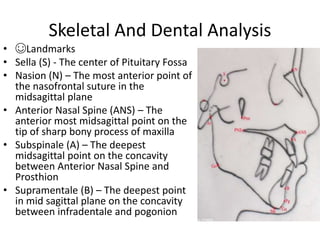
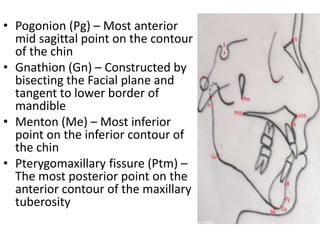
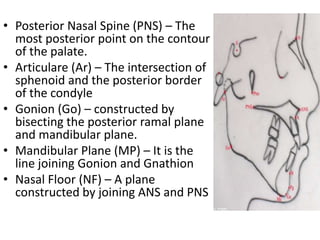
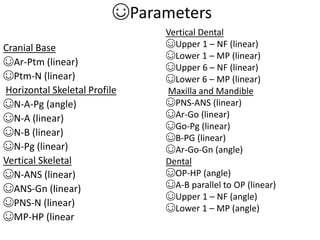
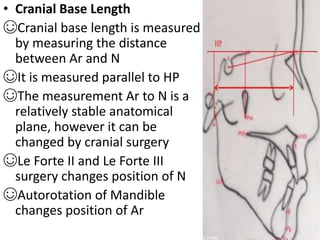
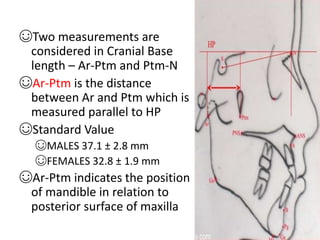
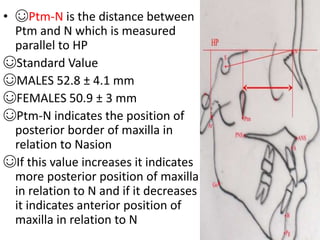
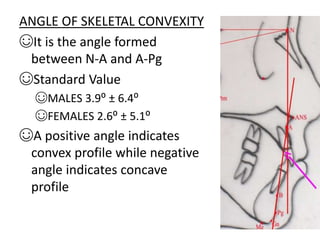
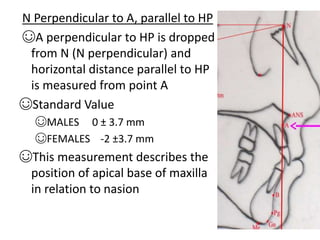
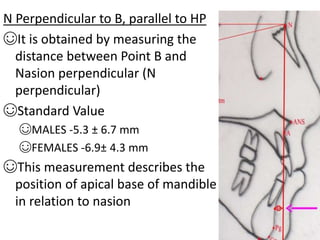
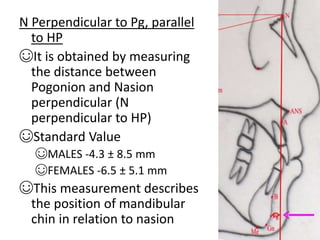
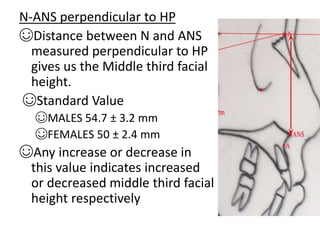
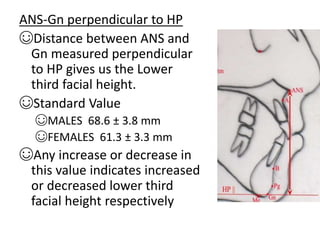
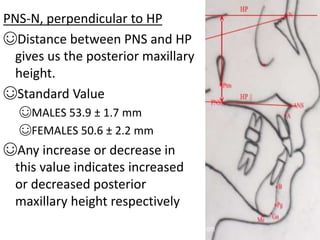
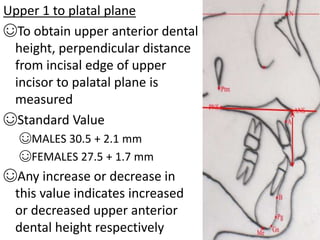
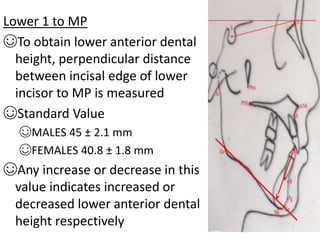
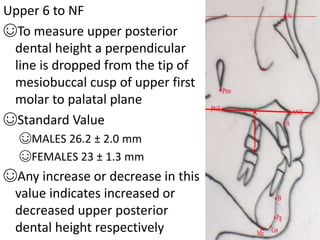
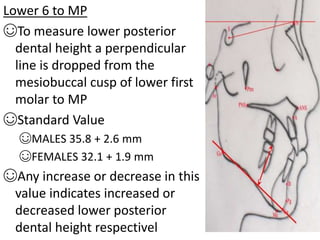
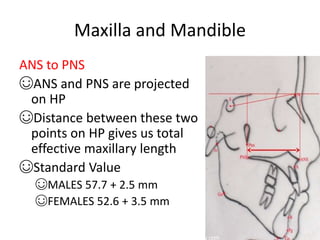
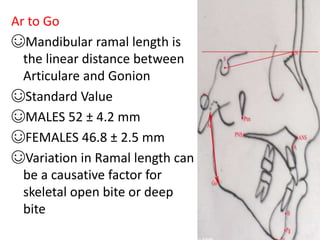
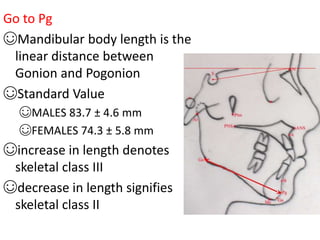
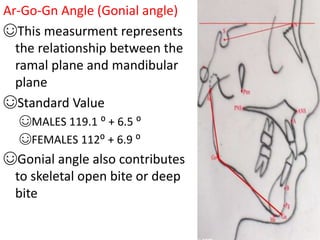
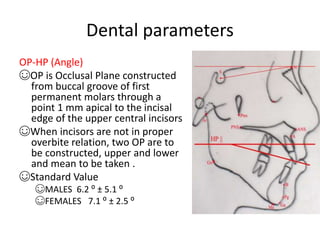
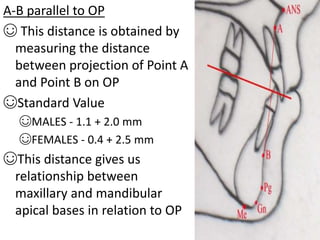
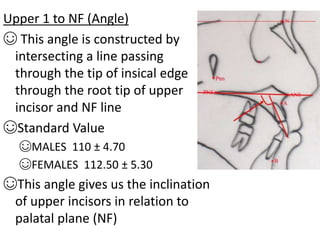
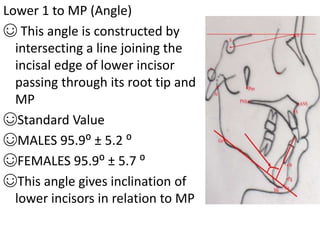
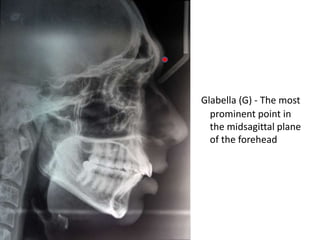
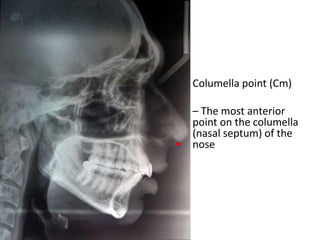
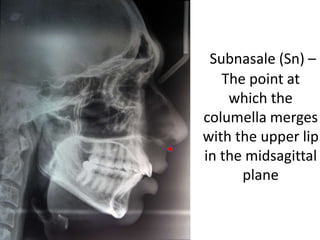
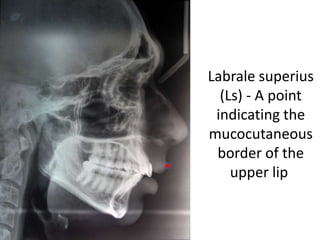
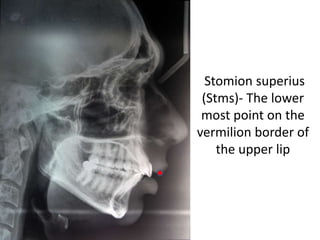
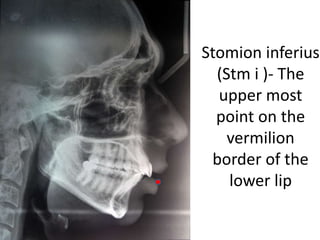
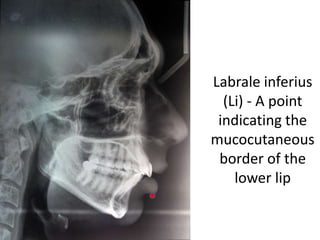
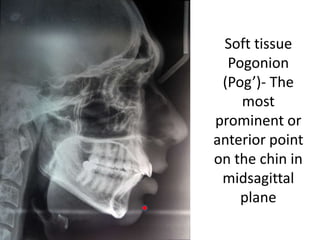
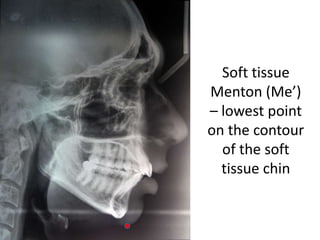
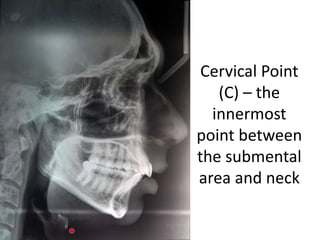
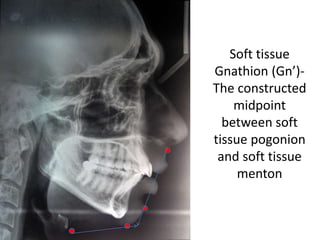
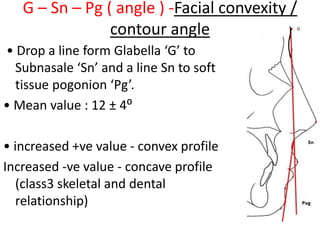
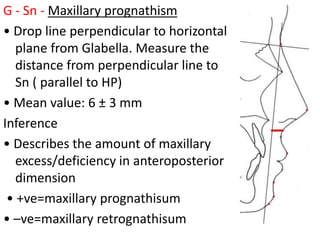
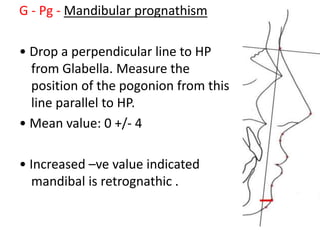
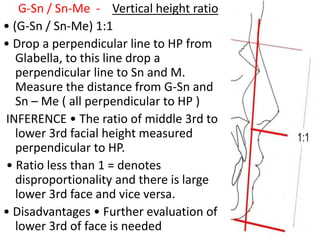
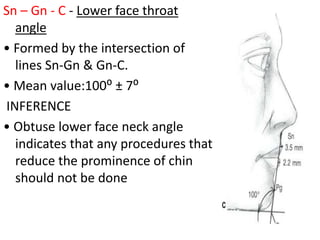
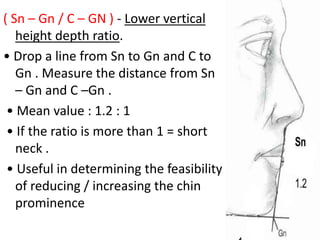
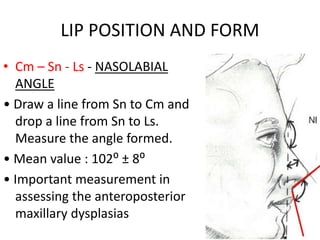
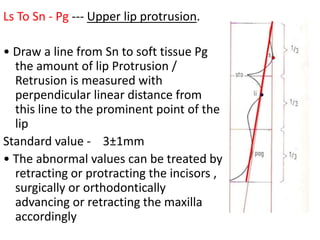
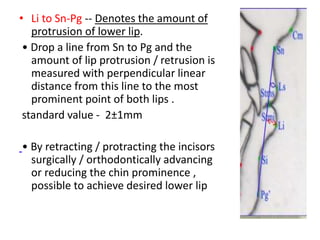
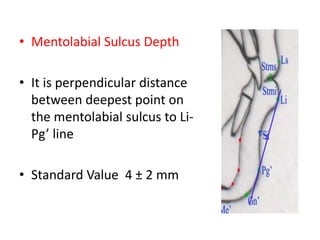
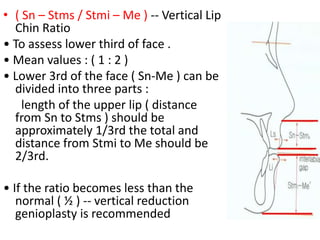
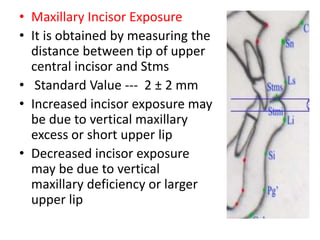
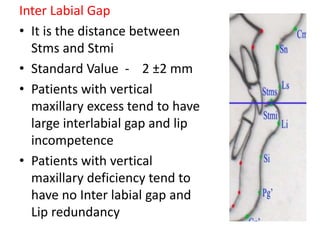
This document provides an overview of cephalometric analysis for orthognathic surgery (COGS). It describes the skeletal, dental, and soft tissue landmarks used in COGS and defines various linear and angular measurements between these landmarks. These measurements assess aspects of the cranial base, maxilla, mandible, dentition, facial height and depth, and soft tissue contours to evaluate skeletal and dental relationships for surgical treatment planning.