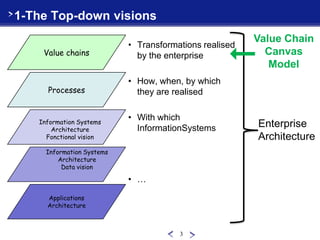
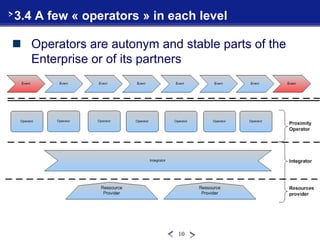
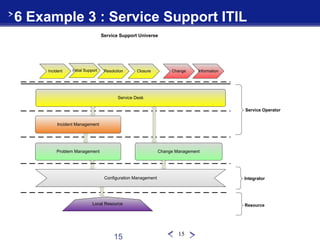
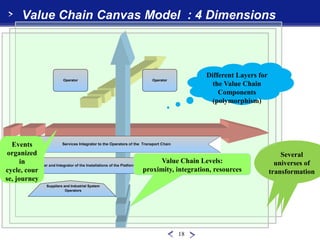
This document introduces the Value Chain Canvas Model (VCCM), a top-down approach created by René Mandel to visualize an enterprise's value chains and transformations. The VCCM represents an enterprise's ecosystem through "universes" bounded by events. Within each universe, value chains comprise three levels - proximity, integration, and resources - connected by operators. The document provides examples of applying the VCCM to an airport, retail offering creation, IT service support, and a call for proposals. It describes how the flexible multi-dimensional model can be adapted to changing enterprise boundaries and transformations.