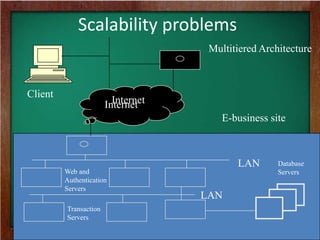
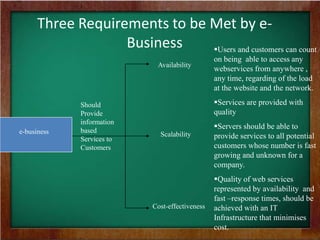
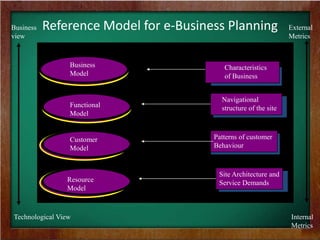
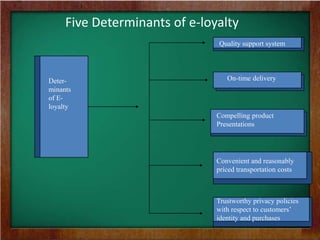
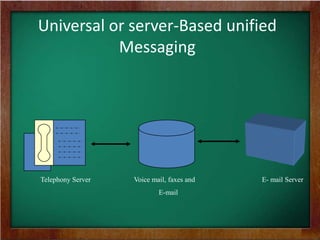
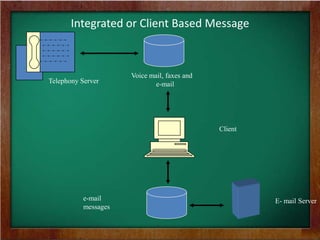
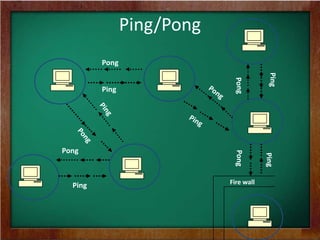
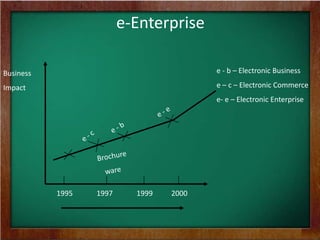
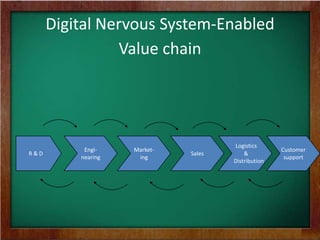
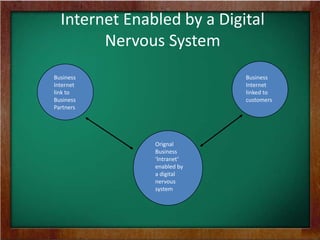
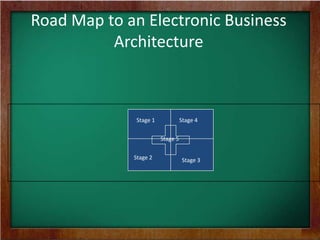
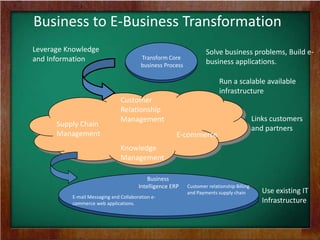
The document discusses the key requirements and models for e-business, highlighting the importance of availability, scalability, and cost-effectiveness in providing web services. It outlines the essential elements for fostering e-loyalty and emphasizes the role of a robust IT infrastructure in enhancing customer experience. Additionally, it presents a roadmap for transforming traditional businesses into e-businesses, leveraging technology to optimize customer relationships and operations.