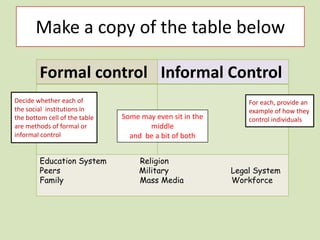
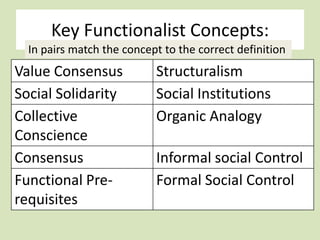
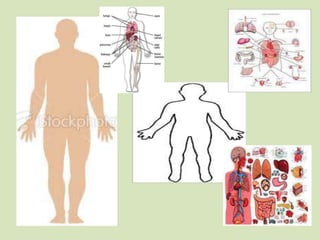
This document provides an introduction to the functionalist perspective of society. It explains that functionalism views society as a system of interconnected institutions that work together to maintain social order and solidarity. It describes how functionalists believe institutions like the family, government, economy, education and religion shape human behavior through formal and informal social control. The document gives examples of how different institutions could represent organs in the body to illustrate functionalism's view of society operating like a single organism. It outlines key concepts of functionalism and tasks for understanding and applying the functionalist perspective.