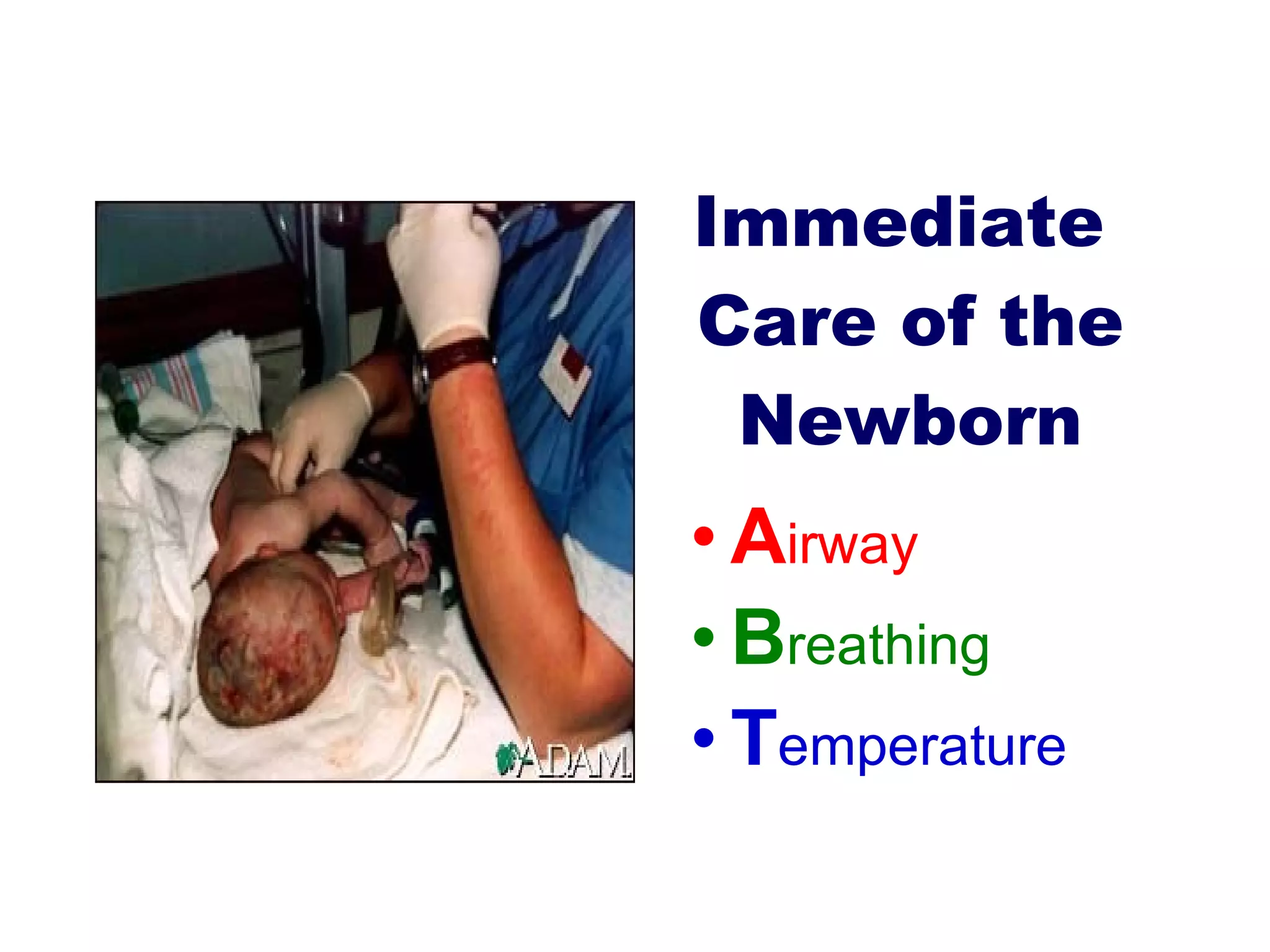
The document discusses care of the newborn in the first 24 hours of life and in the nursery. It covers immediate care including establishing airway and breathing, maintaining temperature, and APGAR scoring. It also discusses components of newborn care like identification, bathing, measurements, eye prophylaxis, vitamin K administration, and assessments.