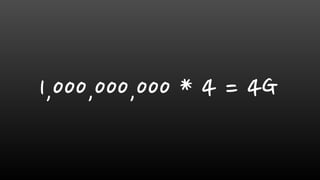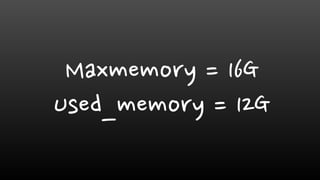This document discusses troubleshooting Redis. Some key points:
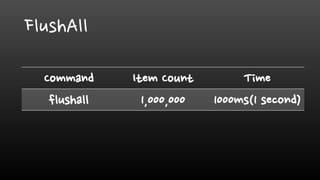
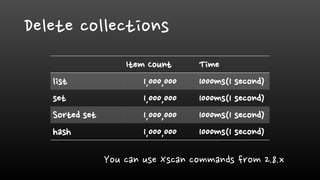
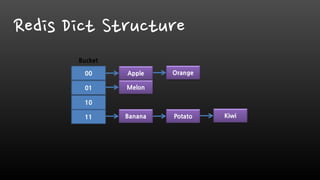
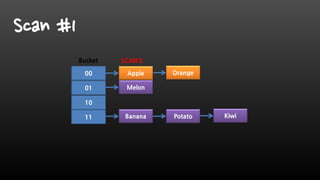
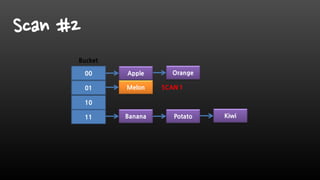
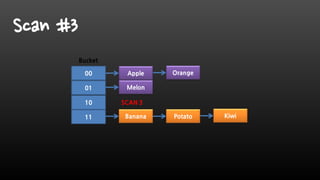
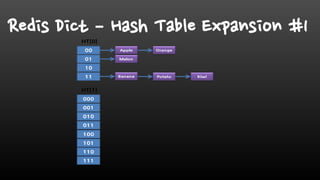
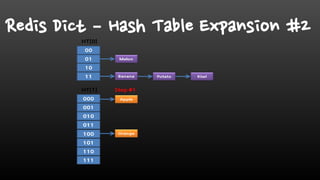
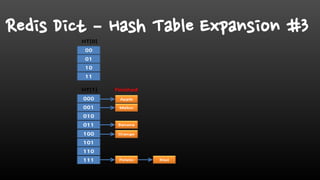
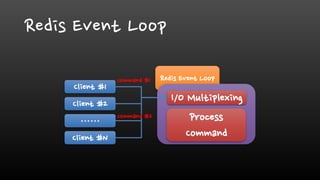
- Redis is single-threaded, so commands like KEYS, FlushAll, and deleting large collections can be slow. It's better to use SCAN instead of KEYS.
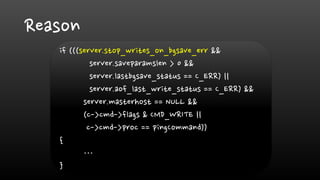
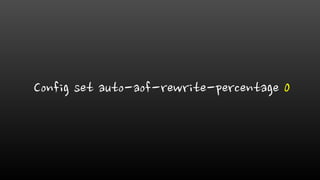
- Creating Redis database snapshots (RDB files) and rewriting the append-only file (AOF) can cause high disk I/O and CPU usage. It's best to disable automatic rewrites.
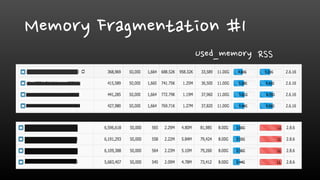
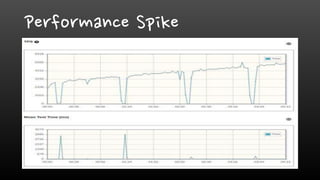
- Monitoring memory usage and fragmentation is important to avoid performance issues. The maxmemory setting also needs monitoring to prevent out-of-memory errors.
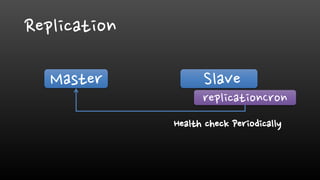
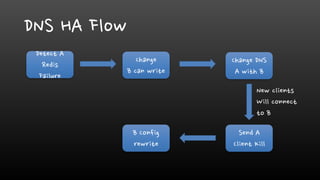
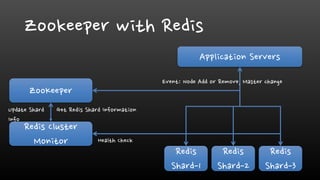
- Network and replication failures need solutions like DNS failover or using Zookeeper for coordination to maintain high availability of Redis














![KEYS – Iterating all Keys
di = dictGetSafeIterator(c->db->dict);
allkeys = (pattern[0] == '*' && pattern[1] == '0');
while((de = dictNext(di)) != NULL) {
……
stringmatchlen(pattern,plen,key,sdslen(key),0)
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/troubleshootingredis-160515111926/85/Troubleshooting-redis-17-320.jpg)
![FlushAll – Deleting all items
for (i = 0; i < ht->size && ht->used > 0; i++) {
dictEntry *he, *nextHe;
if ((he = ht->table[i]) == NULL) continue;
while(he) {
nextHe = he->next;
dictFreeKey(d, he);
dictFreeVal(d, he);
zfree(he);
ht->used--;
he = nextHe;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/troubleshootingredis-160515111926/85/Troubleshooting-redis-18-320.jpg)