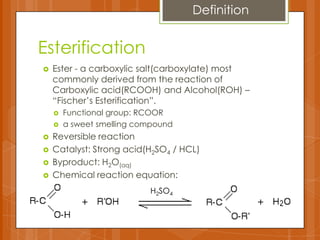
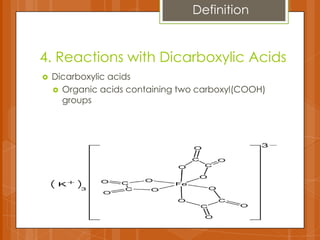
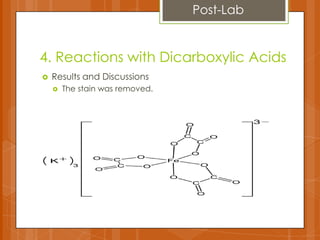
The document summarizes experiments conducted on carboxylic acids and their derivatives. It discusses (1) esterification reactions between acetic acid and ethanol catalyzed by sulfuric acid, (2) using ferric chloride tests to detect phenols and enols, (3) hydrolysis reactions of anhydrides and benzamide producing carboxylic acids and ammonia, and (4) using dicarboxylic acids to remove stains. Key points covered include the mechanisms of esterification and hydrolysis, results of qualitative tests, and observations made during the experiments.