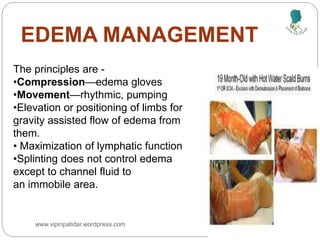
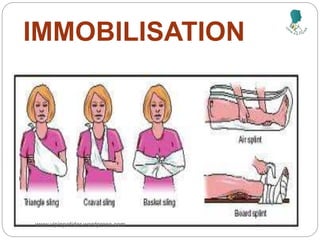
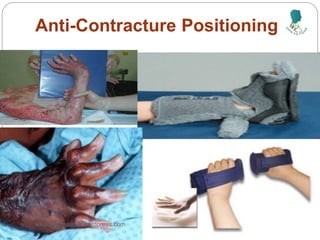
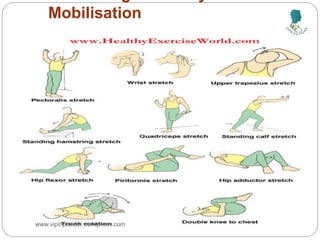
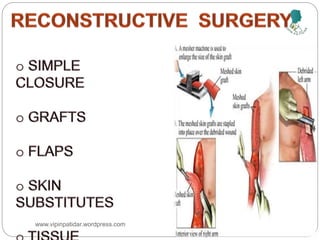
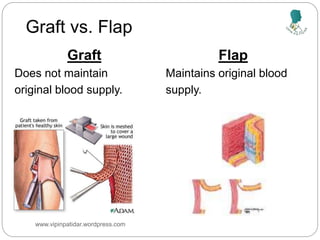
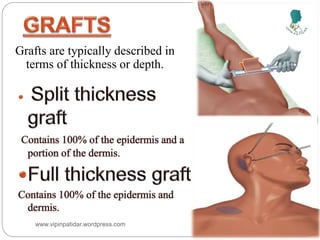
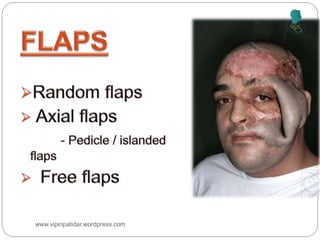
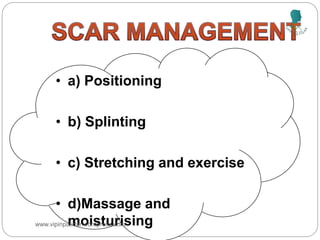
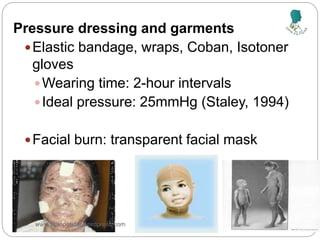
The document outlines the rehabilitation process for patients recovering from injuries, illness, or disease, focusing on regaining physical, sensory, and mental capabilities. It covers pain control, edema management, early and later stages of rehabilitation, skin graft techniques, and complications related to skin grafts. Additionally, it addresses psychosocial aspects of recovery, including emotional reactions and body image alterations.