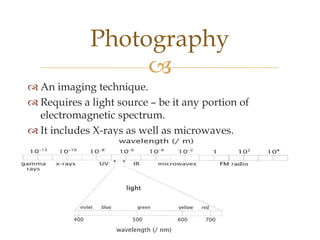
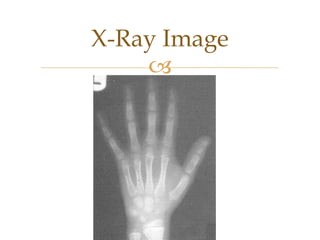
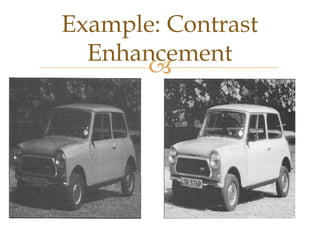
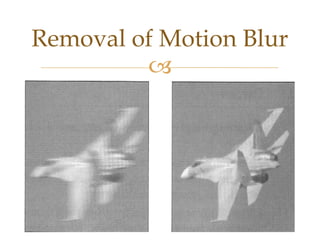
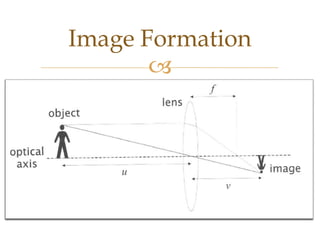
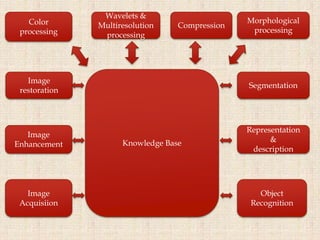
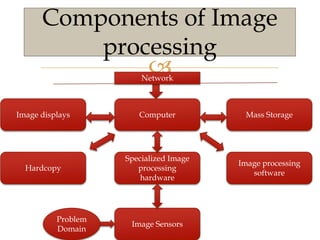
Images are visual representations that can be used to record and present information. There are various techniques for acquiring, processing, and manipulating digital images with computers. The fundamental steps in digital image processing typically involve image acquisition, enhancement, restoration, compression, and segmentation. Imaging systems cover a wide range of the electromagnetic spectrum and light is commonly used for imaging due to its safe, reliable, and controllable properties.