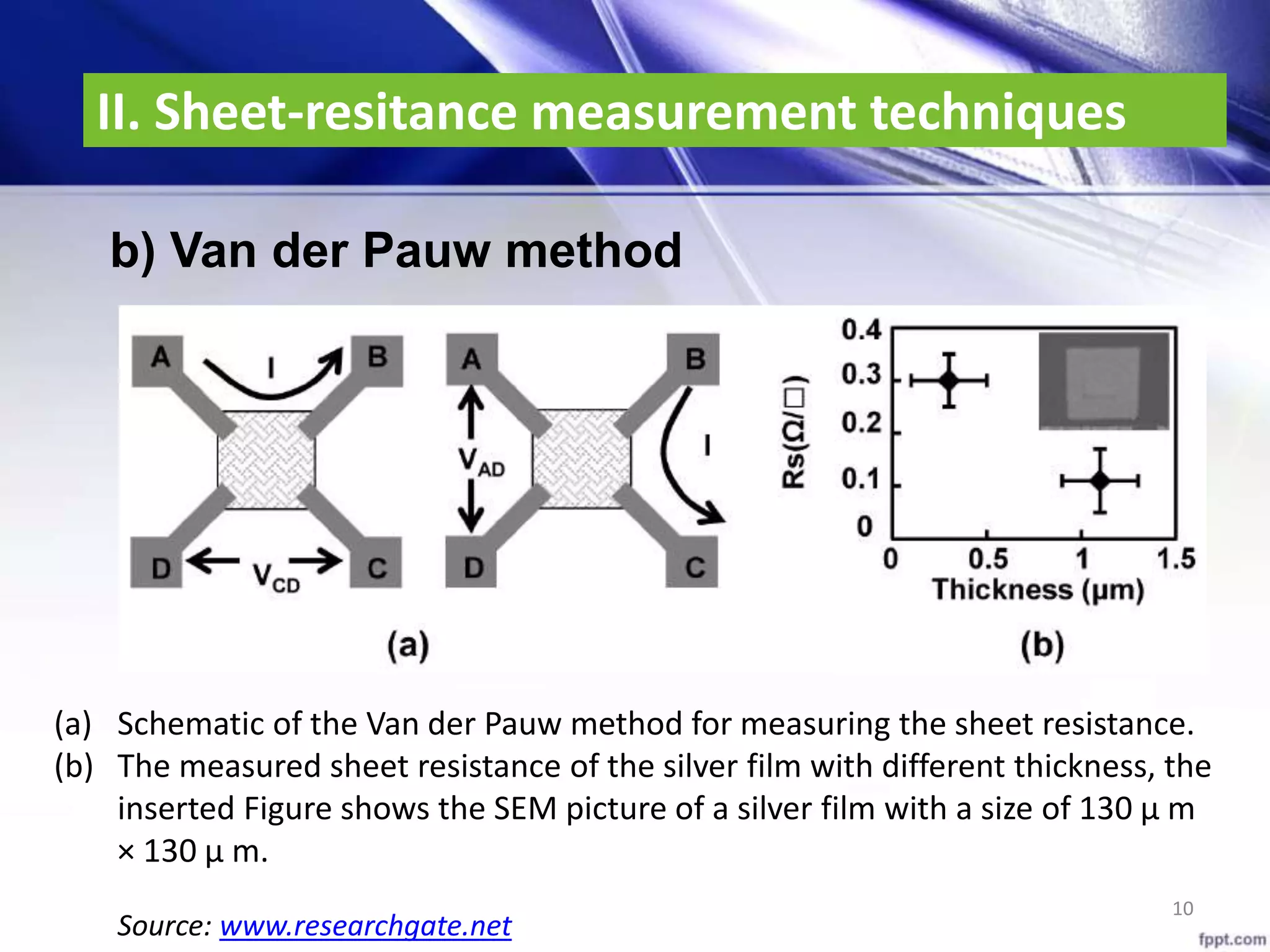
b) Van der Pauw method
𝑹 =
𝟏
𝟒
[
𝑽 𝟏𝟐
𝑰 𝟑𝟒
+
𝑽 𝟐𝟑
𝑰 𝟒𝟏
+
𝑽 𝟑𝟒
𝑰 𝟏𝟐
+
𝑽 𝟒𝟏
𝑰 𝟐𝟑
]
𝑹 𝑺 =
𝝅
𝒍𝒏𝟐
𝑭 𝑸 . 𝑹
F(Q): correction factor (depend
on the shape of the sample)
Square => F(Q) = 1; 𝑅 𝑆 = 4.53𝑅
Source: “Công nghệ chế tạo mạch vi điện tử”
– GS.Nguyễn Đức Chiến](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/junction-depthsheet-resitancemeassurement-161207065345/75/Junction-depth-Sheet-resitance-meassurement-11-2048.jpg)
