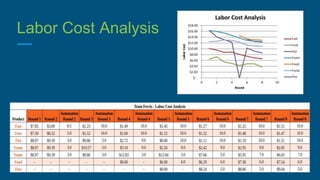
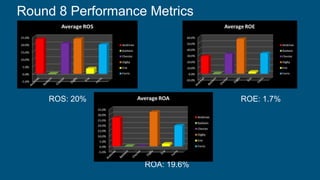
Ferris focused on offering excellent design, value, and accessibility to customers. In Round 8, Ferris achieved a ROS of 20%, ROA of 19.6%, ROE of 1.7%, stock price of $191.72, and market share of 22% through conservative pricing, optimizing automation and plant utilization, and transitioning its underperforming Fist product to the traditional segment. Ferris withstood competitor moves through rounds 1-8 by gaining market share, improving forecasting, and increasing production capacities for top-selling products like Feat and Fume to meet high customer demand.