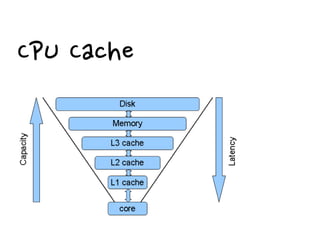
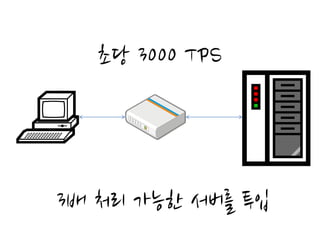
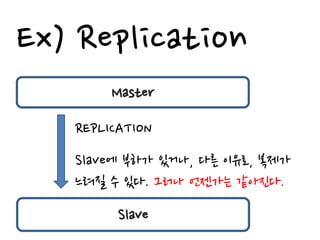
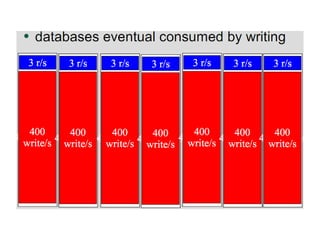
This document discusses using caching to improve performance for web applications. It provides three key points:
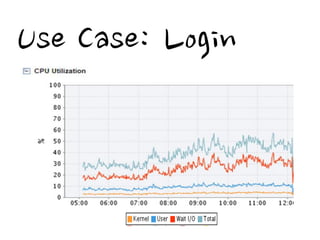
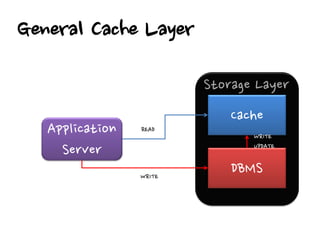
1. Cache stores data to serve future requests faster by avoiding accessing the database. It is commonly used for things like login information, page content, and API responses.
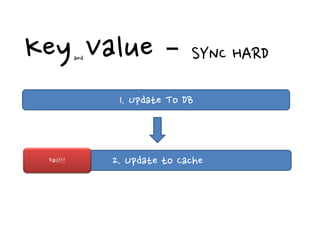
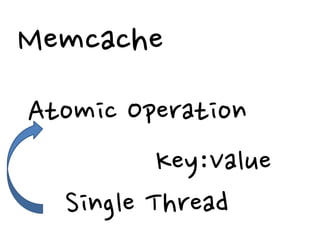
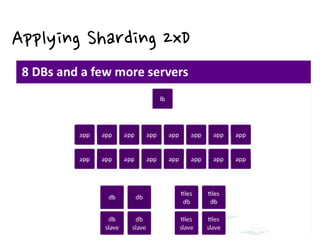
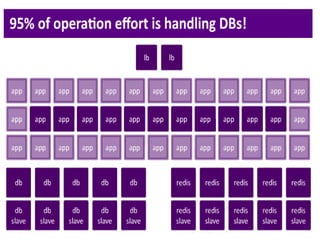
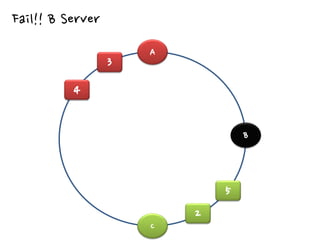
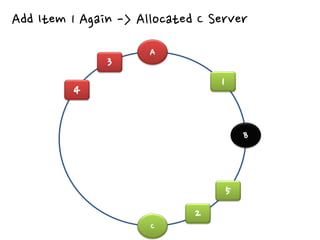
2. There are different cache architectures like memcached and Redis that support storing data in-memory for fast retrieval. Factors like data size, update frequency, and consistency requirements determine the appropriate caching strategy.
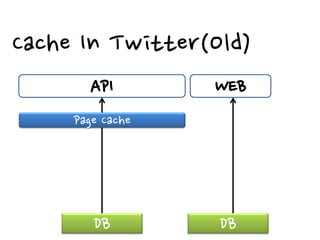
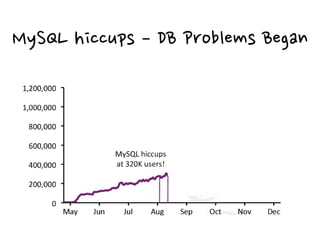
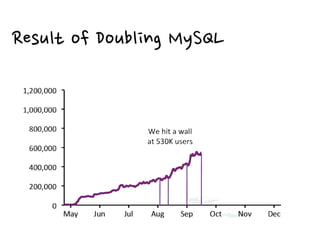
3. Real-world examples show how companies like Facebook, Twitter, and Wonga use caching extensively to handle high volumes of traffic and database requests. Caching is critical to scaling applications in a cost-effective way.