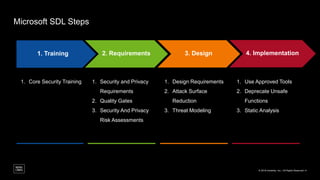
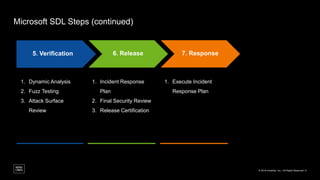
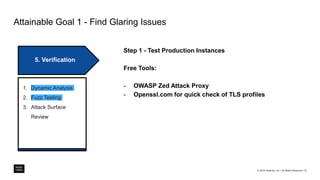
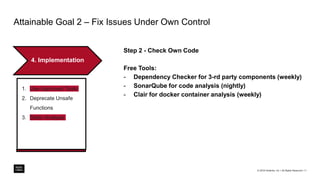
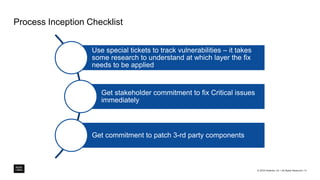
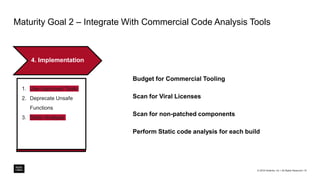
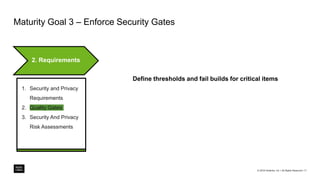
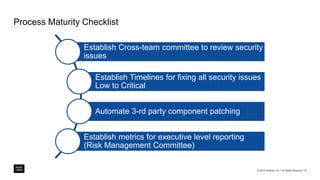
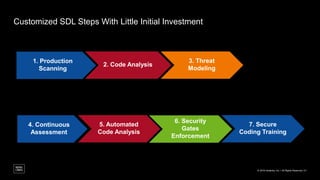
The document outlines a framework for building application security with minimal initial investment, emphasizing the importance of establishing an effective security program through smart tooling and training. It details the Microsoft Security Development Lifecycle (SDL) steps including training, requirements, design, implementation, verification, release, and response; as well as goals for maturity in application security practices. Various free tools are suggested for assessing and fixing security vulnerabilities at different stages of the application lifecycle.