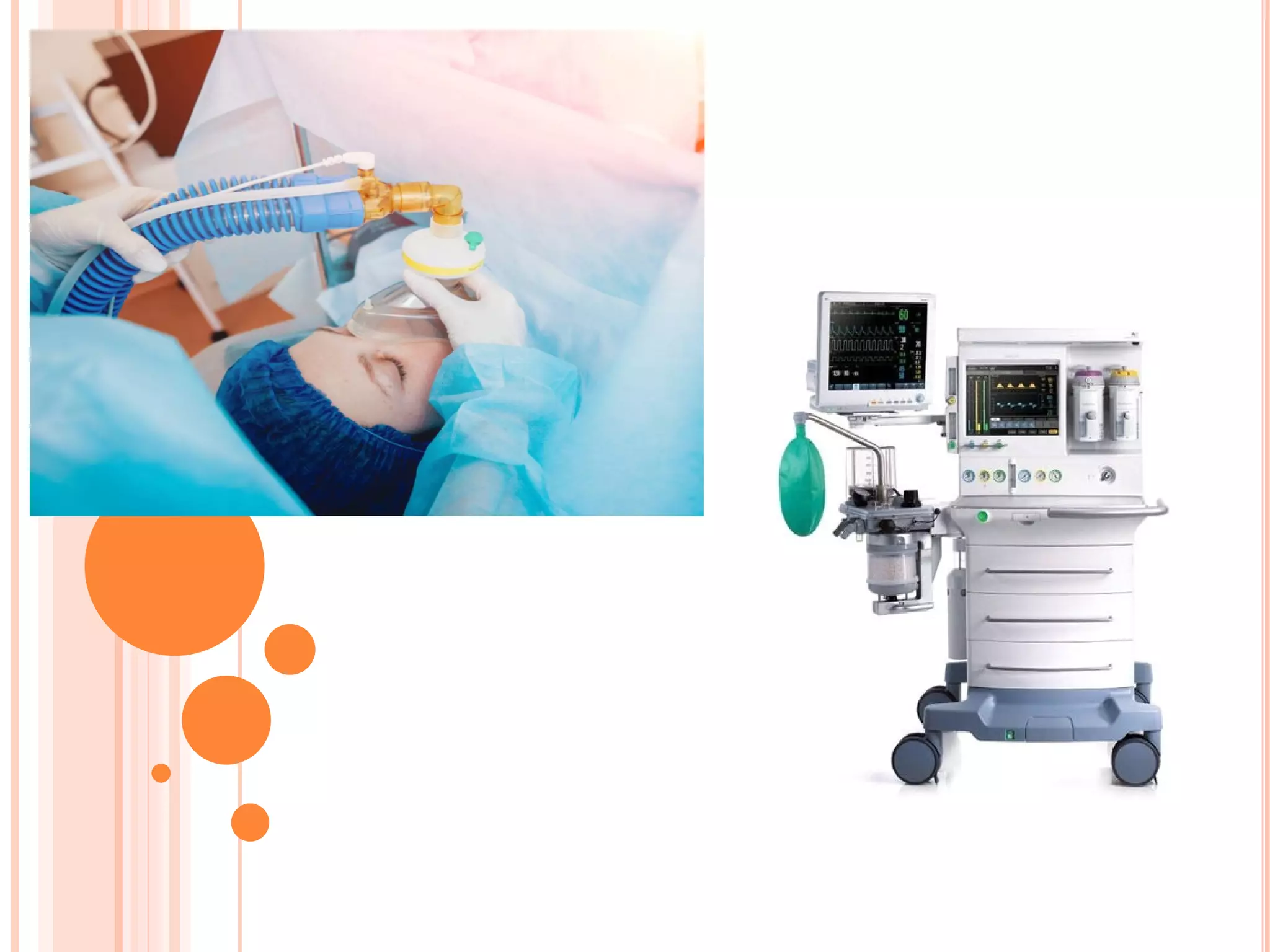
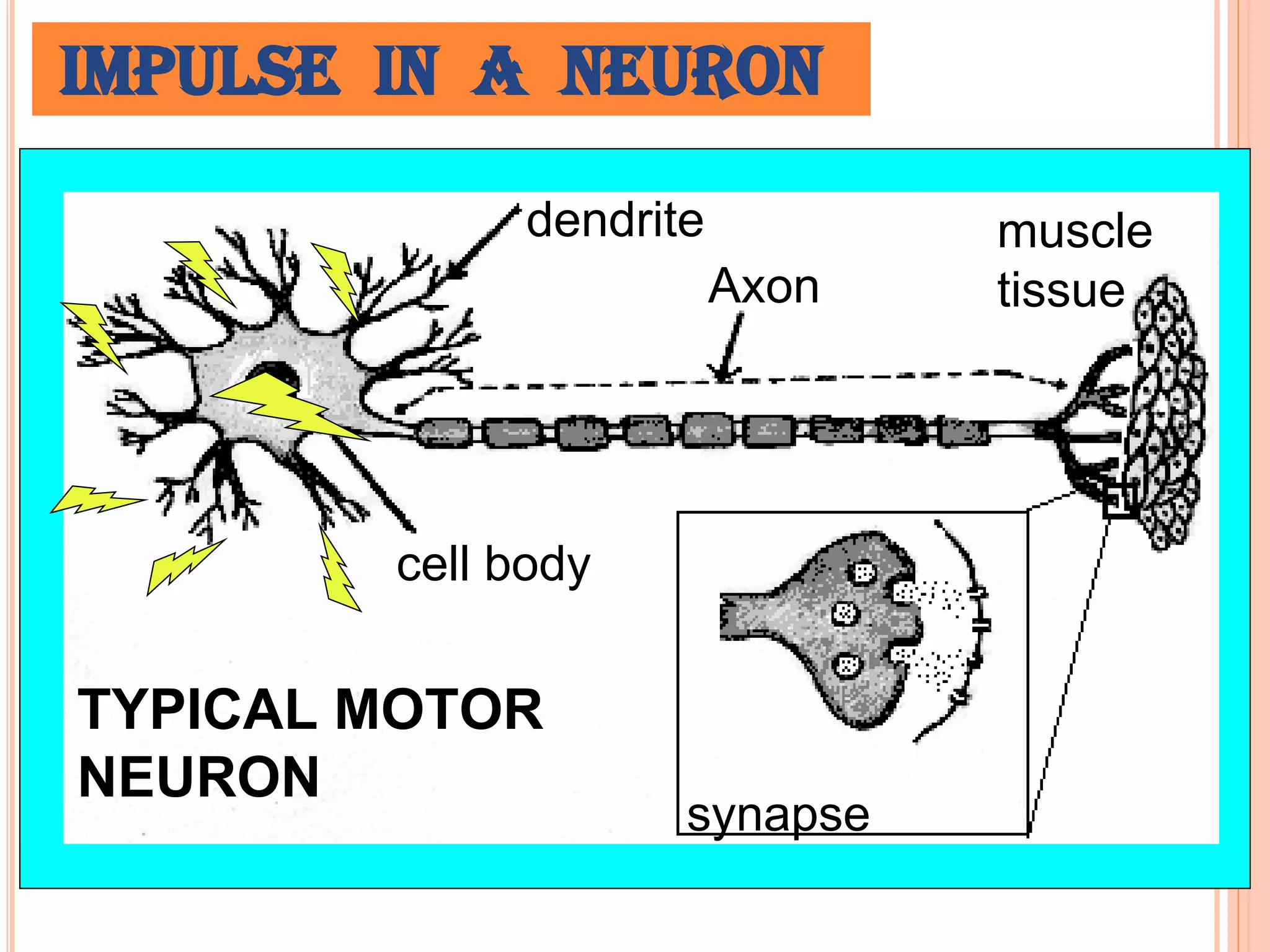
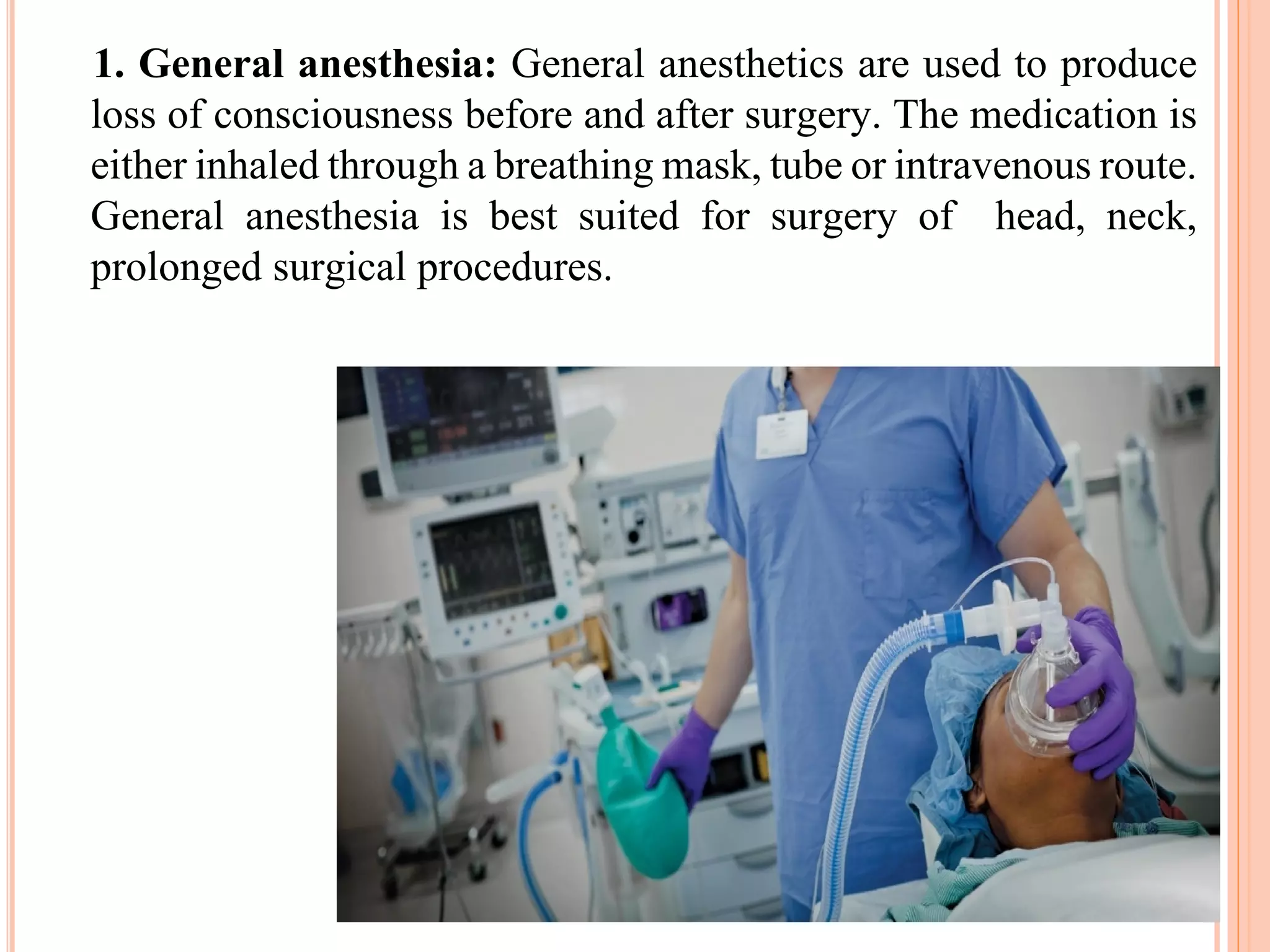
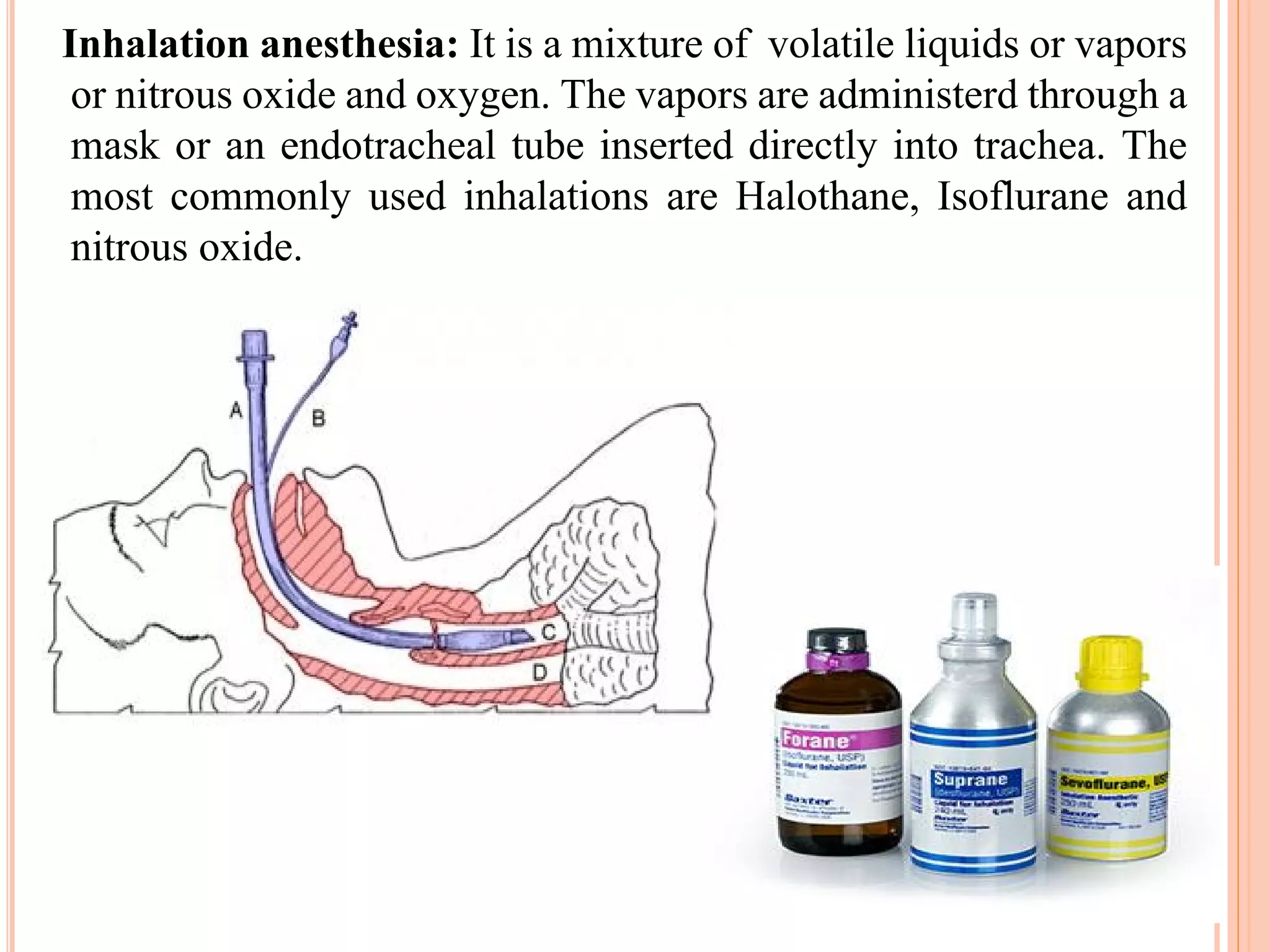
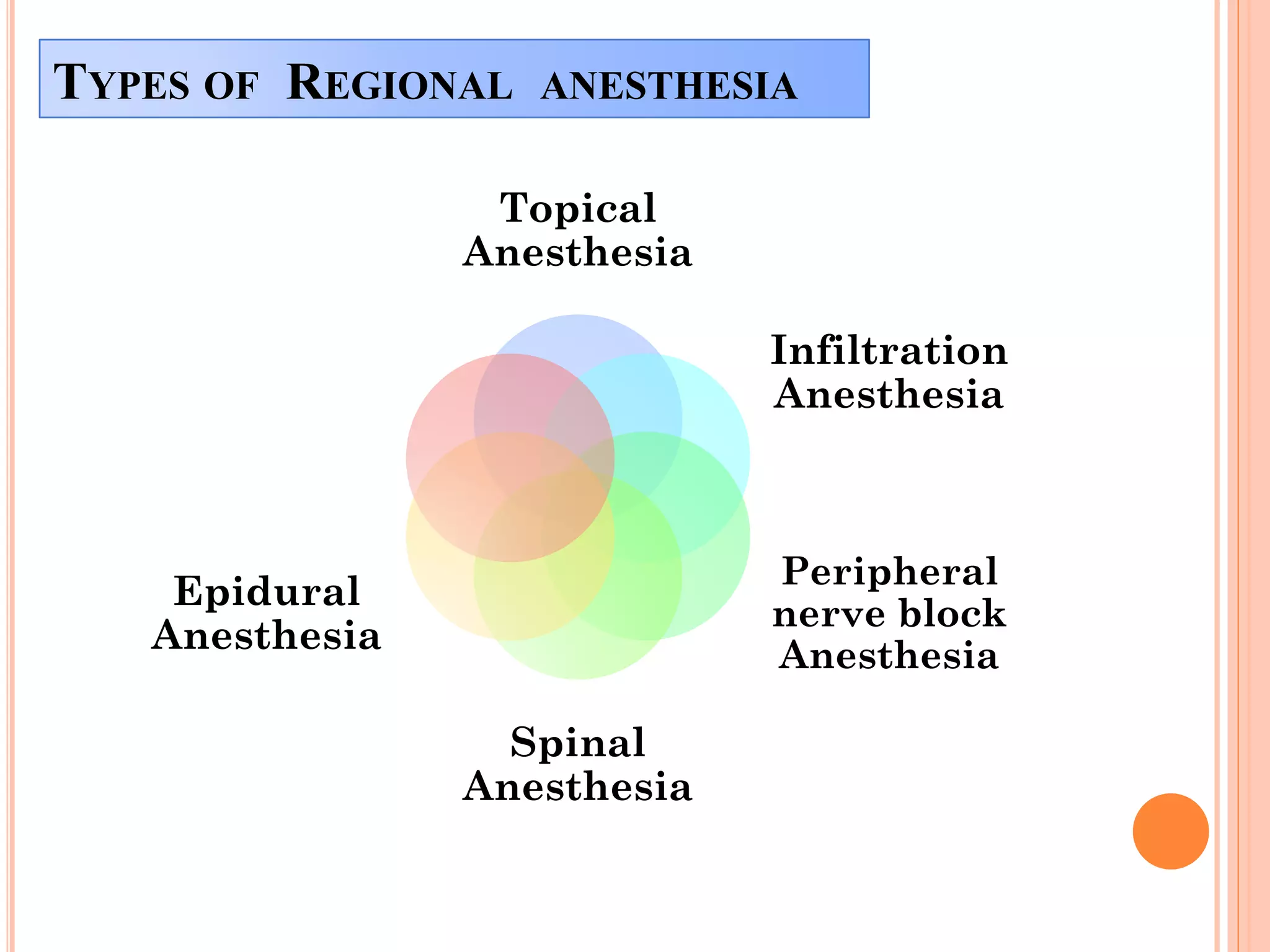
The document provides an overview of anesthesia, defining it as an artificially induced state of partial or total sensation loss, either with or without loss of consciousness. It classifies anesthesia into general and regional types, detailing stages of general anesthesia and various administration methods, including intravenous and inhalation. Additionally, it outlines complications associated with anesthesia, such as nausea, hypotension, and neurological issues.