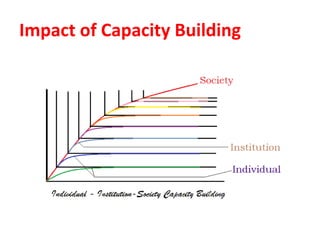
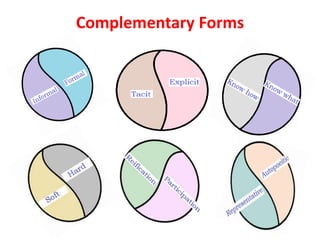
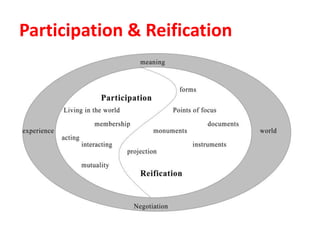
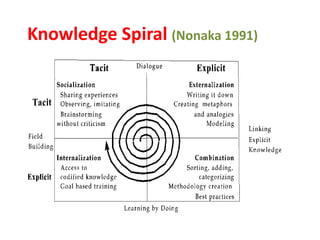
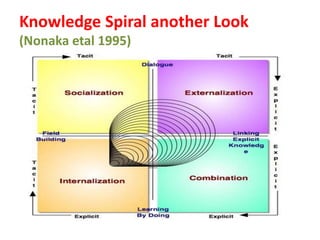
This document discusses capacity building and knowledge creation in organizations. It defines capacity building as developing skills, abilities, and resources to help organizations adapt and thrive. Capacity building can occur at the individual, institutional, and societal levels. It is important for innovation, efficiency, effectiveness, stability, and survival. However, capacity building does not happen naturally and requires recognizing needs, strategies, and investing time and money. Knowledge is at the base of capacity building and exists in both formal and informal ways. It can be created through participation and reification using a knowledge spiral process of socialization, externalization, combination, and internalization. For educational institutions, knowledge creation can occur through curriculum reforms, continued learning opportunities, knowledge services, dynamic