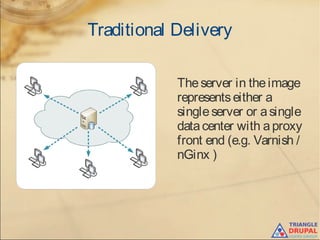
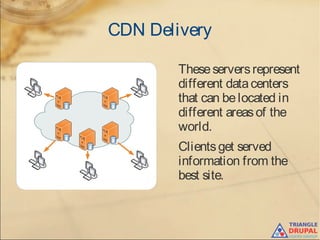
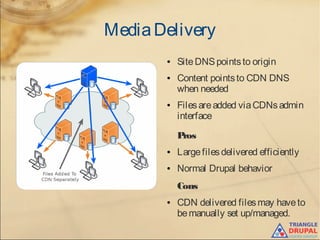
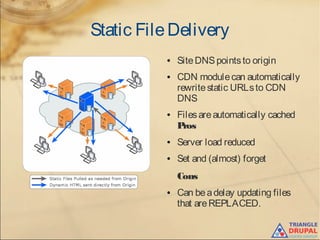
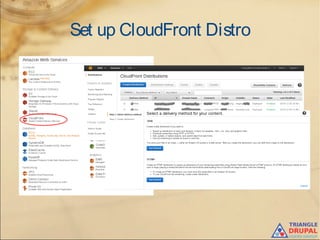
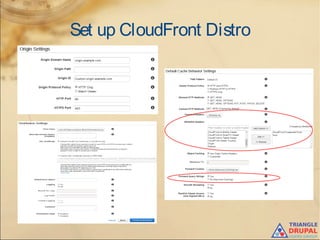
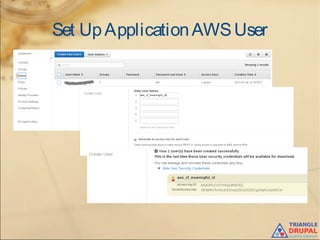
The document discusses the use of content delivery networks (CDNs) with Drupal, explaining their purpose of enhancing content delivery performance and availability by distributing content across multiple servers. It outlines the benefits of utilizing CDNs, such as improved user experience and reduced server load, as well as common issues and strategies for integrating CDNs with Drupal. Key points include the selection of CDN services, challenges related to cache management, and practical setup instructions with examples and modules for implementation.
















![.htaccessSetup
Redirect login'sto origin site:
# Redirect logins to nonCDN site
RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} !^origin.college.edu [NC]
RewriteRule ^user/login$ https://origin.college.edu/user/login [R=301,L]
RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} !^origin.college.edu [NC]
RewriteRule ^user$ https://origin.college.edu/user [R=301,L]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tridug-cdns-150319164410-conversion-gate01/85/Using-Content-Delivery-Networks-with-Drupal-25-320.jpg)

![Settings.php Setup
Thefollowing codeletstheCDN support HTTPS. Needsto bein
thesettings.php file.
if (isset($_SERVER['HTTP_CLOUDFRONT_FORWARDED_PROTO']) &&
$_SERVER['HTTP_CLOUDFRONT_FORWARDED_PROTO'] == 'https') {
$_SERVER['HTTPS'] = 'on';
$_SERVER['HTTP_X_FORWARDED_PROTO'] = 'https';
}
// The following are only needed if the 'nonCDN' site can be
// accessed by more than 1 host name E.g., initially an internal
// DNS entry and then moved to a client DNS entry.
if ( isset($_SERVER['HTTP_HOST']) &&
$_SERVER['HTTP_HOST'] == 'collegeorigin.longsight.com') {
$_SERVER['HTTP_HOST'] = 'origin.college.edu';
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tridug-cdns-150319164410-conversion-gate01/85/Using-Content-Delivery-Networks-with-Drupal-27-320.jpg)




