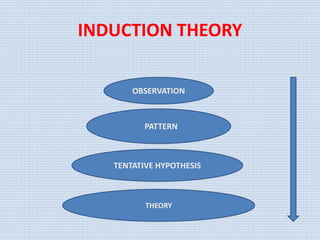
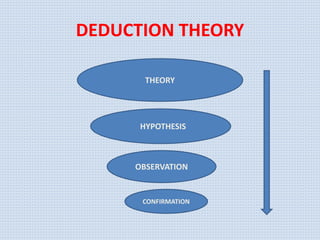
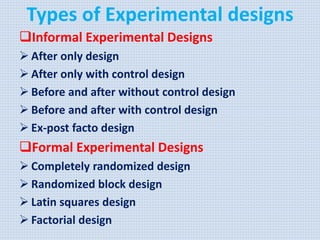
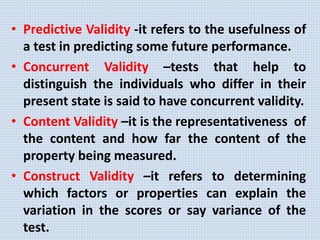
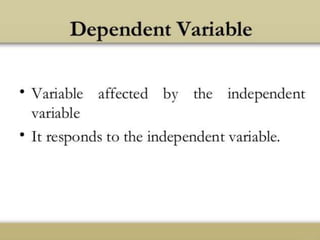
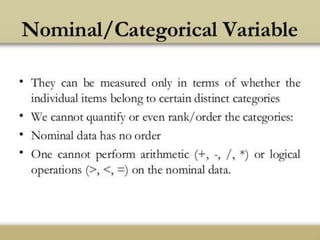
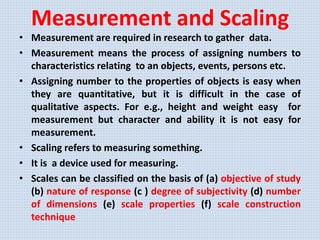
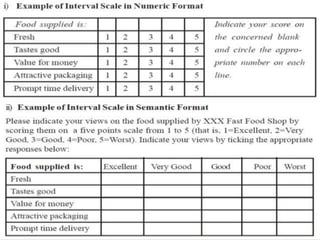
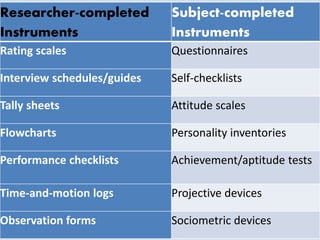
The document discusses various aspects of research methods and processes. It defines research as the gathering of new knowledge from primary and secondary sources through systematic investigation. It notes that research involves identifying and formulating the problem, conducting an extensive literature review, developing hypotheses, preparing the research design, collecting and analyzing data, and preparing a research report. The key steps in the research process are formulating the problem, literature survey, developing a synopsis, identifying variables, setting hypotheses, research design, sampling, data collection, analysis, testing hypotheses, and reporting. The types of research designs discussed are exploratory, descriptive, causal, and experimental.