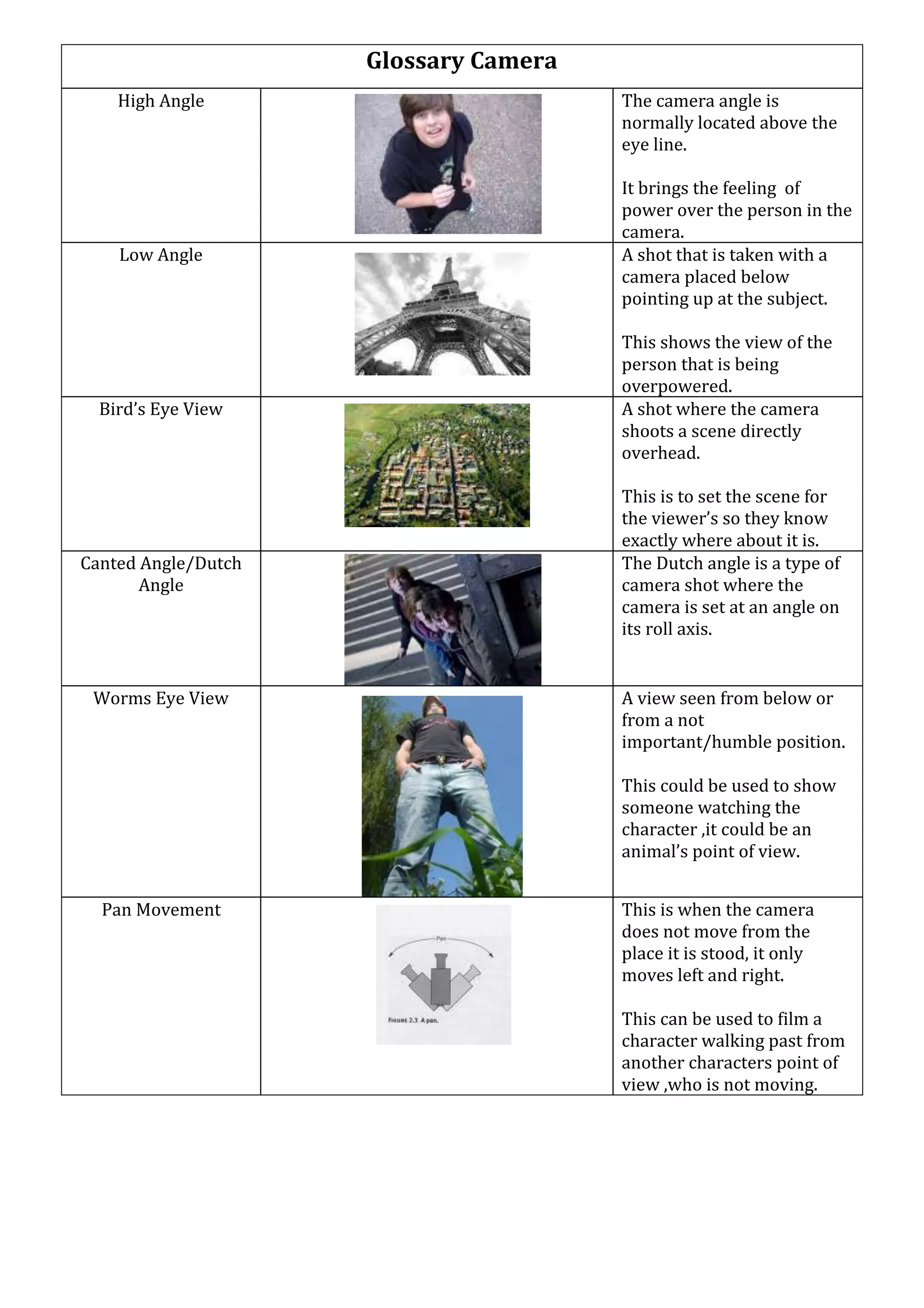
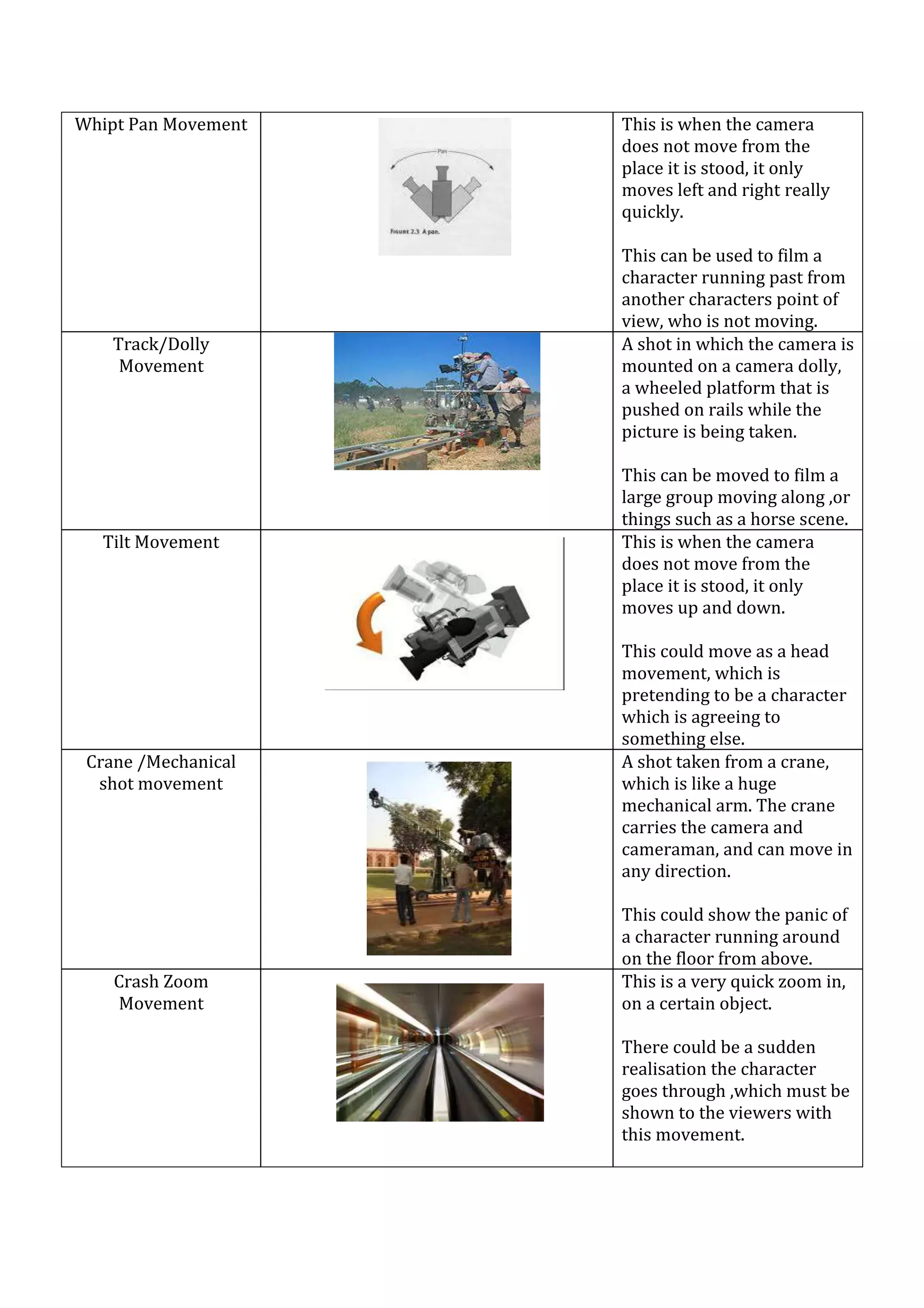
This document defines and describes various camera shots, angles, movements, and compositions used in filmmaking. High angle shots look down on a subject to convey power, while low angles look up to convey being overpowered. Bird's eye views shoot directly overhead to set the scene. Dutch angles use tilted cameras. Worm's eye views see from below. Pan and whip pan movements rotate the camera horizontally. Track/dolly movements use wheeled cameras on rails. Tilts rotate vertically. Cranes move cameras in any direction. Crash zooms quickly zoom in. Steadicams follow subjects steadily through crowds. Zooms smoothly change perspective. Handheld cameras move shakily. Deep focus keeps everything in focus while shallow focus