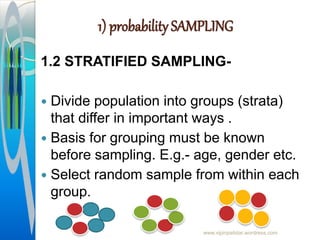
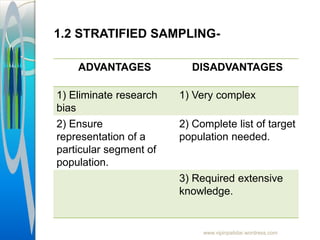
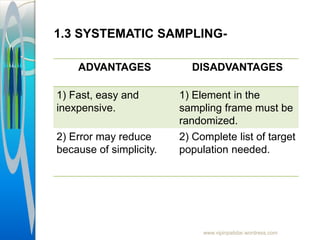
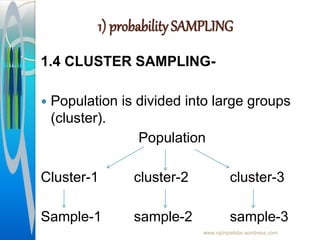
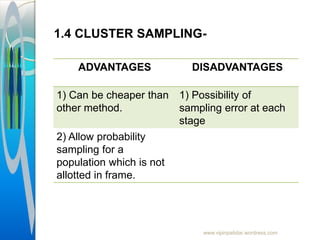
The document provides an overview of sampling in research, defining key terms such as population, sampling error, and bias. It discusses the importance of sampling as a method to gather data from a subset of the population, detailing various sampling techniques including probability and non-probability sampling. Additionally, it highlights the advantages and disadvantages of each sampling method and outlines the sampling process.