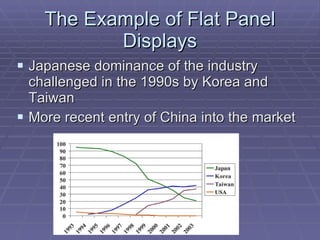
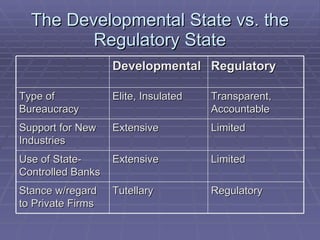
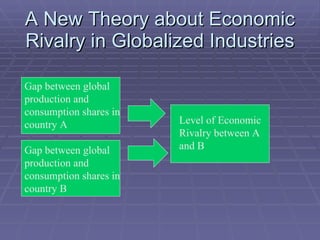
The document discusses geopolitical factors that influence international competitiveness. It provides examples of how government policies adopted in response to regional economic rivalries shaped competition in the digital TV and flat panel display industries. Specifically, it discusses how rivalry between North America, Western Europe, and Japan led each to adopt incompatible digital TV standards. It also discusses how Japanese dominance of flat panel displays was later challenged by rivals from Korea and Taiwan, and more recently China. The document advocates that theories of industrial policy must account for how globalization influences economic rivalry between nations.

![Contact information Department of Political Science Woodburn Hall 210 Bloomington, IN 47405 Email: [email_address] Web: http://mypage.iu.edu/~hartj](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/casic2011-110405114556-phpapp01/85/Casic-2011-2-320.jpg)