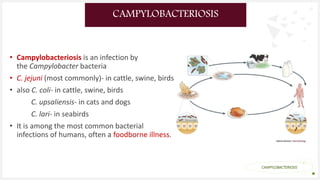
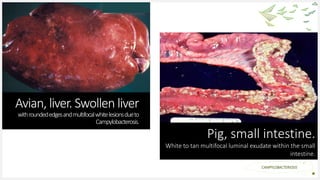
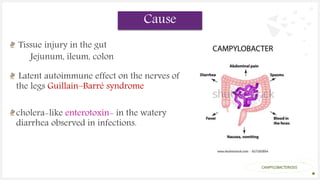
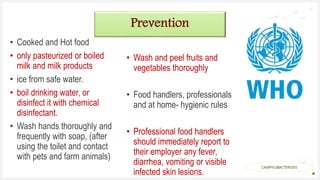
Campylobacteriosis is an infection caused by Campylobacter bacteria, most commonly C. jejuni found in cattle and birds. It is a common foodborne illness that causes diarrhea, abdominal pain, and fever within 1-5 days. Symptoms usually last 2-10 days. While usually self-limiting, it can occasionally cause complications in young children or immunocompromised individuals. The disease is typically transmitted by eating undercooked meat or drinking contaminated water. Diagnosis involves testing a stool sample. Treatment focuses on rehydration, and antibiotics may be used in severe cases. Prevention involves proper food handling and cooking, hand washing, and avoiding cross-contamination.

![Your Logo or Name Here
Meat, Meat Products
Milk, Milk Products
Water and
Beverages
5
• First 24 hours:
Prodromal symptoms- fever, headache, and myalgia
(which can be severe)
• After 1–5 days:
diarrhea (~ 10 watery, frequently bloody, bowel
movements per day)
or dysentery, cramps, abdominal pain, and fever [as
high as 40 °C (104 °F)].
• In most people, the illness lasts for 2–10
days:
invasive/inflammatory diarrhea, also described
as bloody diarrhea or dysentery.
CAMPYLOBACTERIOSIS
There are other diseases showing similar
symptoms.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/campylobacteriosis-180625125331/85/Campylobacteriosis-5-320.jpg)





![Your Logo or Name Here
References
Webliography
CAMPYLOBACTERIOSIS
• [http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Fil
e:A_large_blank_world_map_with_ocea
ns_marked_in_blue.PNG].)
• http://www.sinobiological.com/what-is-
elisa-mechanism.html
• https://www.news-
medical.net/health/Campylobacteriosis-
Symptoms.aspx
• https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Campylobac
teriosis
• http://parasites.ftz.czu.cz/food/parasite.p
hp?idParasite=52
• https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NiPTc
CK9vX0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/campylobacteriosis-180625125331/85/Campylobacteriosis-16-320.jpg)
