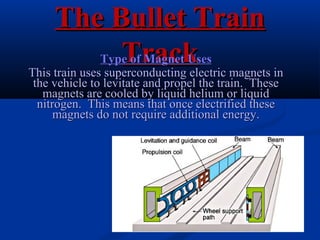
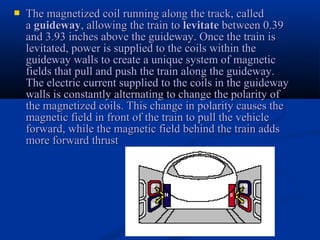
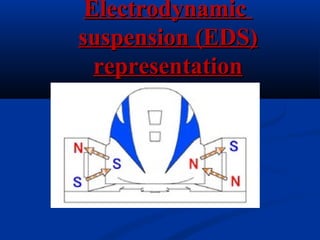
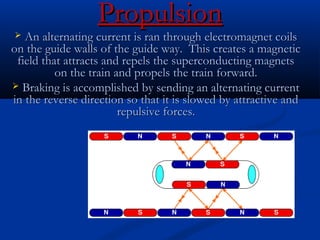
Bullet trains use electromagnetic levitation to suspend and propel trains along guideways using magnets rather than wheels. This allows bullet trains to reach high speeds of over 300 mph with little friction or noise. Bullet trains are also very safe, efficient to operate, and better for the environment compared to conventional trains that run on tracks.