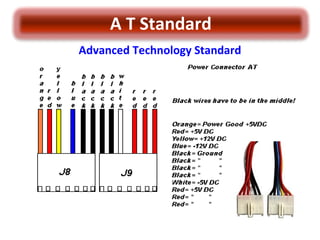
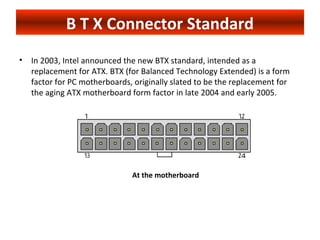
The document discusses different power supply standards for PCs, including AT, ATX, and BTX. It provides details on the connectors, pinouts, and voltages associated with each standard. It also addresses questions about compatibility between different form factors and how to identify a defective power supply.