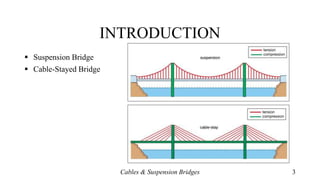
This document discusses the key elements and design considerations of cable-stayed and suspension bridges. It covers:
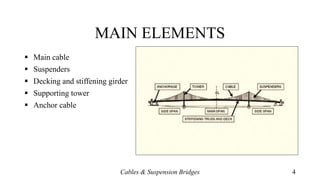
- The main components of these bridges, including main cables, suspenders, decking, towers, and anchor cables.
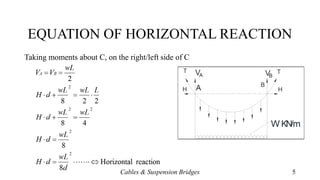
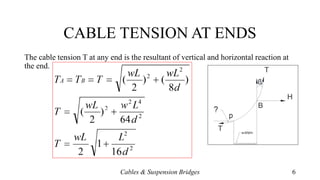
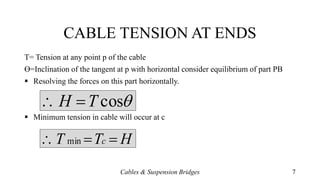
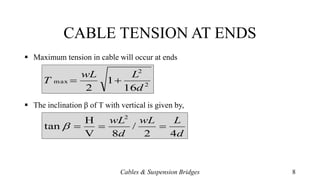
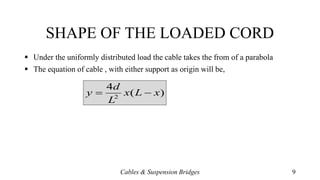
- Equations for calculating horizontal reactions, cable tension at various points, and the parabolic shape of loaded cables.
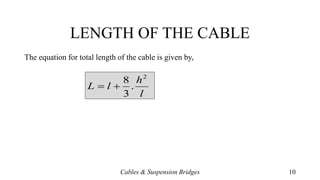
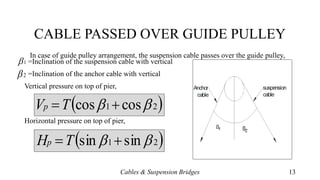
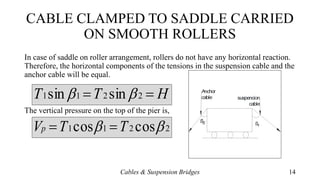
- Methods for determining the total cable length and anchoring cables to the ground via guide pulleys or saddle arrangements on piers.
- The use of a three-hinged stiffening girder to support the bridge deck between cable supports.