Embed presentation
Downloaded 16 times


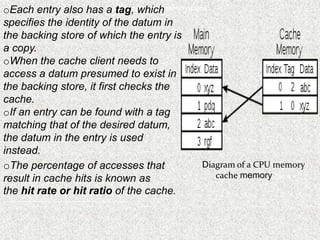







Each entry in a CPU cache contains a tag specifying the datum in backing storage that the entry copies. When accessing data, the cache is checked first, and if a matching tag is found, the cached datum is used instead of retrieving from storage. The percentage of accesses served from the cache is known as the hit rate. There are two write policies - write-through writes synchronously to both cache and storage, while write-back only writes to cache initially before writing back to storage when replacing cache blocks.









