Embed presentation
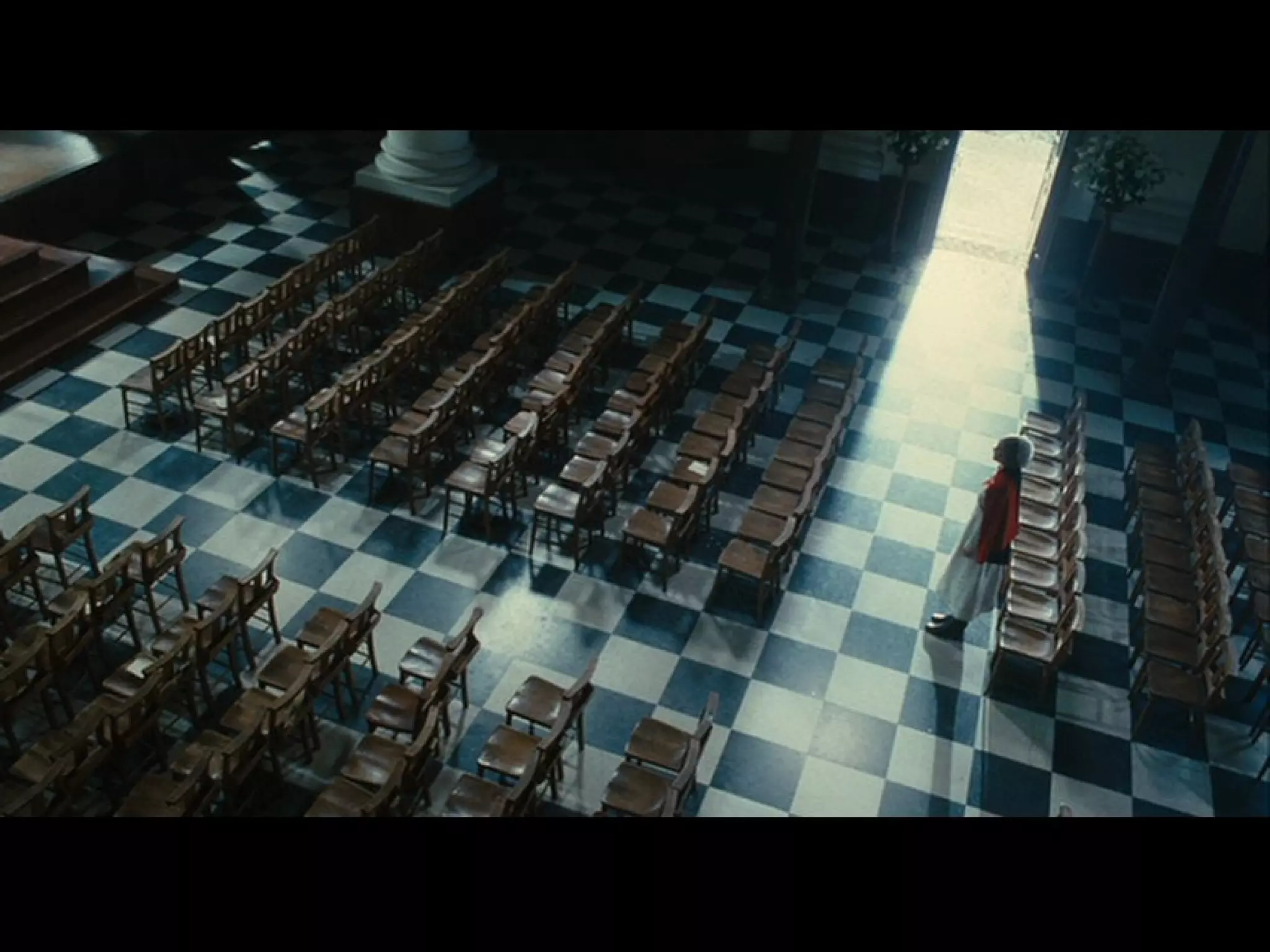

















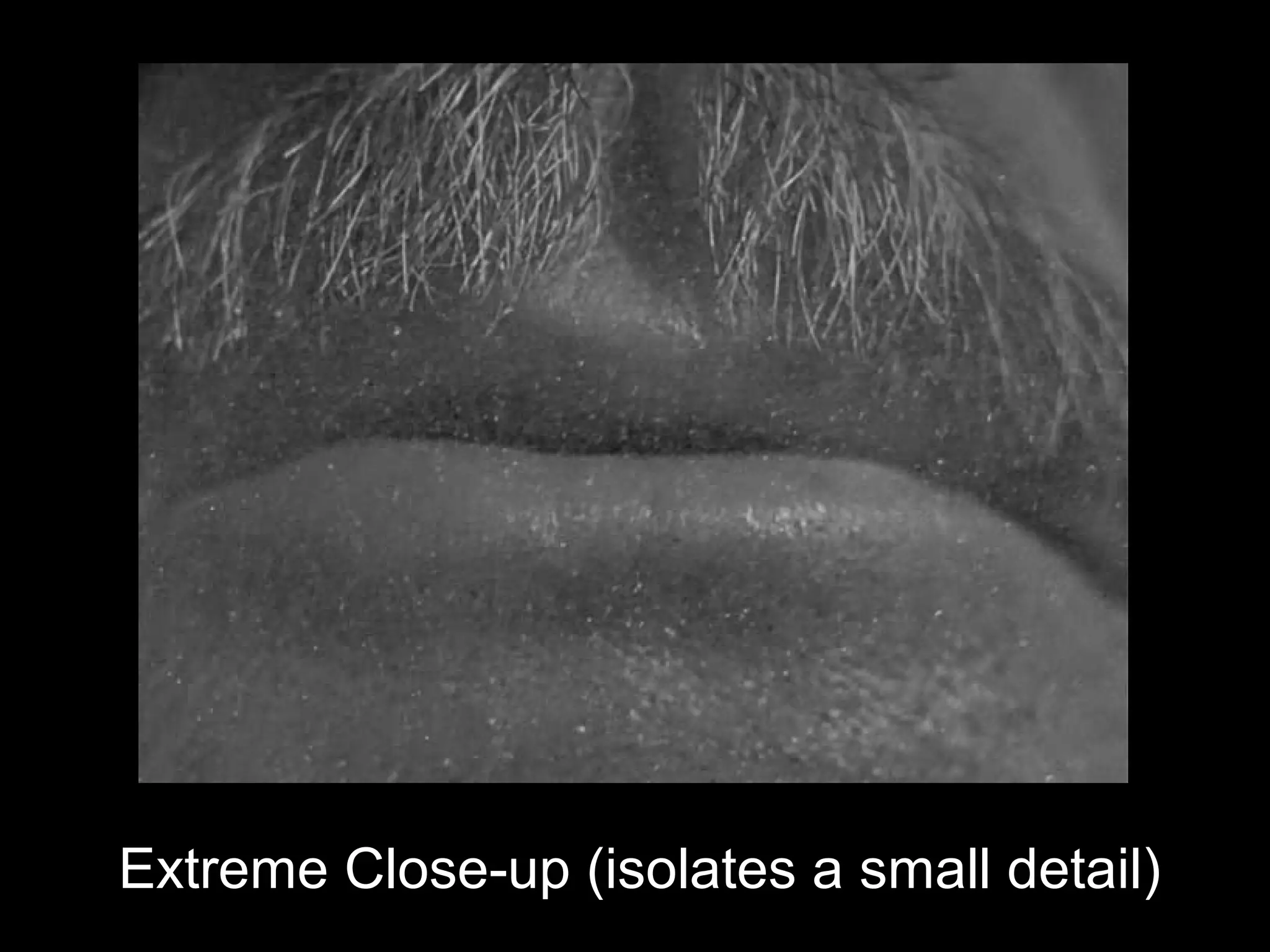


















Camera distances and angles can influence the viewer's perspective and emphasis in a shot. Standard distances include extreme long shot, long shot, medium long shot, medium shot, medium close-up, close-up, and extreme close-up. Camera angles such as eye level, low-angle, and high-angle affect whether the viewer looks up or down at the subject. Framing and point of view are also important, as different framing implies different perspectives or viewpoints of the scene.




































