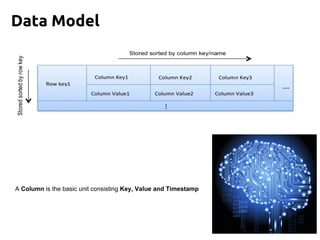
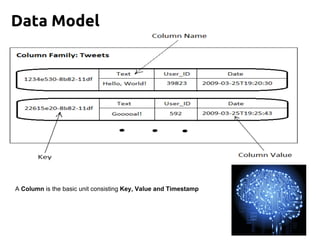
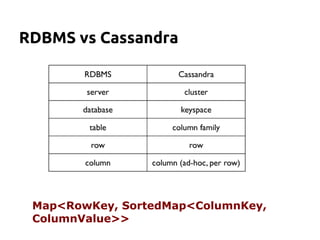
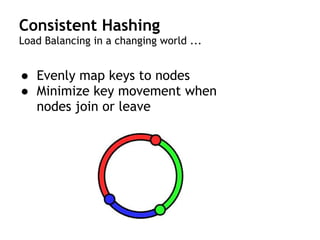
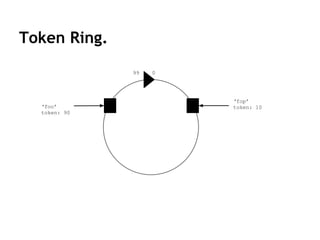
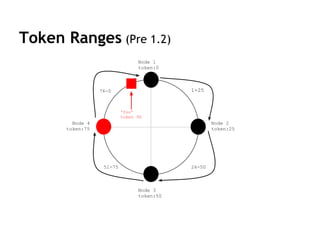
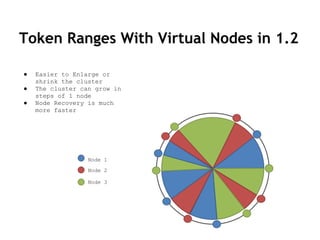
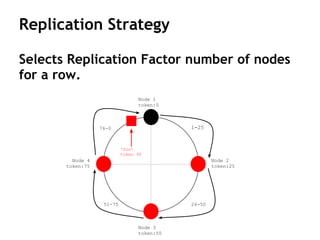
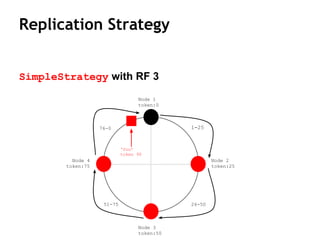
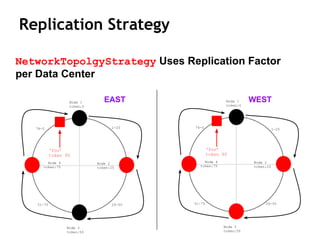
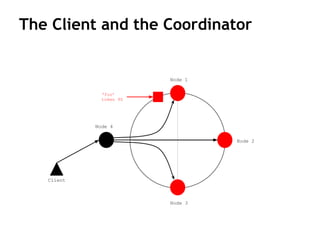
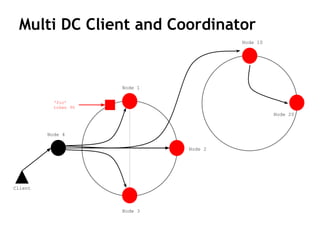
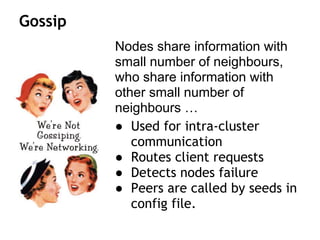
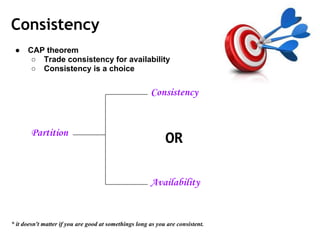
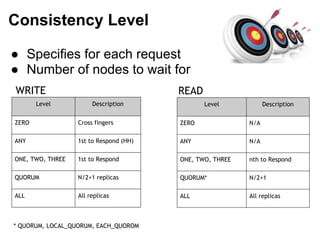
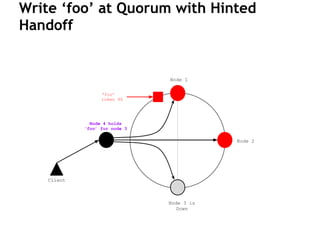
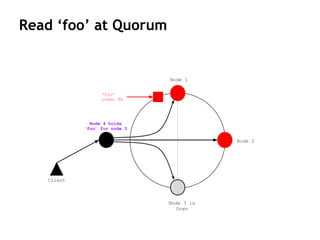
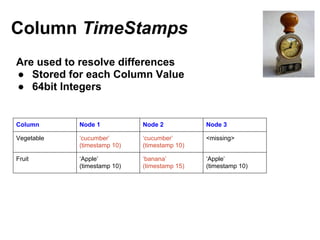
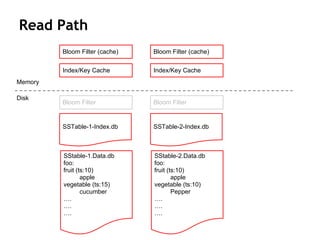
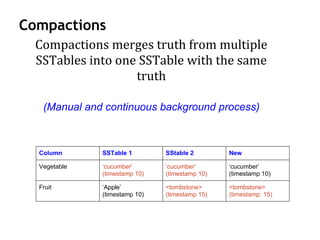
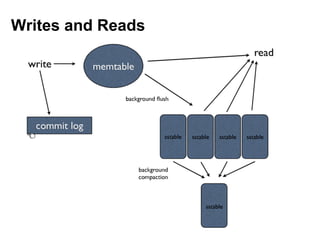
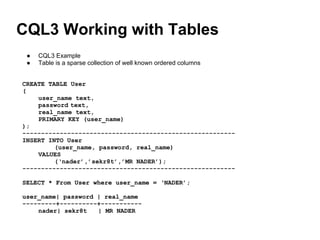
Cassandra is a distributed, column-oriented database that scales horizontally and is optimized for writes. It uses consistent hashing to distribute data across nodes and achieve high availability even when nodes join or leave the cluster. Cassandra offers flexible consistency options and tunable replication to balance availability and durability for read and write operations across the distributed database.