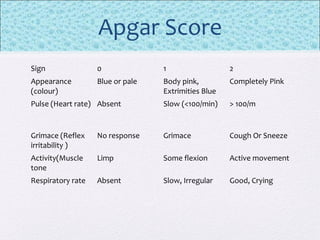
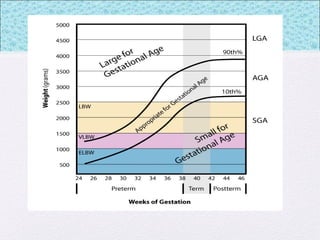
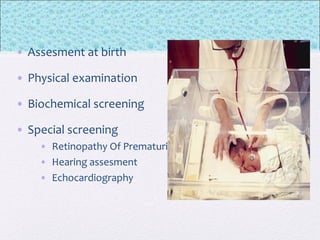
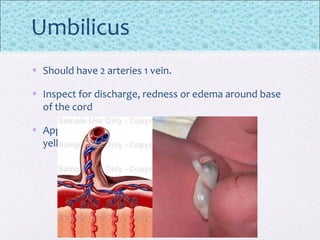
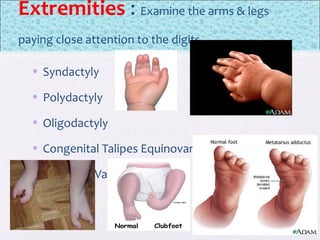
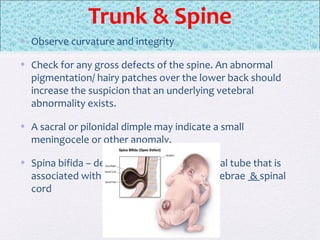
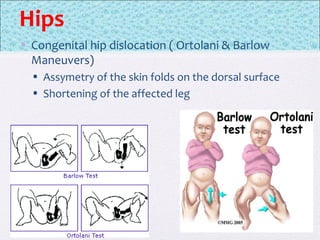
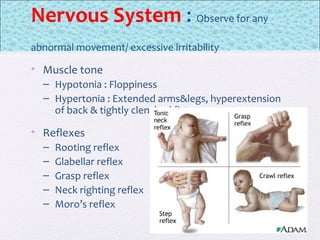
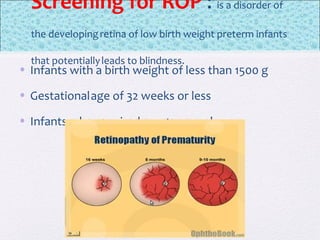
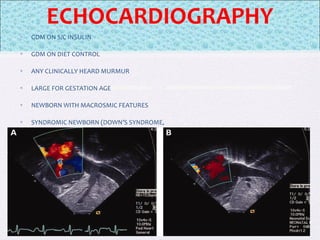
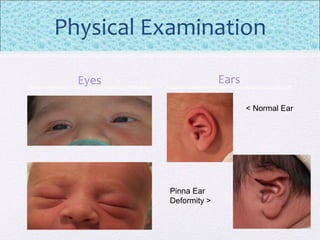
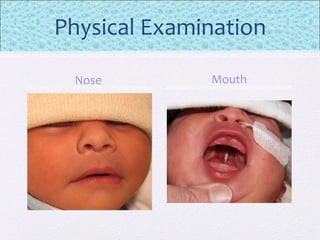
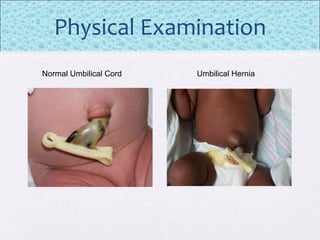
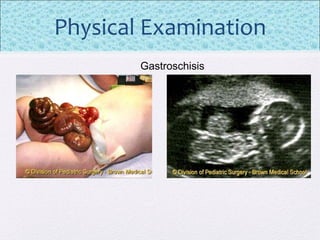
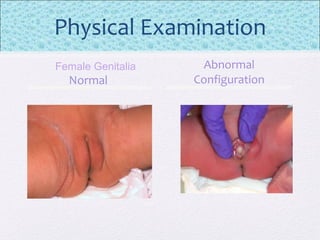
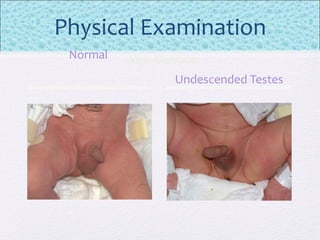
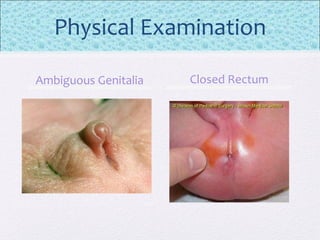
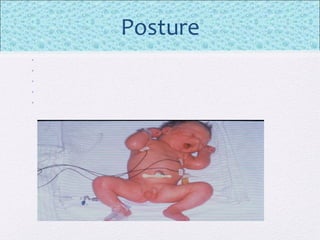
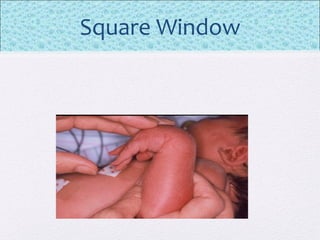
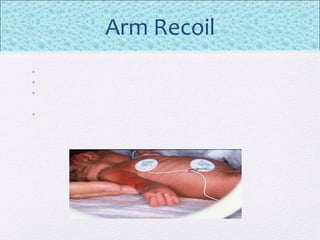
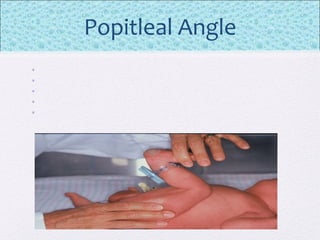
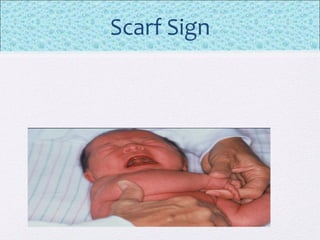
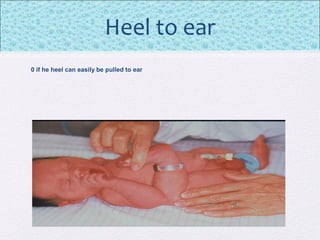
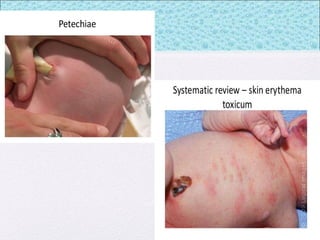
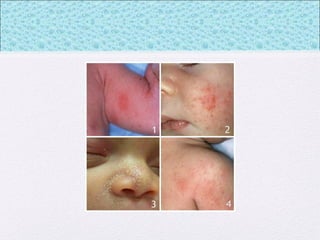
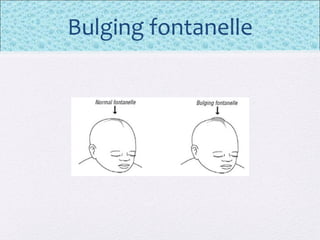
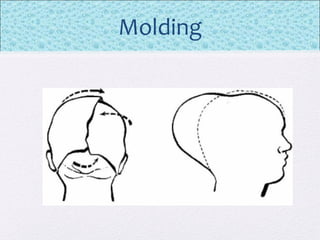
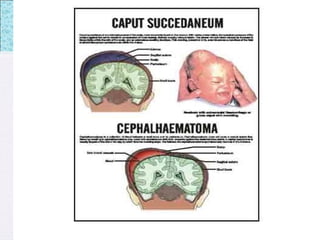
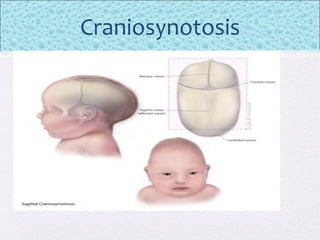
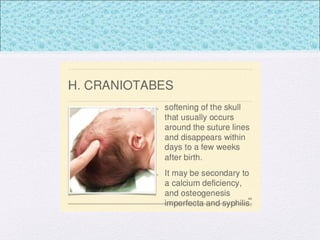
The document outlines the comprehensive health assessment process for newborns, which includes initial assessments, transitional evaluations, gestational age assessments, behavioral evaluations, and systemic physical examinations. It details the use of the Apgar scoring system for initial assessments and emphasizes the importance of observing various physiological parameters, as well as performing biochemical screenings. Key aspects such as nutritional needs, diagnostic tests, and signs of potential abnormalities in physical appearance and reflexes are also discussed.