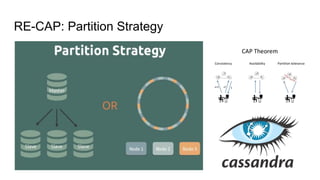
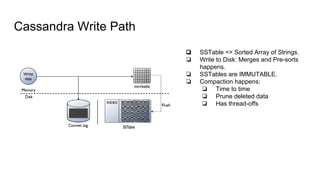
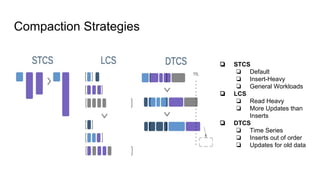
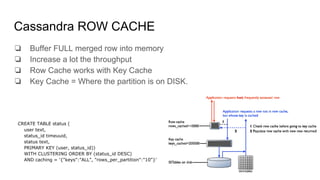
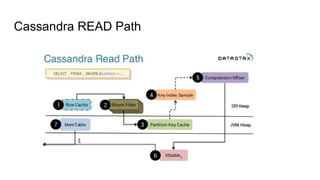
This document summarizes Diego Pacheco's presentation on Cassandra. It covers the Cassandra write path, tombstones, compaction strategies, row and bloom filters, SASI indexes, materialized views, counter families, and anti-patterns. It also discusses Cassandra's implementation at Uber using Mesos. The presentation addresses how data is written to disk in immutable SSTables and compacted over time to remove tombstones, and different compaction strategies for various workloads. It explains techniques like row caching, bloom filters, secondary indexes, materialized views and counters.