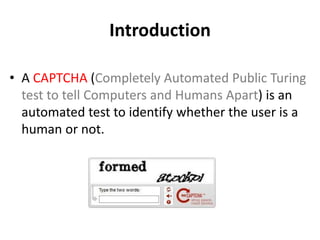
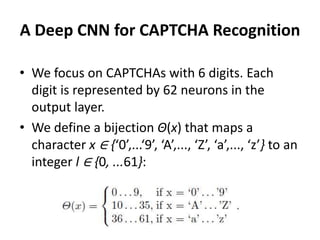
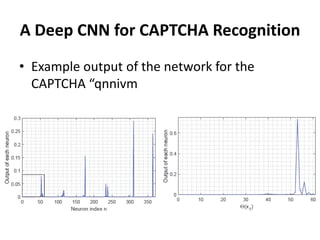
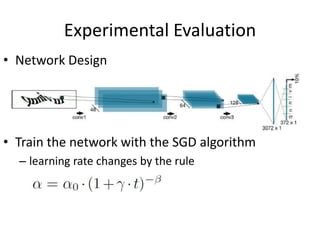
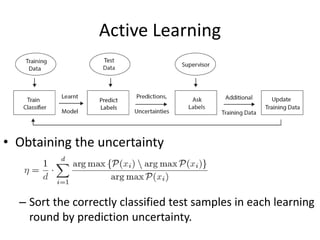
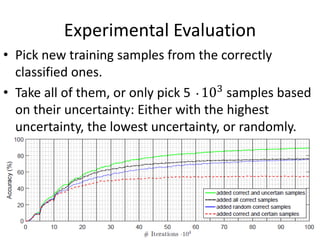
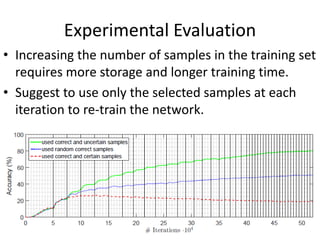
This document proposes an active deep learning approach to CAPTCHA recognition using a small initial training set. A convolutional neural network is trained on CAPTCHAs containing 6 digits. During testing, samples that are classified correctly but with high uncertainty are added back to the training set to improve the model in subsequent rounds of learning, without needing human labels. The method is evaluated on CAPTCHAs generated using different configurations, and performance is shown to improve significantly with each round of active learning by selecting additional uncertain samples for retraining.