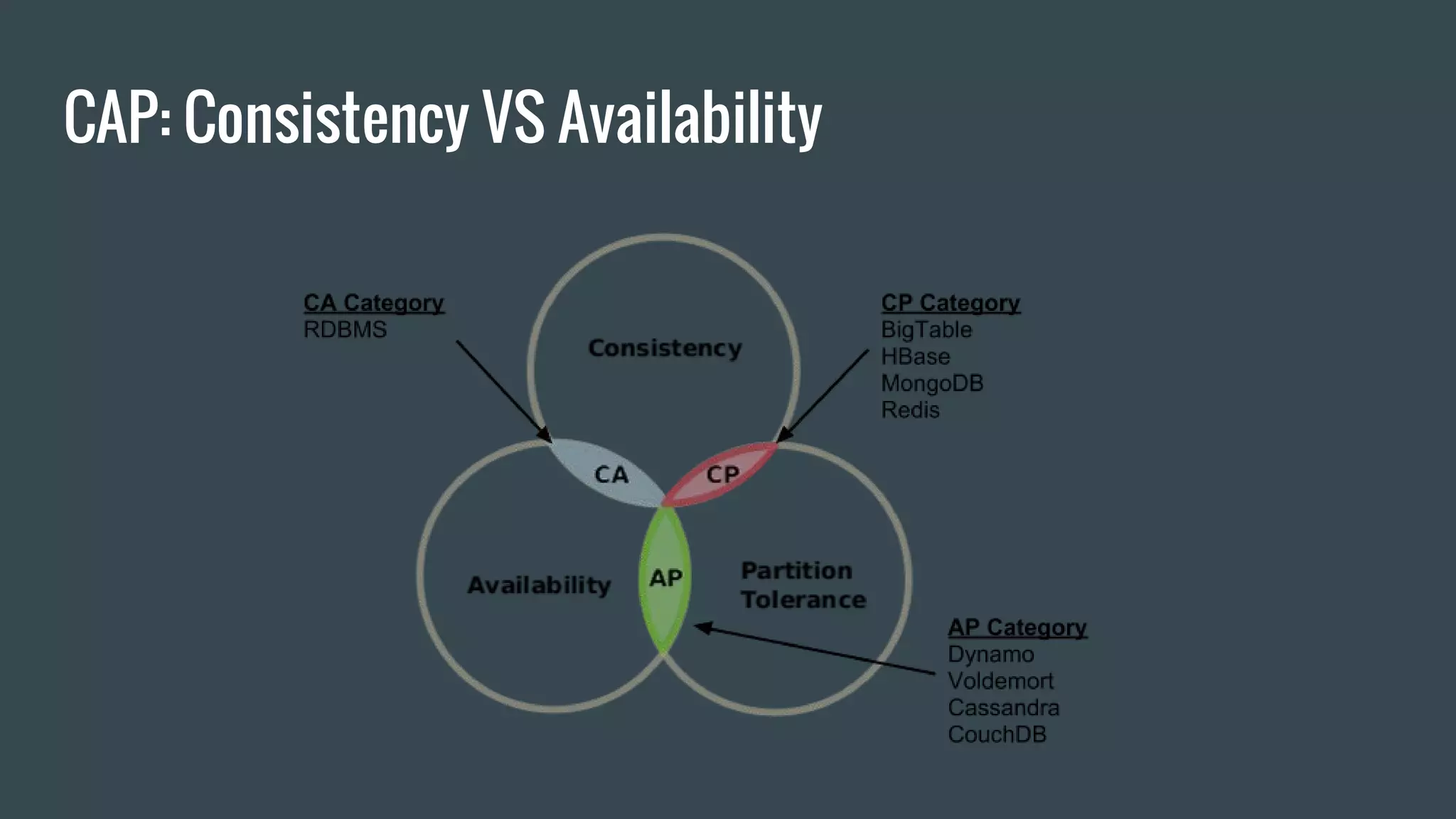
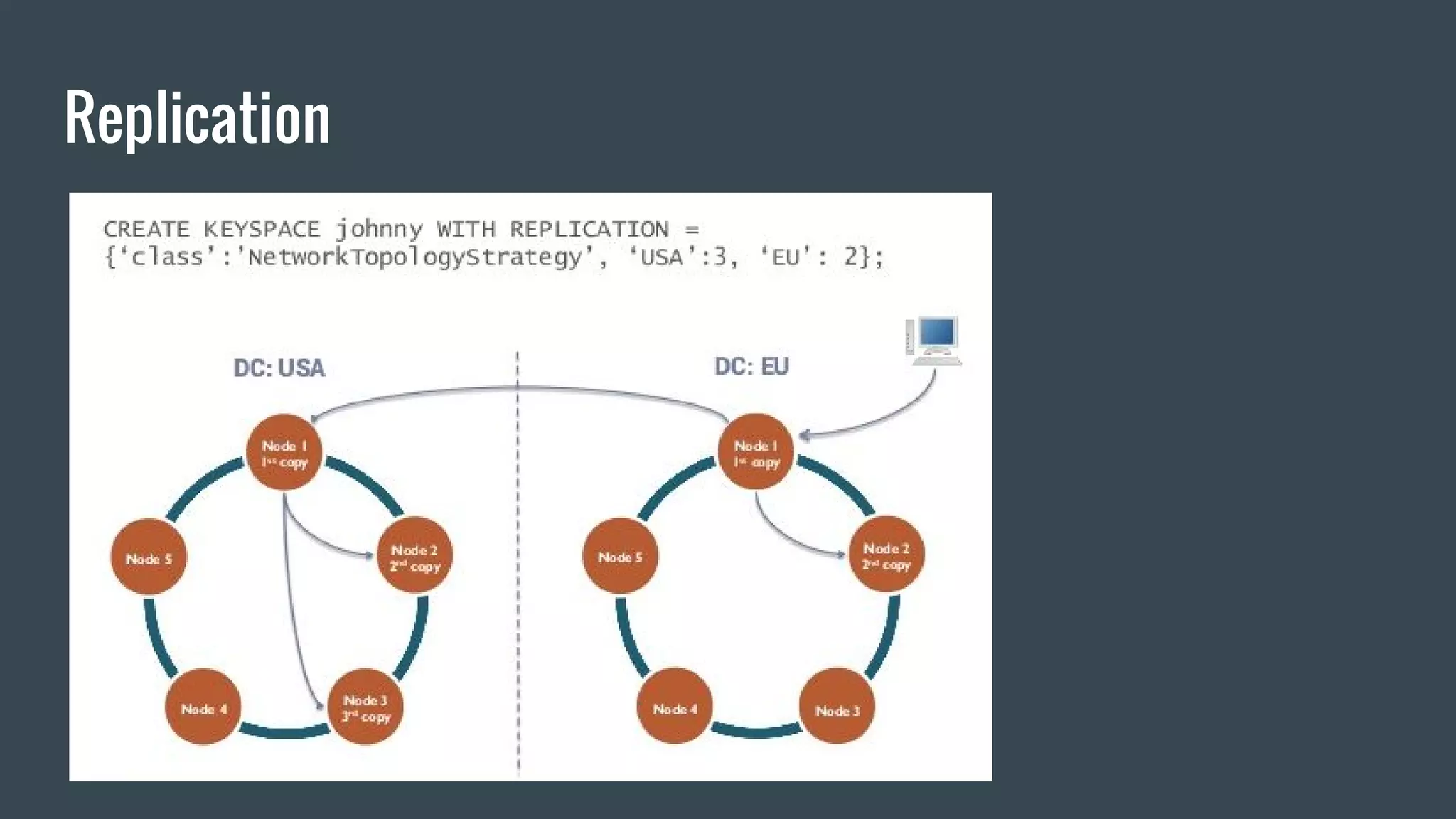
This document provides an overview of Apache Cassandra, an open source, distributed, wide column store NoSQL database. It discusses key features like scalability, high availability, fault tolerance, and replication across datacenters. Cassandra can handle 1 million writes per second and has been battle tested by many large companies. The document also covers topics like consistency models, data partitioning, replication strategies, indexing, storage, and the Java driver.