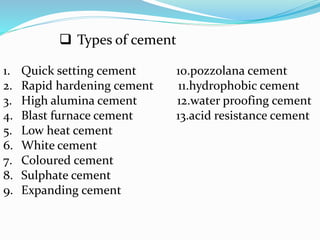
The document discusses various building materials used in civil engineering projects. It describes the properties and uses of common materials like stone, brick, lime, cement, timber, sand, aggregates, mortar and concrete. For each material, it covers types/classes, composition, properties and applications in construction. The key materials discussed include stone, which is used for foundations, walls and arches. Bricks are made from clay and come in traditional and modular sizes. Lime is a cementing material used to make mortar and concrete. The document also examines portland cement and its various types, as well as the uses of timber, sand, aggregates, mortar and concrete in civil works.