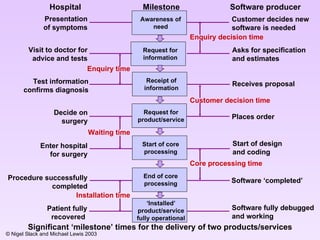
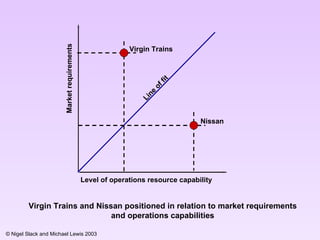
The document discusses several key aspects of operations strategy:
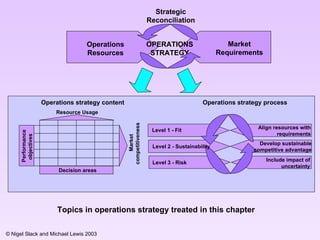
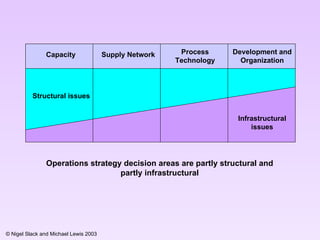
1) It defines operations strategy as the intersection of performance objectives (e.g. quality, cost) and operations decisions areas (e.g. capacity, supply network).
2) It explains the three levels of operations strategy - fit, sustainability, and risk. Fit refers to aligning resources with market requirements. Sustainability is developing a competitive advantage. Risk considers the impact of uncertainty.
3) It provides an example of a polar diagram that illustrates the relative importance of different performance objectives for current and new products at a medical company. This helps analyze strategic fit and gaps.