Embed presentation
Downloaded 347 times





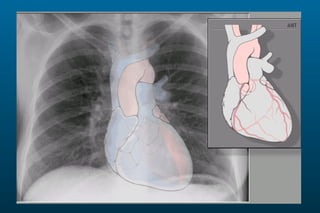
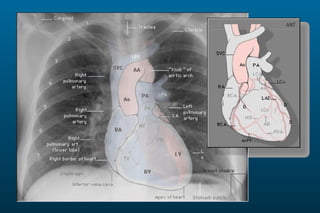
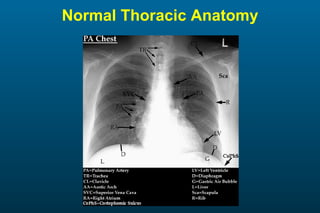
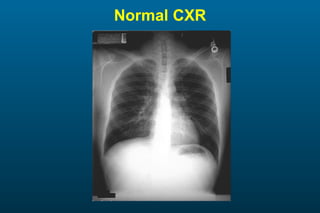
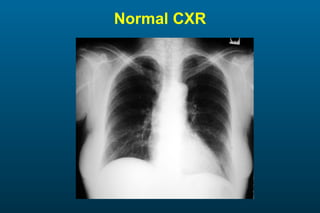
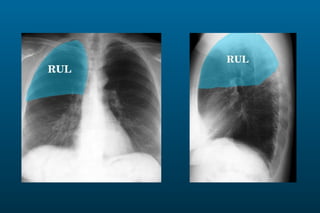
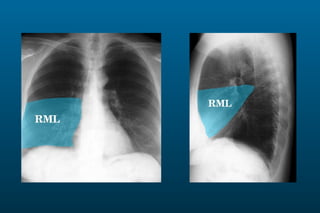
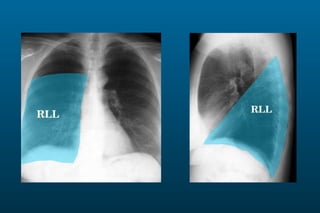
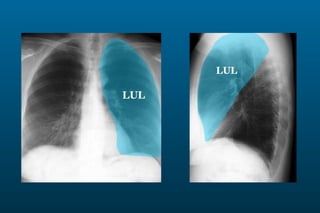
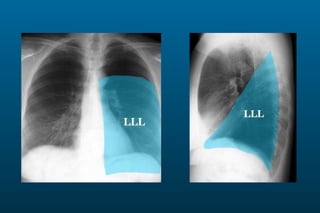
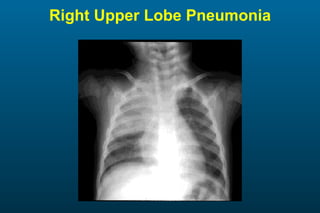
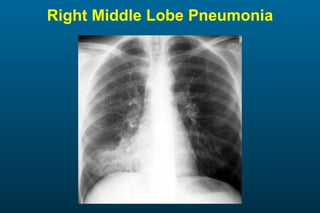
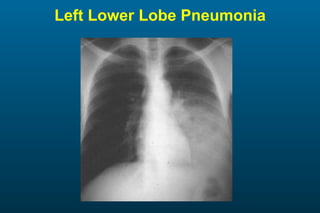
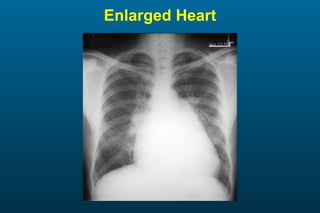
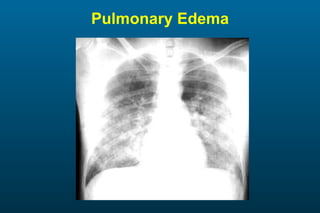
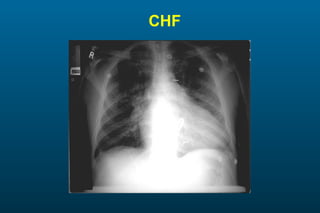
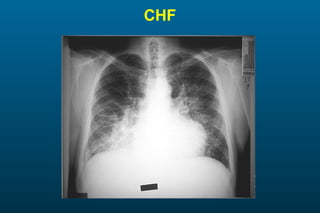
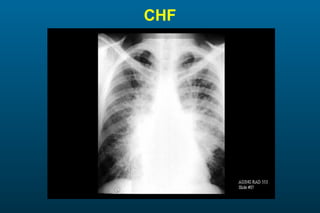
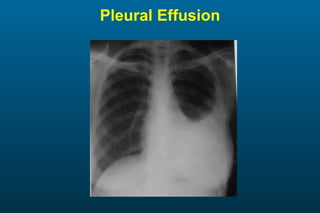
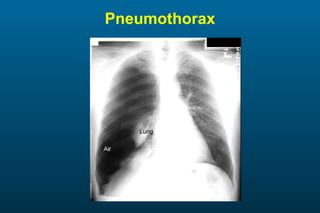
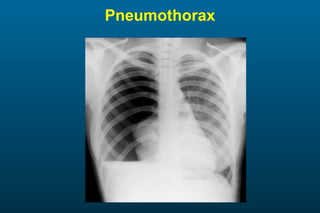
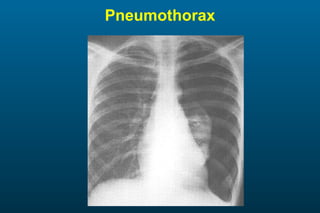
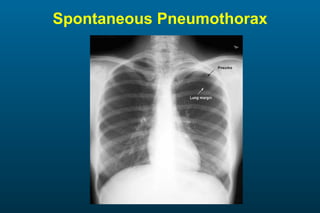
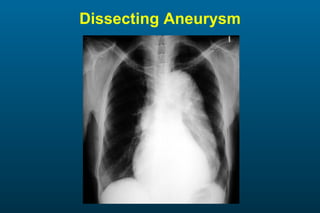
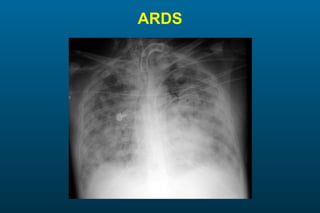
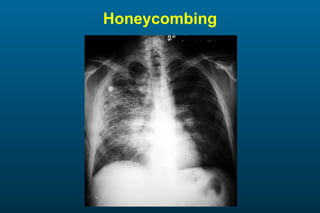
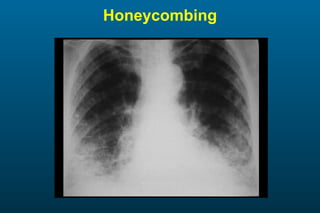
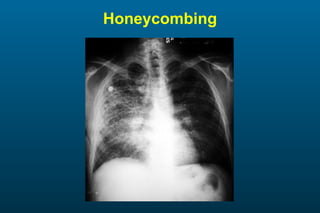
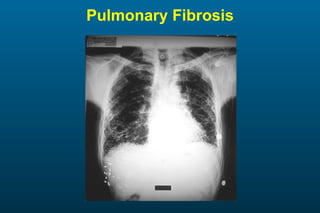
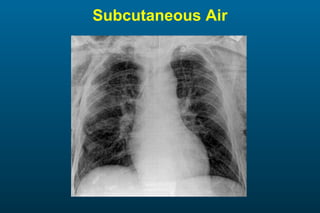
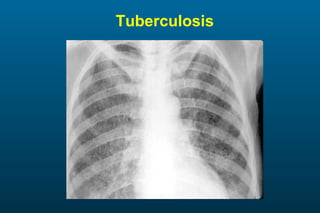
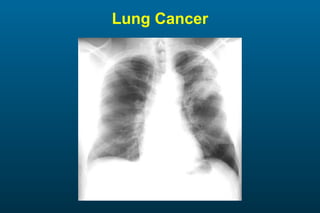
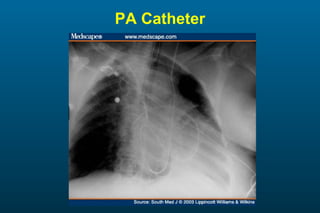
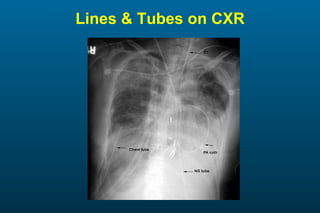

1) The posterior-anterior (PA) view is the standard and most reliable technique for a chest x-ray. It allows detection of air under the diaphragm. 2) A lateral view helps localize infiltrates and evaluate the cardiomediastinal silhouette, effusions, and left atrial dilation. 3) An anterior-posterior (AP) view is used when a patient is too ill to be transported, but image quality is poorer and structures may appear enlarged compared to a PA view.






































