This document discusses the key aspects of trade cycles including:
1. It defines trade cycles as fluctuations in economic activity over time, encompassing periods of expansion and contraction that affect production, employment, investment and prices in irregular intervals.
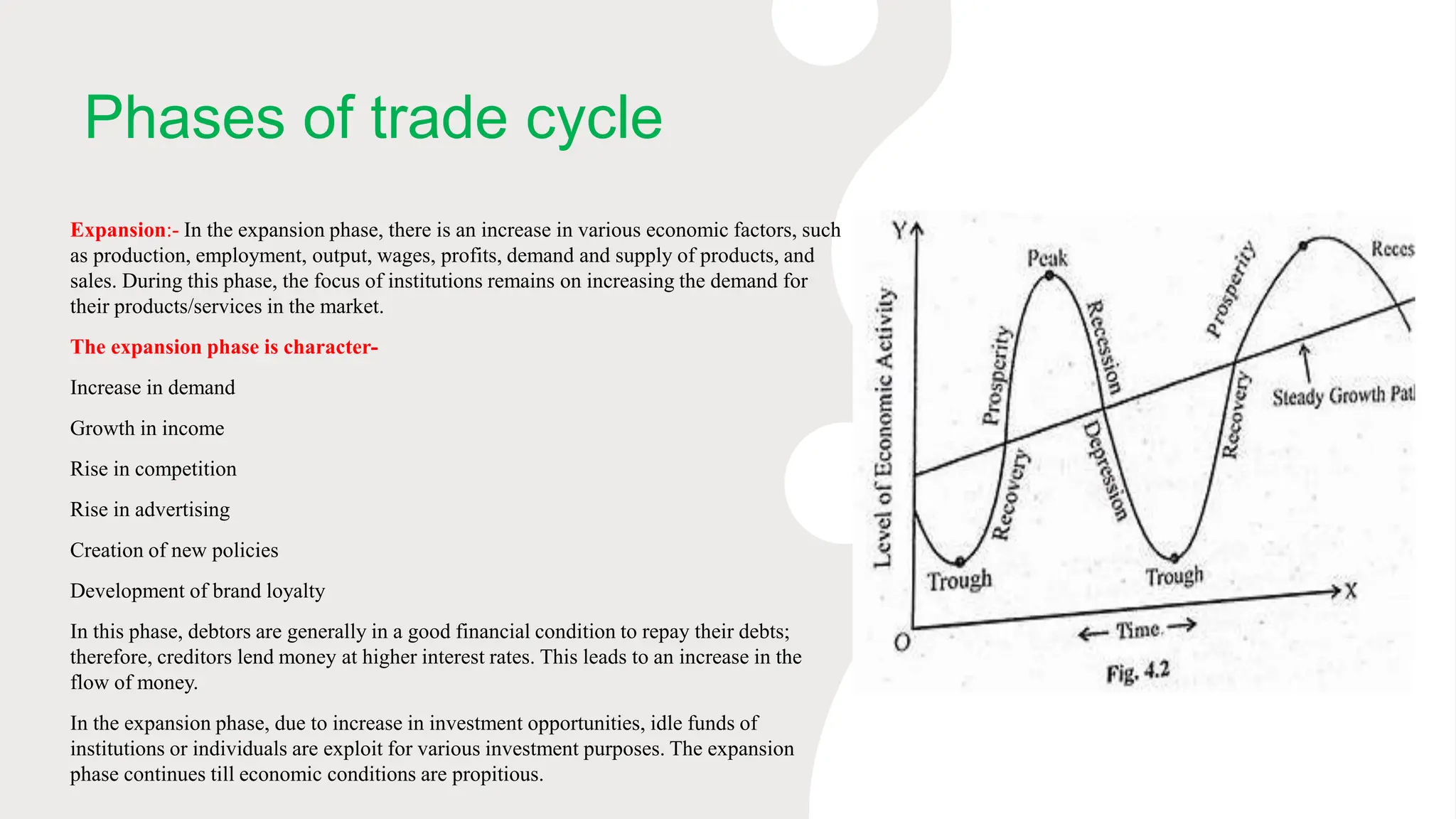
2. It outlines the main phases of trade cycles as expansion, peak, contraction and trough and describes the characteristics of each phase.
3. It identifies several causes of trade cycles including overinvestment, underconsumption, changes in money supply, government policies, and external factors like wars and weather.
4. It discusses tools for measuring and controlling trade cycles through monetary policy, fiscal policy, and other macroeconomic stabilization policies.