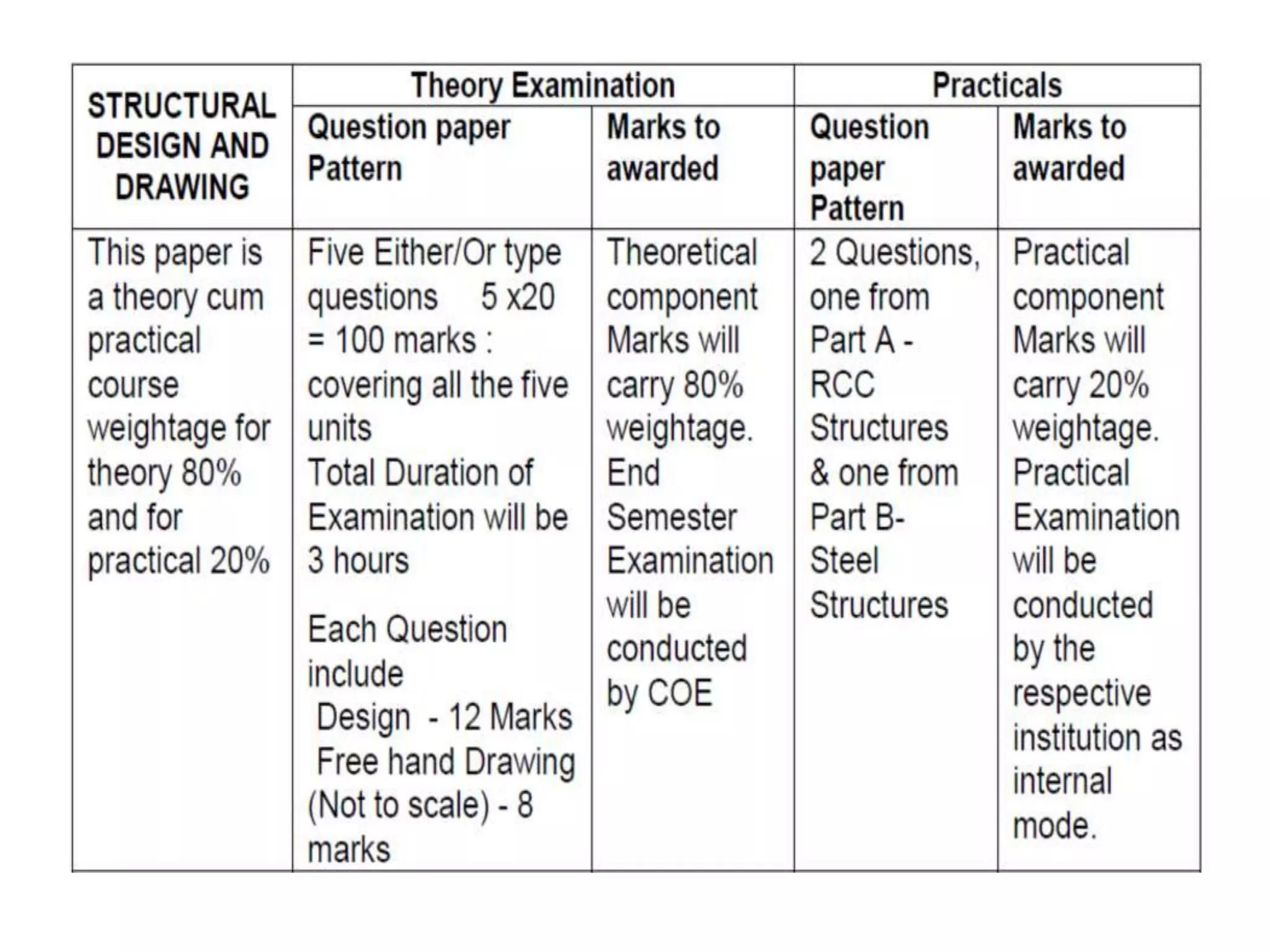
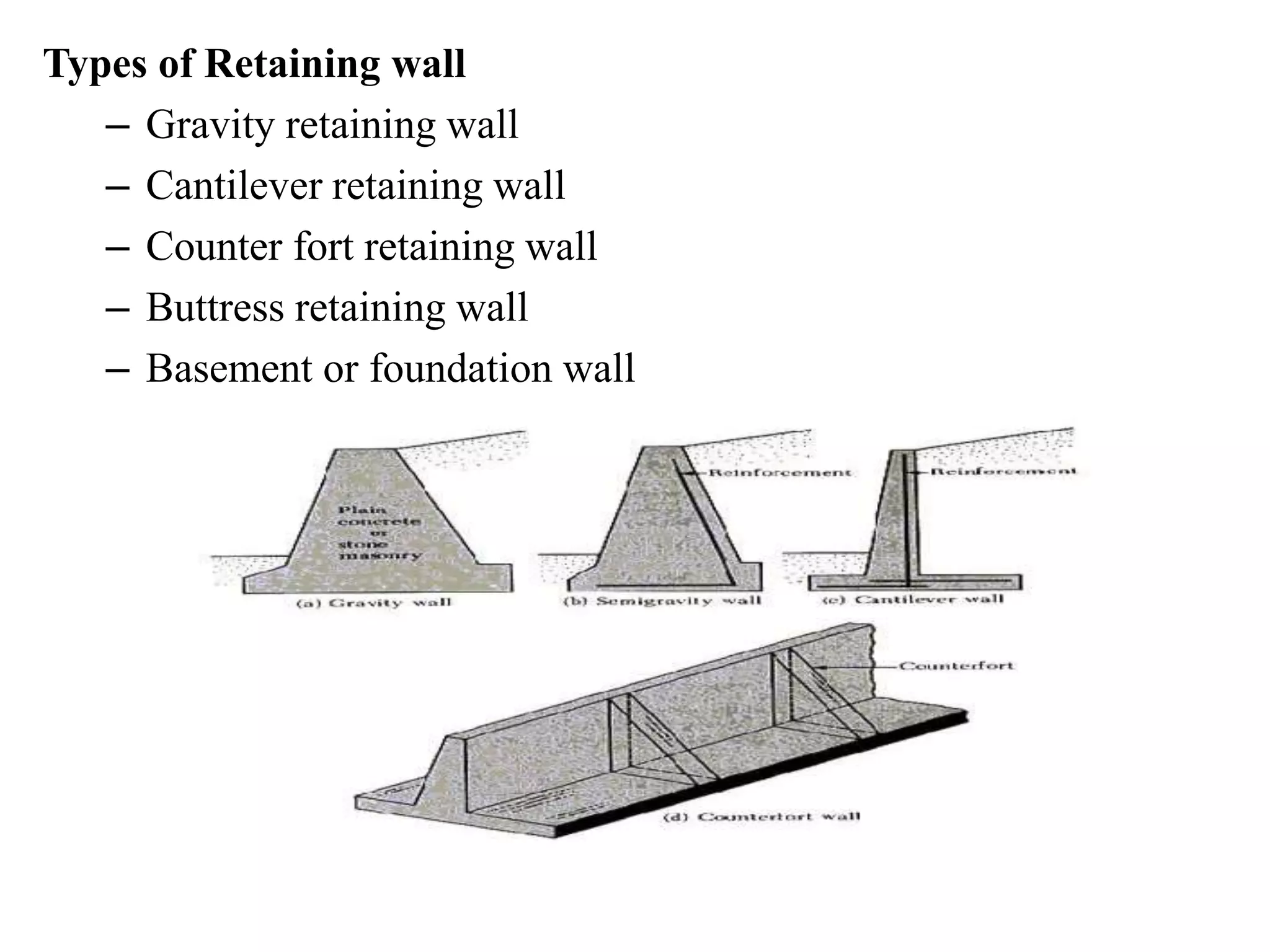
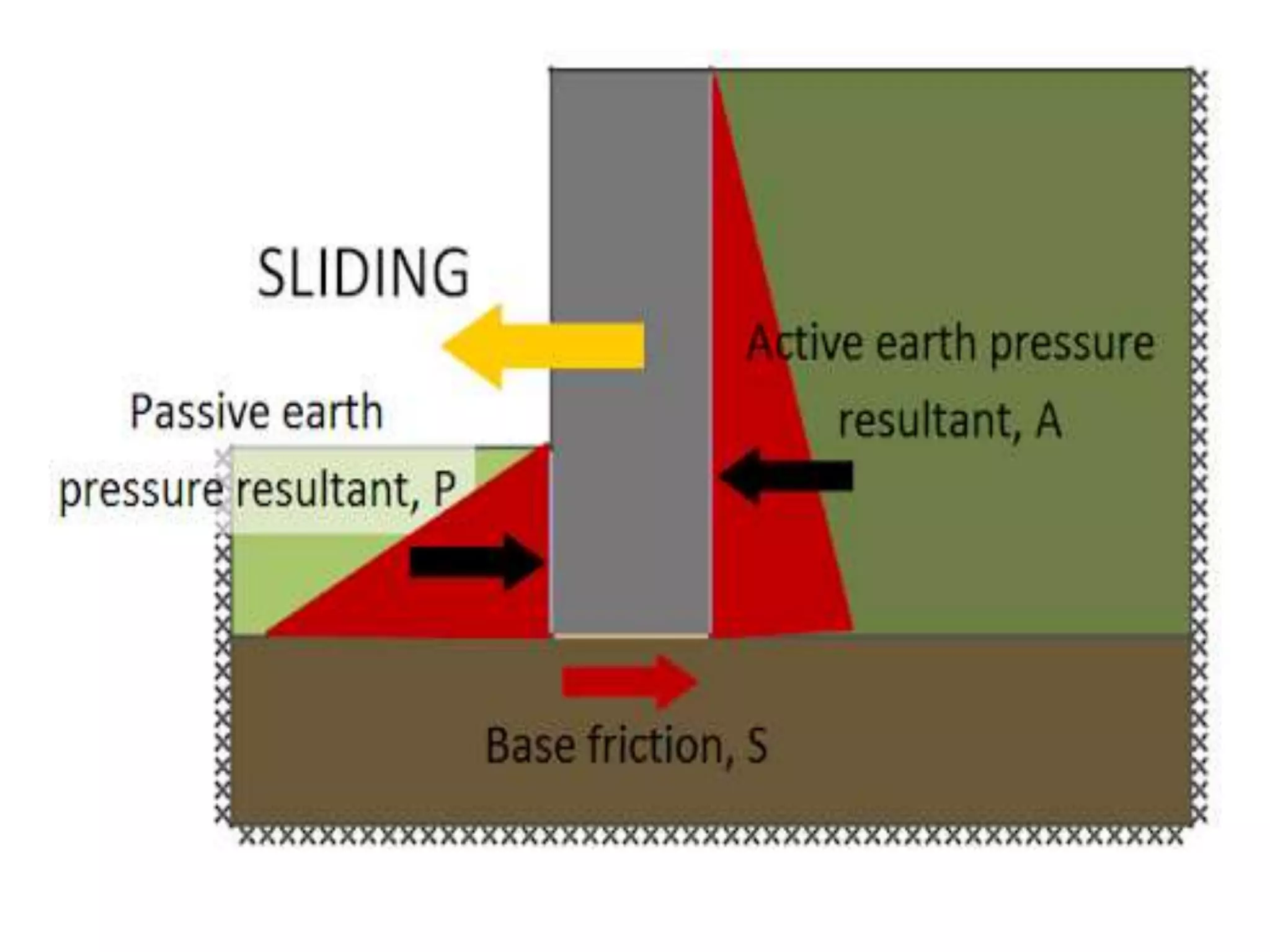
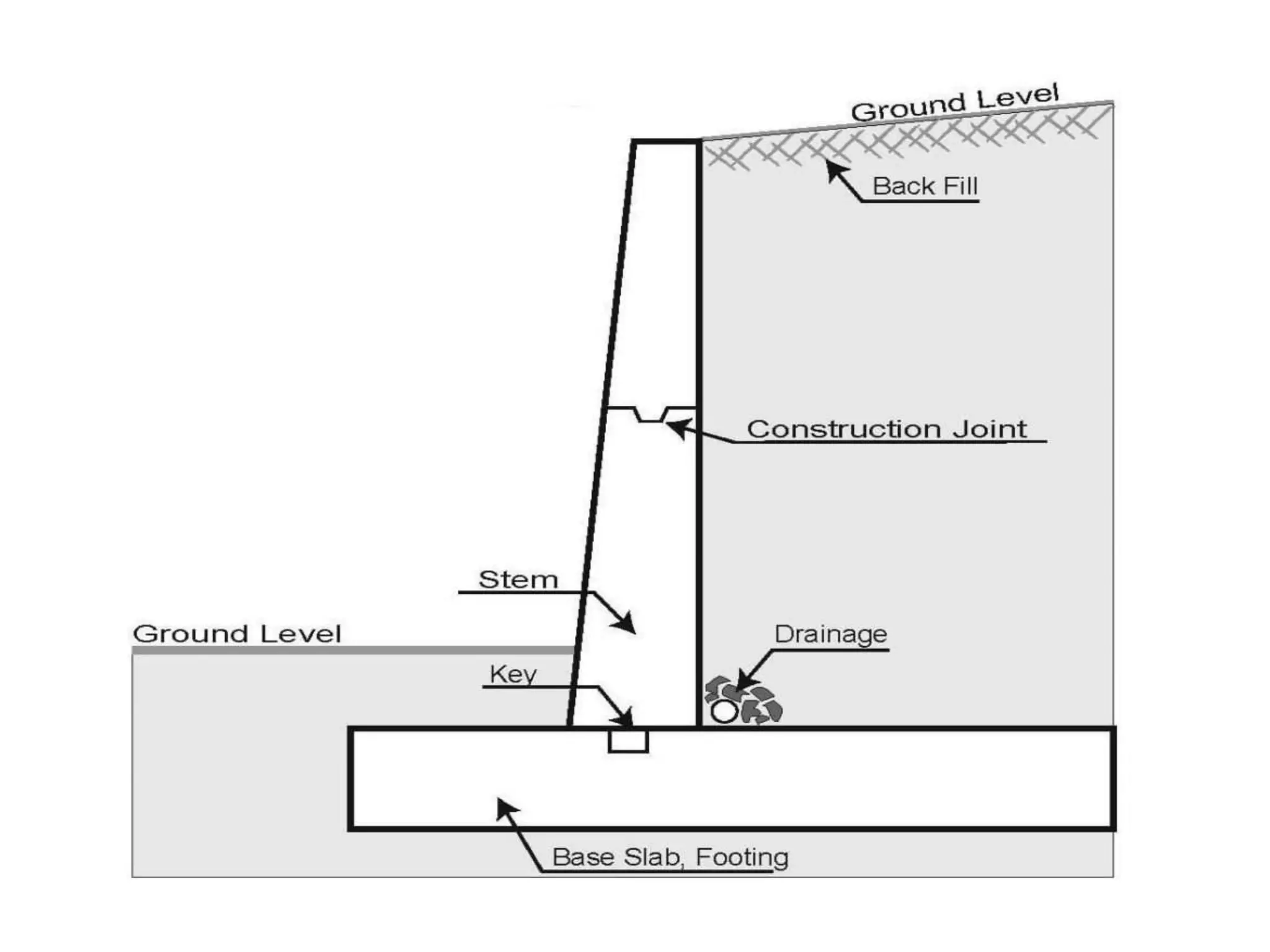
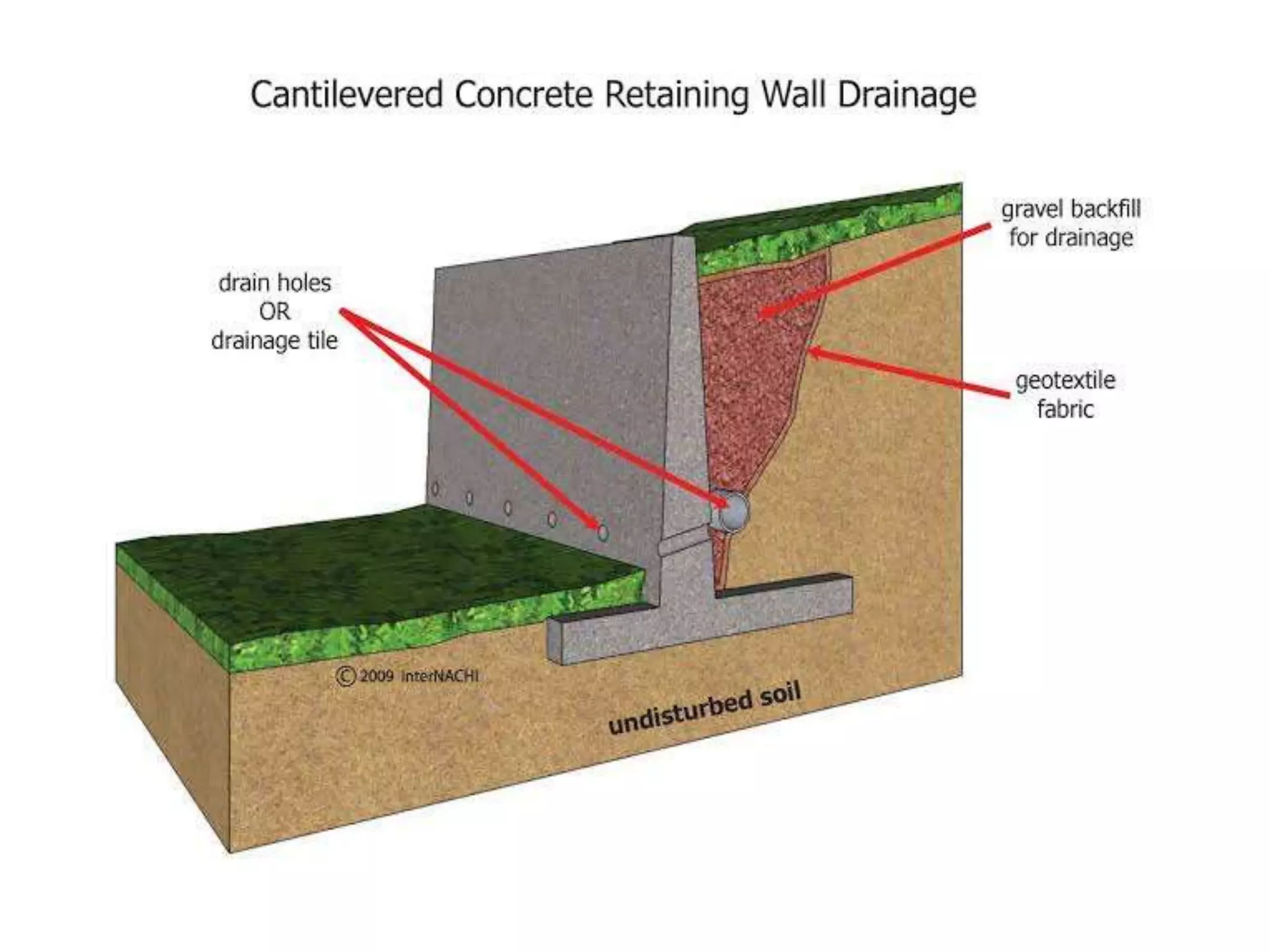
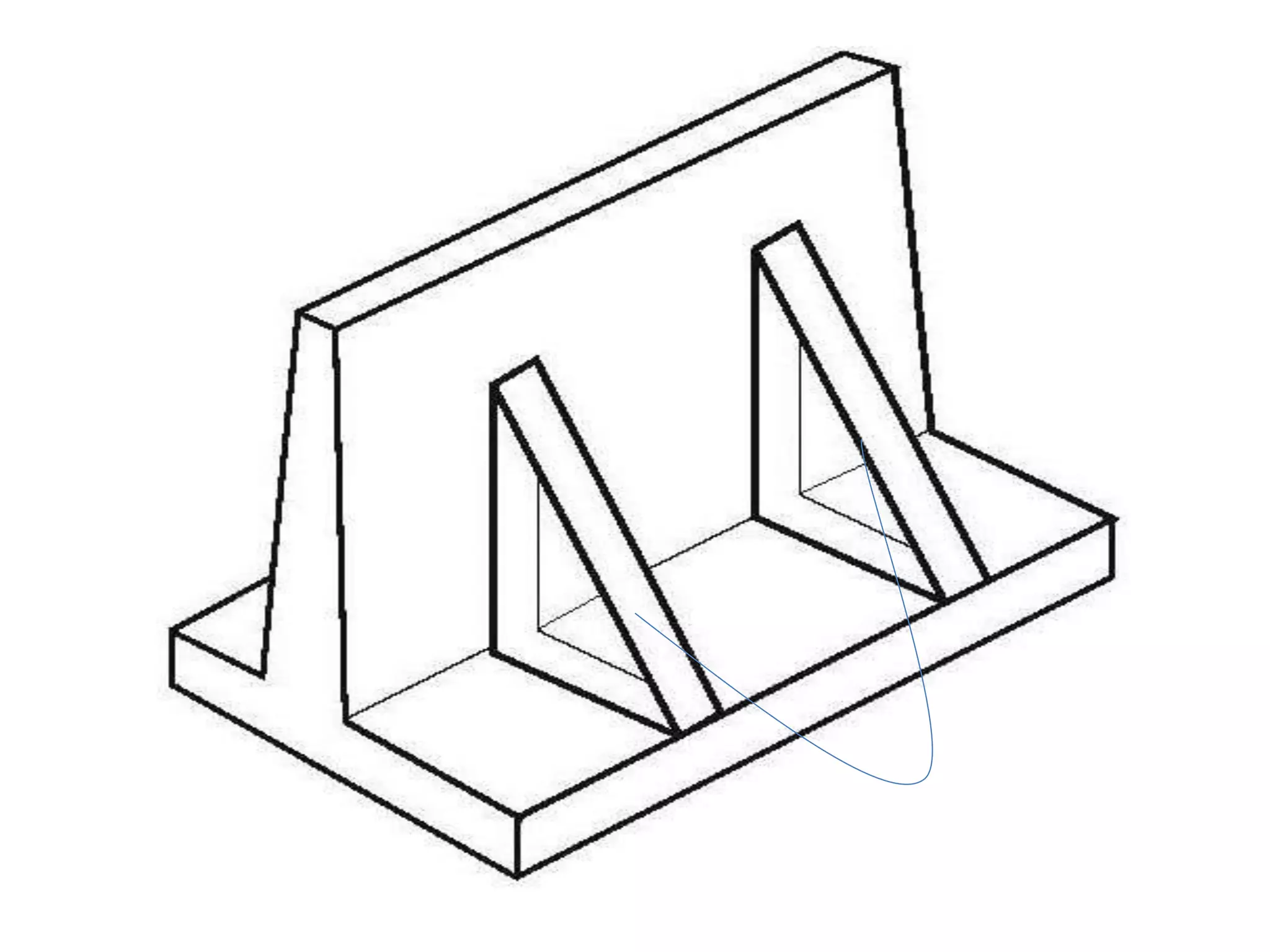
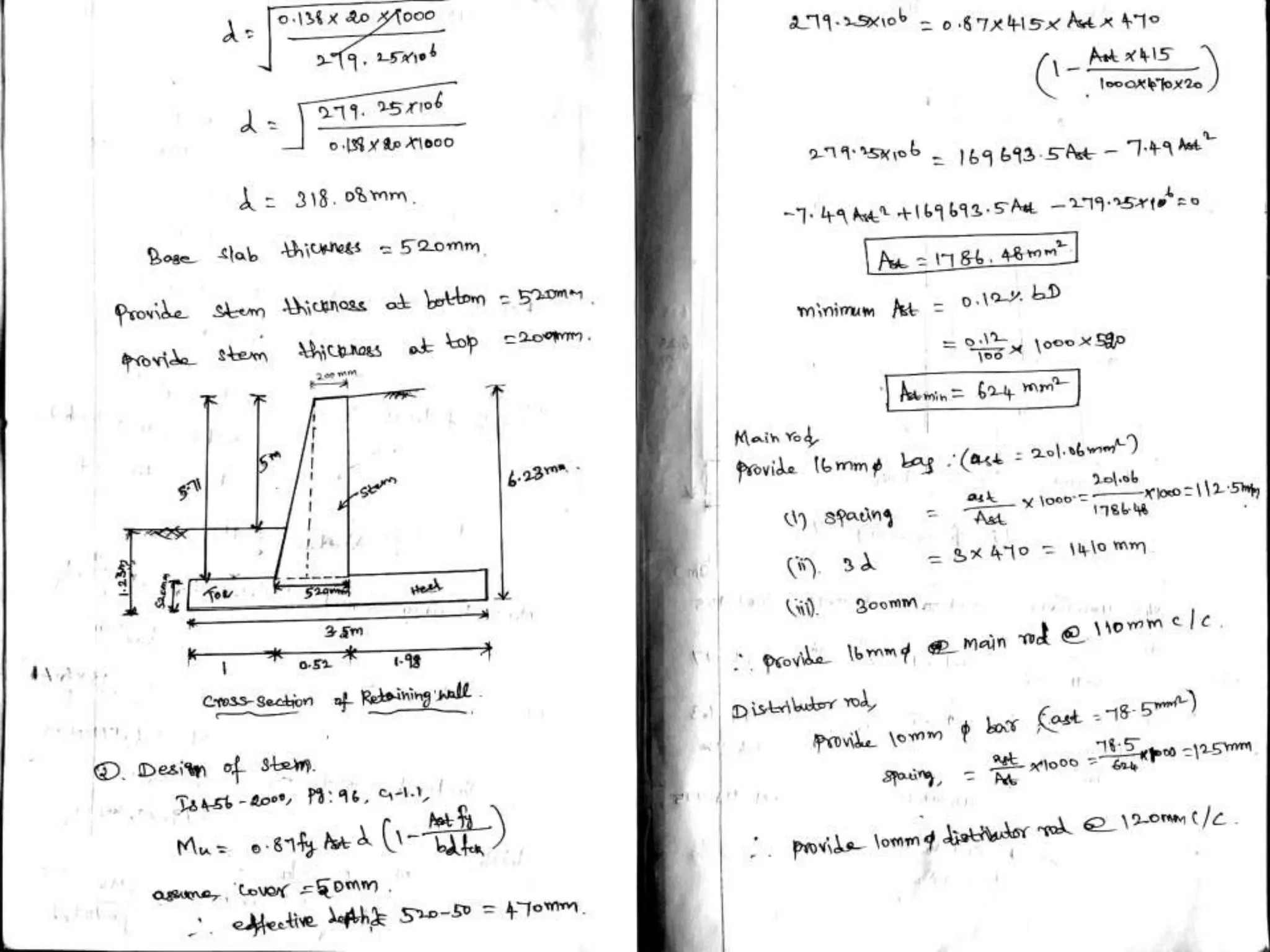
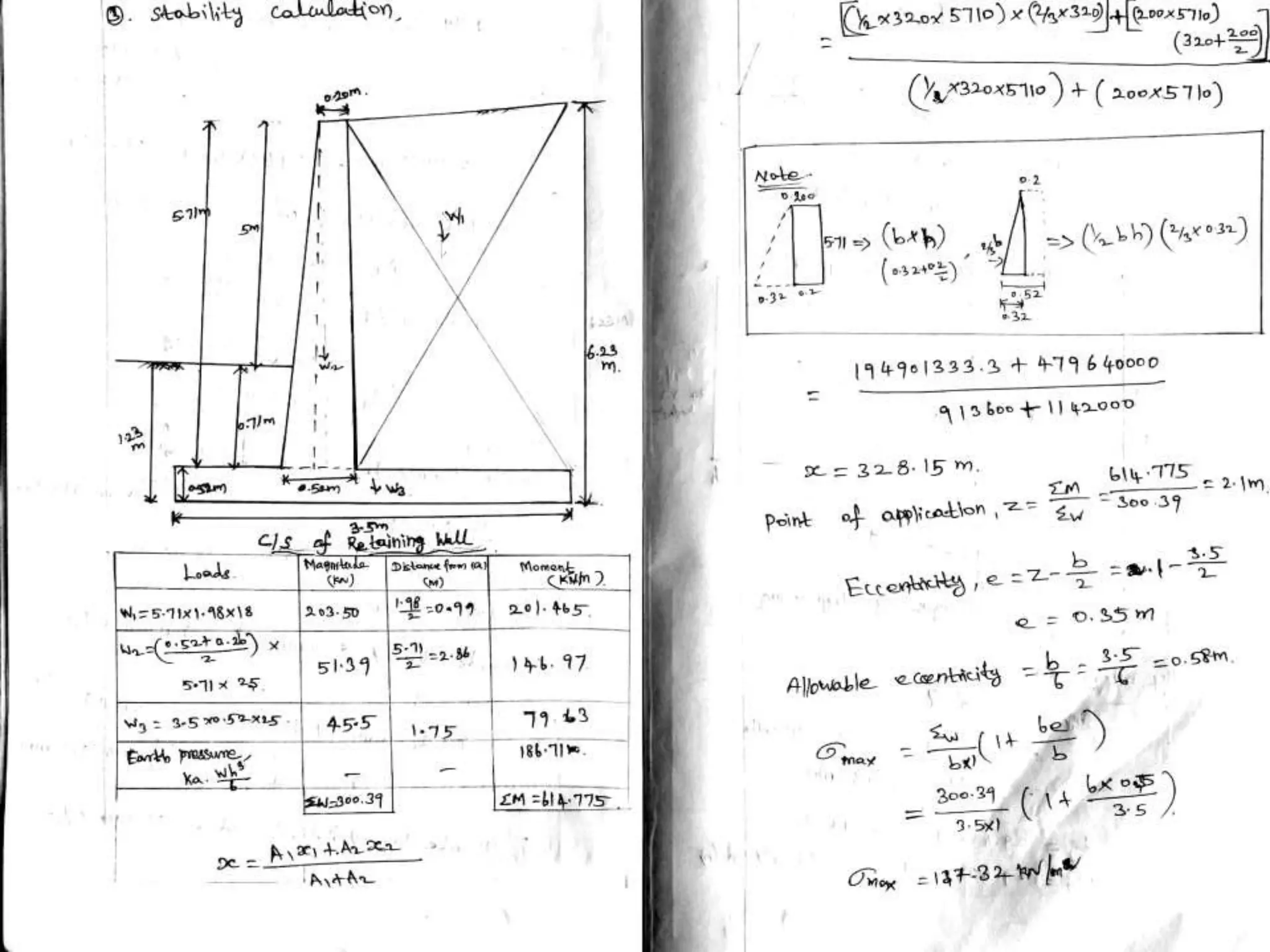
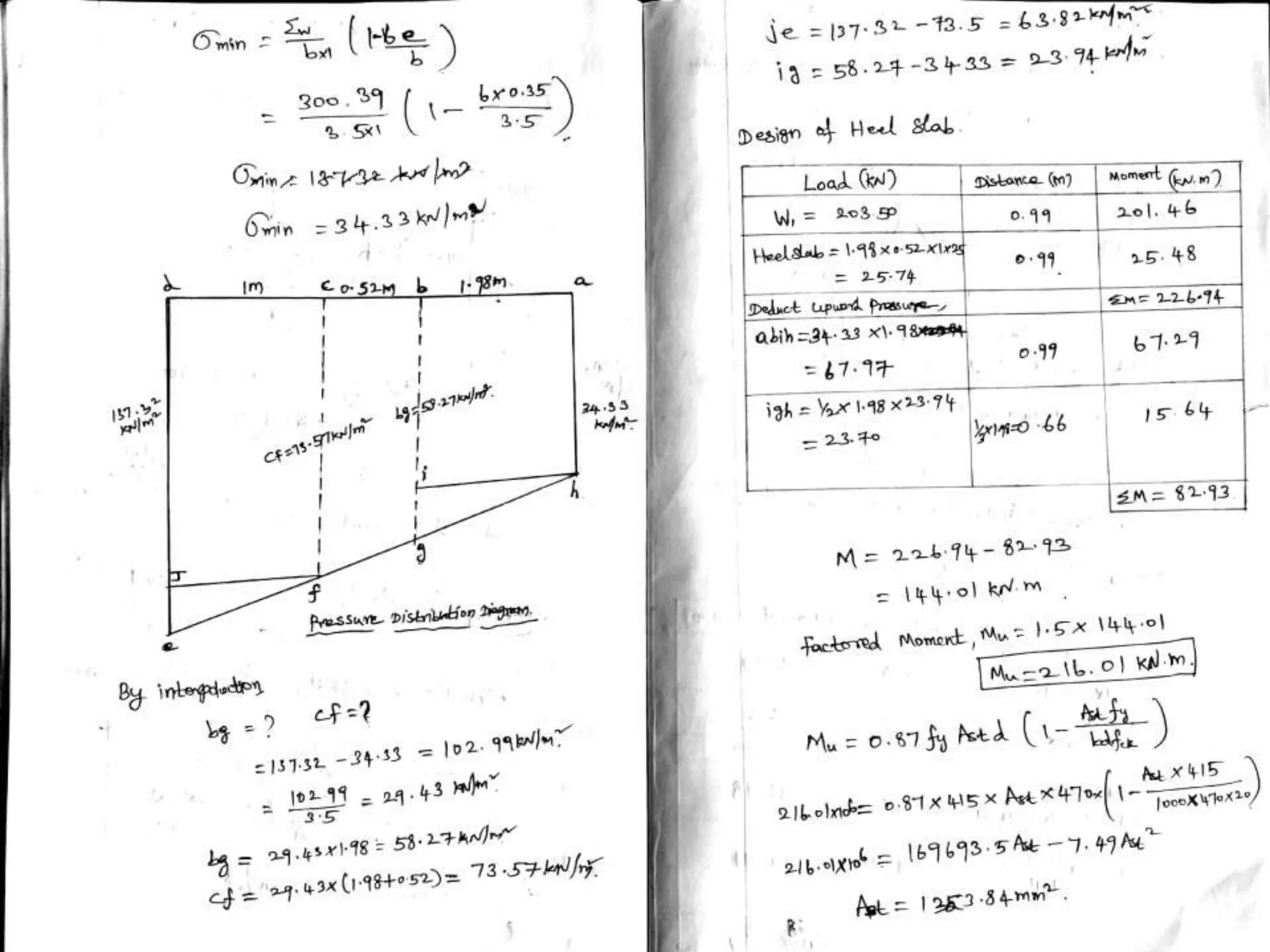
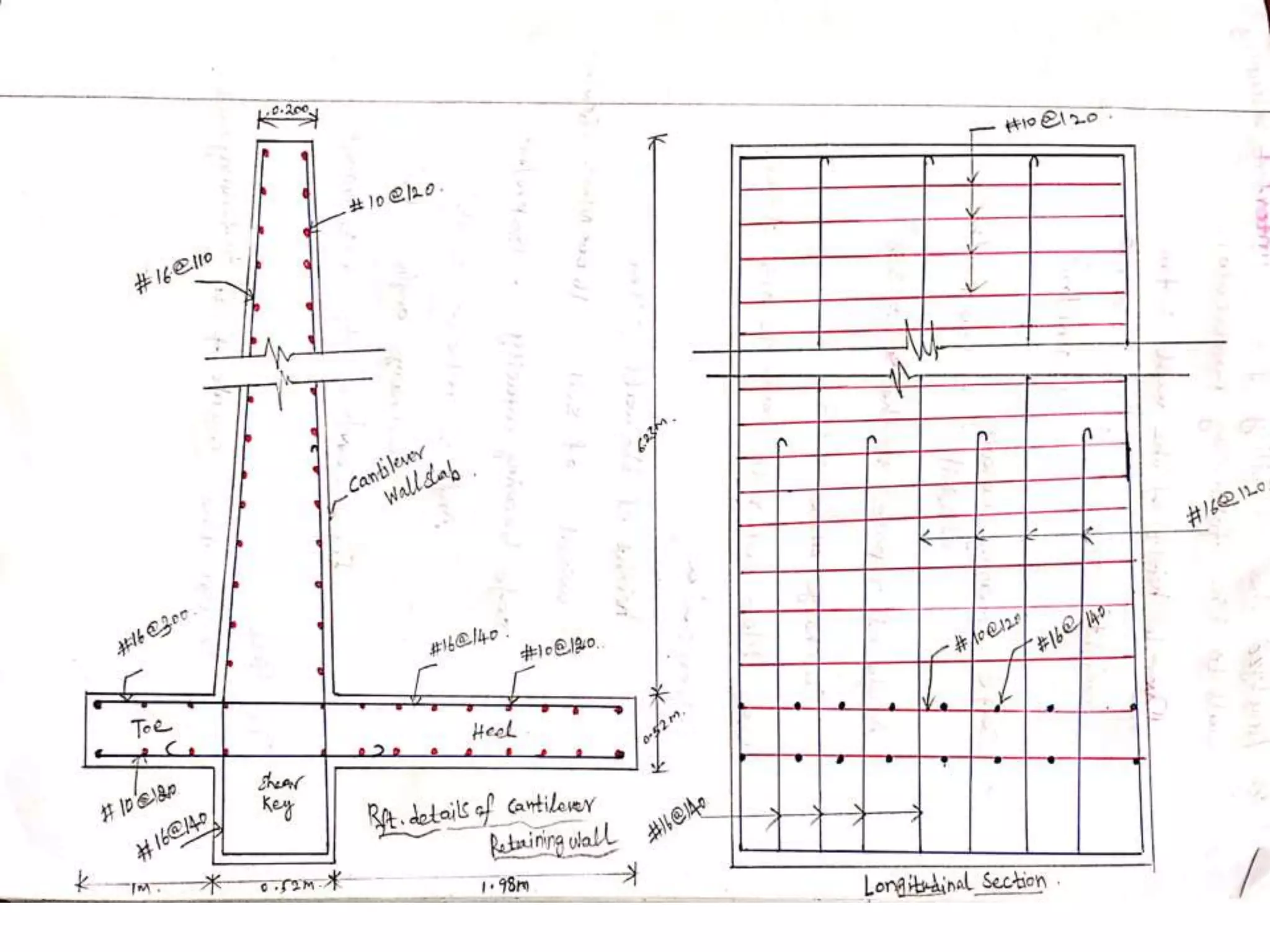
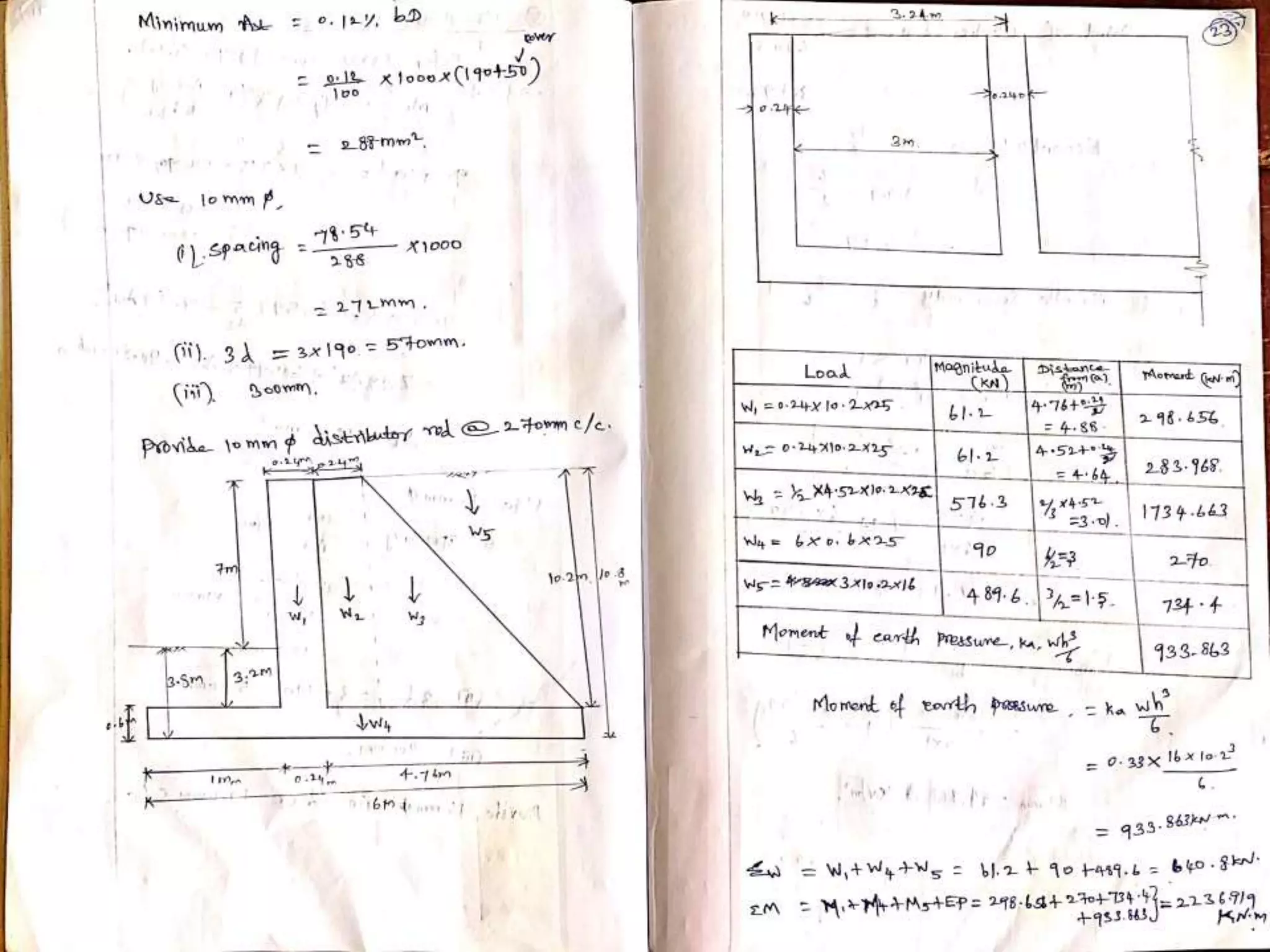
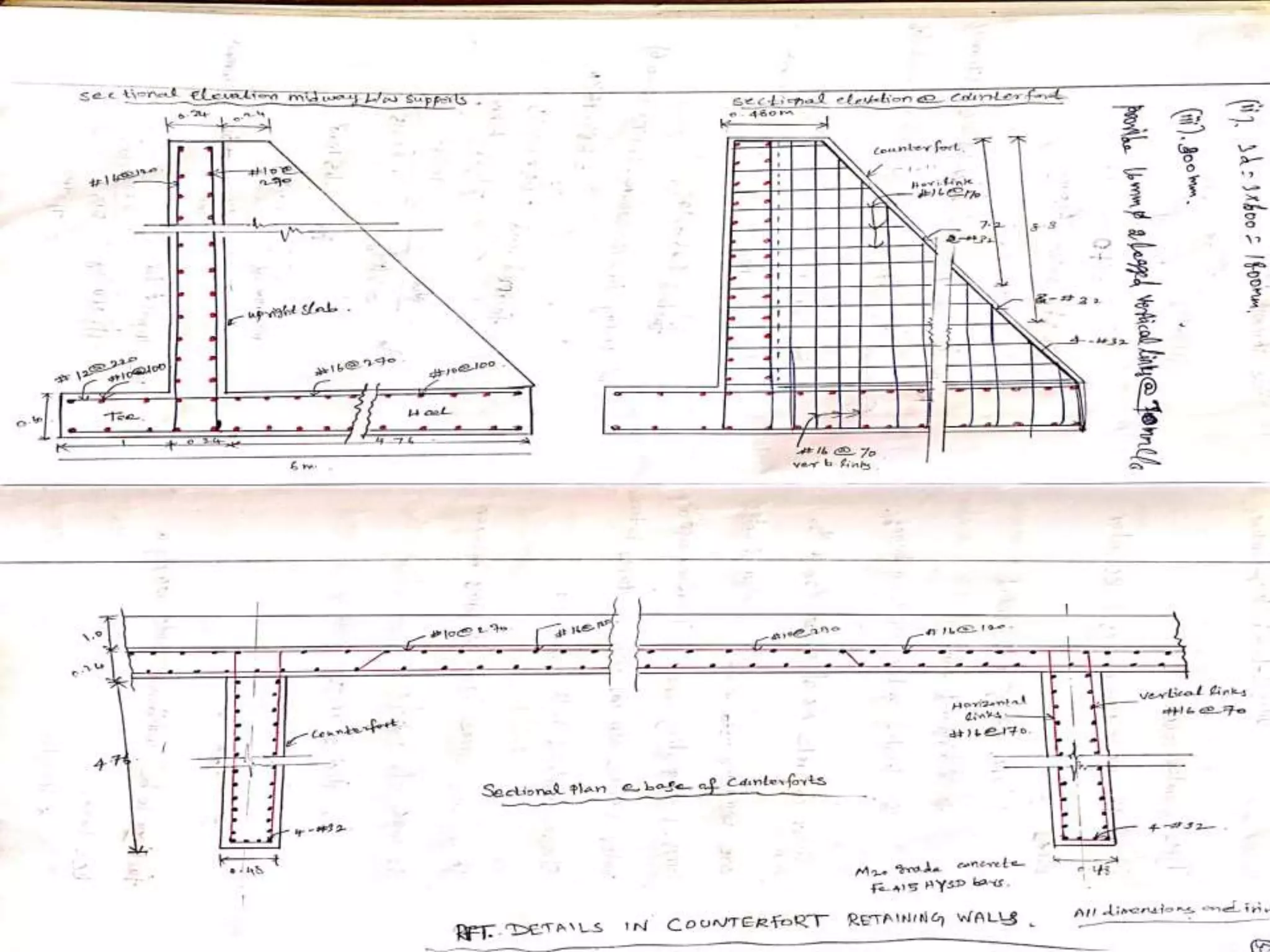
The document provides details about the Structural Design and Drawing course CE8703 taught at Vivekanandha College of Technology for Women. It includes the course objectives, units covered, outcomes, design and drawing exercises, textbooks and code books referenced. The key topics covered in the course are design and drawing of retaining walls, flat slabs, bridges, liquid storage structures, industrial structures, girders and connections. The course aims to provide students with knowledge of structural engineering design principles and skills to design and draw various reinforced concrete and steel structures.