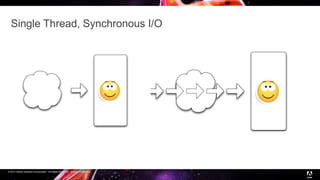
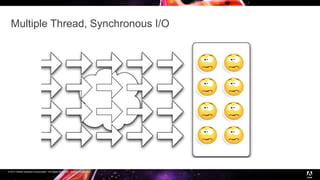
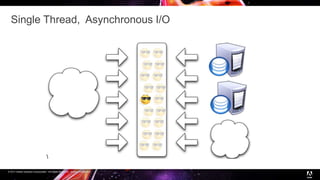
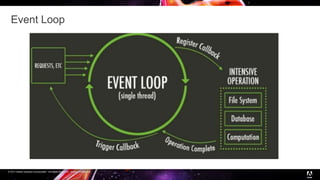
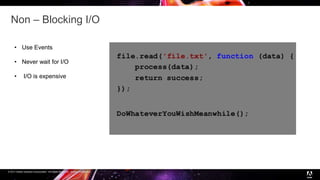
Node.js is a JavaScript runtime built on Chrome's V8 engine that allows JavaScript to run on the server side. It uses asynchronous and event-driven programming to handle thousands of concurrent connections with minimal overhead. The presentation introduces Node.js and its architecture, explaining how it uses a single thread with non-blocking I/O and an event loop to handle asynchronous operations efficiently. Examples are provided to illustrate synchronous vs asynchronous code. Common use cases for Node.js include real-time applications, chat/messaging, and high concurrency applications, while it is less suitable for heavy computation or large web apps.