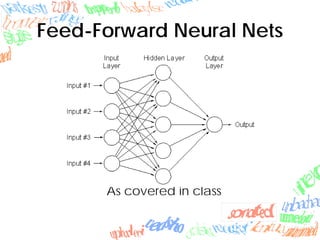
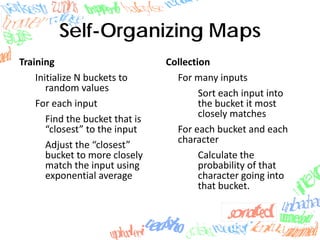
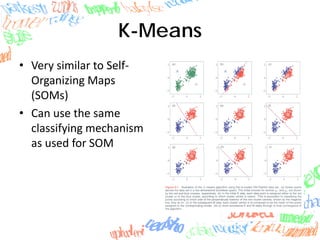
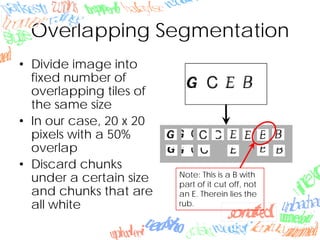
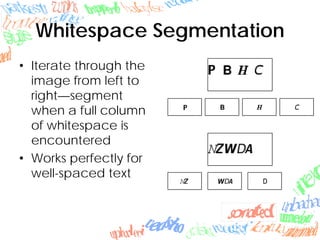
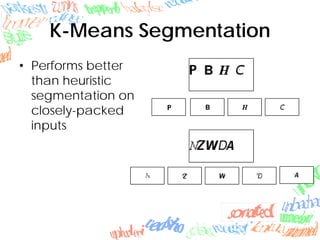
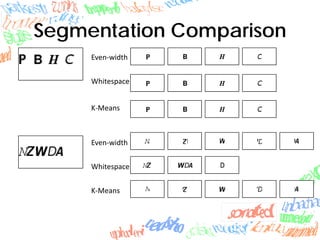
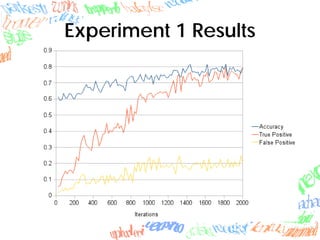
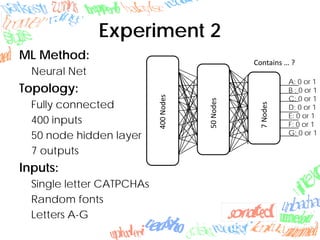
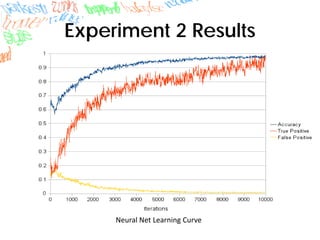
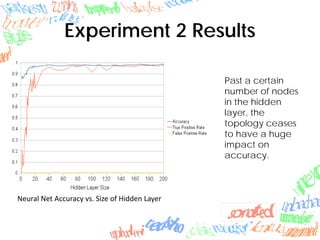
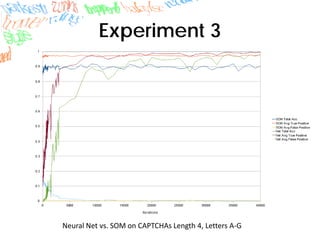
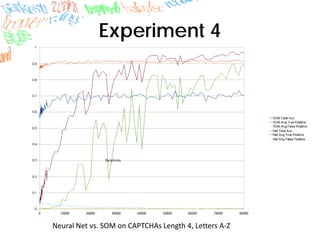
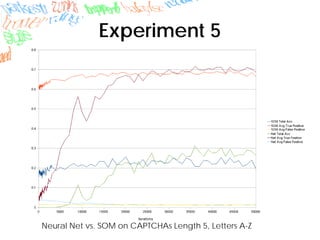
Machine learning methods like neural networks and self-organizing maps can recognize CAPTCHAs with high accuracy using minimal preprocessing of images. Experiments showed neural networks outperformed self-organizing maps on CAPTCHAs with 4 or more letters. Accuracy decreased as the number of letters increased due to worse segmentation. Improving segmentation quality is key to maintaining high true positive rates. Future work involves better segmentation techniques and applying these methods to other problems like handwriting recognition.