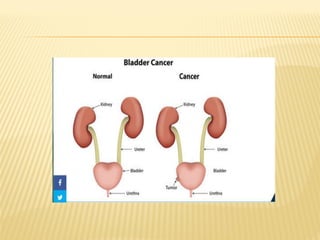
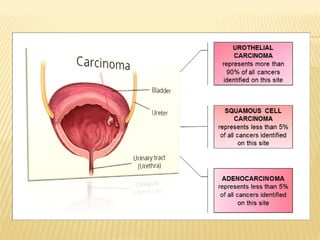
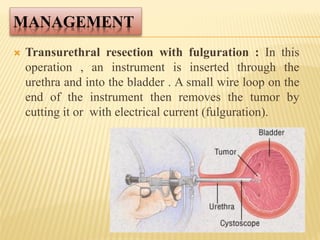
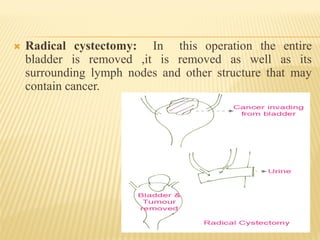
Bladder cancer is a malignant growth in the urinary bladder, primarily arising from three cell types: urothelial, squamous, and adenocarcinoma, with higher prevalence in men and specific risk factors including smoking and age. Symptoms typically include blood in urine, pain during urination, and frequent urination, while treatment options range from surgical procedures like radical cystectomy to chemotherapy and immunotherapy. Nursing management focuses on alleviating symptoms, monitoring vital signs, and providing supportive care during treatment.