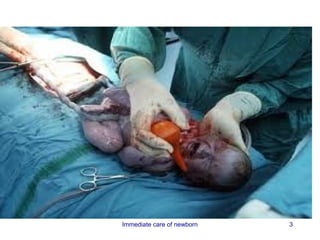
1) The first 24 hours of life require immediate care of the newborn to establish respiratory function, provide warmth, and ensure safety from injury and infection.
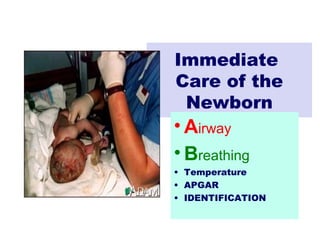
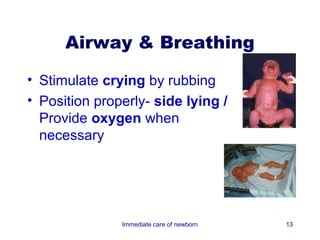
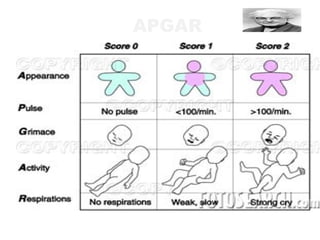
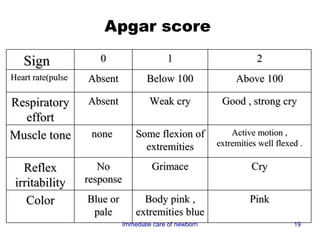
2) Key aspects of immediate newborn care include clearing the airway, maintaining temperature, assessing with the APGAR score, and providing identification.
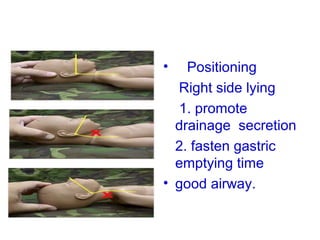
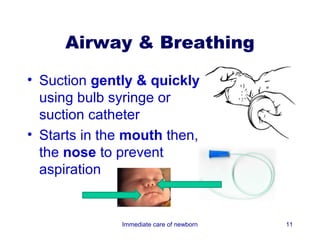
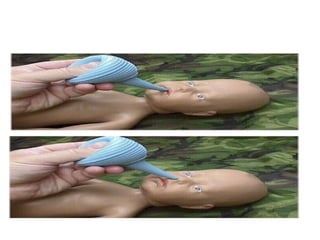
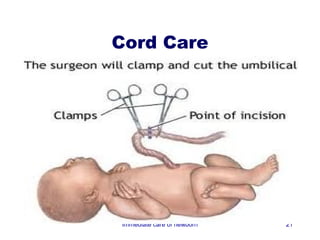
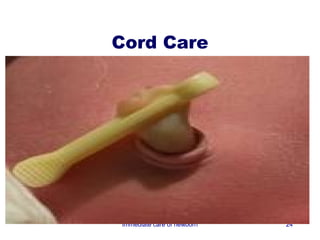
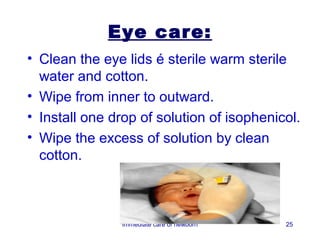
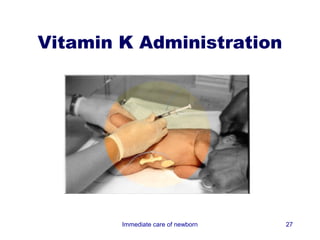
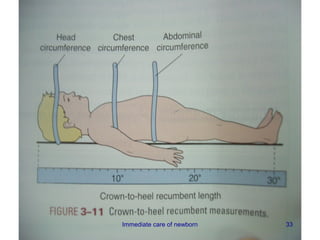
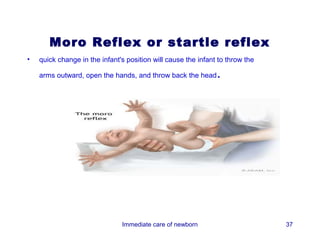
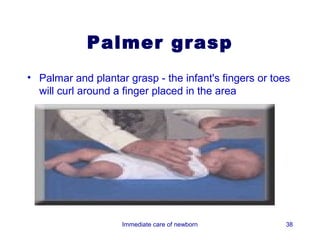
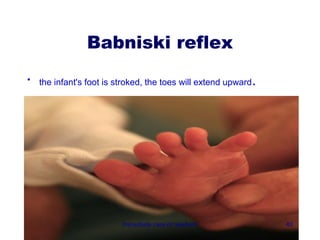
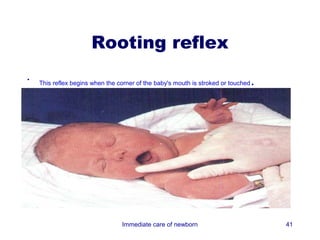
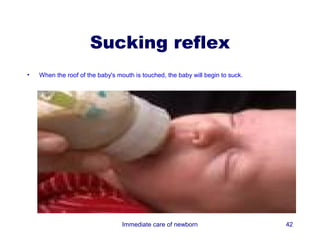
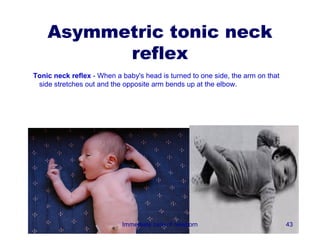
3) Procedures like drying, positioning, suctioning, cord clamping and eye care help support the newborn's transition to extrauterine life. Vital signs, reflexes and growth are also assessed.