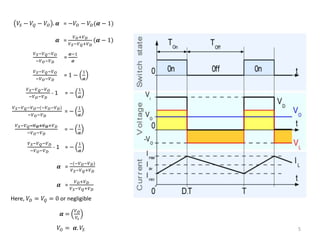
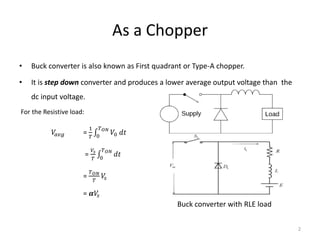
This document describes a buck converter circuit. A buck converter steps down the input voltage and produces a lower average output voltage. It operates by alternately connecting and disconnecting an inductor to the input voltage during switching cycles. The analysis shows that during the on-time, current builds in the inductor, and during the off-time current decreases. By equating the change in inductor current over one switching cycle, the output voltage is derived to be directly proportional to the input voltage multiplied by the duty cycle. The duty cycle is the ratio of on-time to the total switching period.

![4
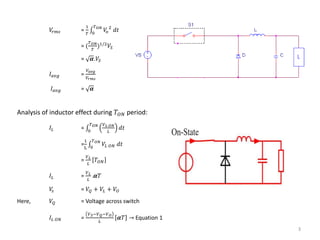
Analysis of inductor effect during 𝑇𝑂𝐹𝐹 period:
𝐼𝐿 = 𝑇 𝑂𝑁
𝑇 𝑉 𝐿 𝑂𝐹𝐹
𝐿
𝑑𝑡
=
1
L 𝑇 𝑂𝑁
𝑇
𝑉𝐿 𝑂𝐹𝐹 𝑑𝑡
=
𝑉 𝐿
𝐿
𝑇 − 𝑇𝑂𝑁
= −
𝑉 𝐿
𝐿
𝜶𝑇 − 𝑇
𝐼𝐿 =
𝑉𝑠−𝑉 𝐿−𝑉 𝑂
𝐿
[𝜶 − 1]. 𝑇
𝑉𝐿 𝑂𝐹𝐹 − 𝑉𝐿 − 𝑉𝐷 = 0
Here, 𝑉𝐷 = Voltage across diode
= −
(𝑉0+𝑉 𝐷)
𝐿
𝜶 − 1 𝑇
𝐼𝐿 𝑂𝐹𝐹 =
−𝑉0−𝑉 𝐷
𝐿
𝜶 − 1 𝑇 → Equation 2
Solving, Equation 1 = Equation 2
𝐼𝐿 𝑂𝑁 = 𝐼𝐿 𝑂𝐹𝐹
𝑉 𝑆−𝑉 𝑄−𝑉 𝑂
𝐿
𝜶𝑇 =
−𝑉0−𝑉 𝐷
𝐿
𝜶 − 1 𝑇](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buckconverter-161005062057/85/Buck-converter-4-320.jpg)