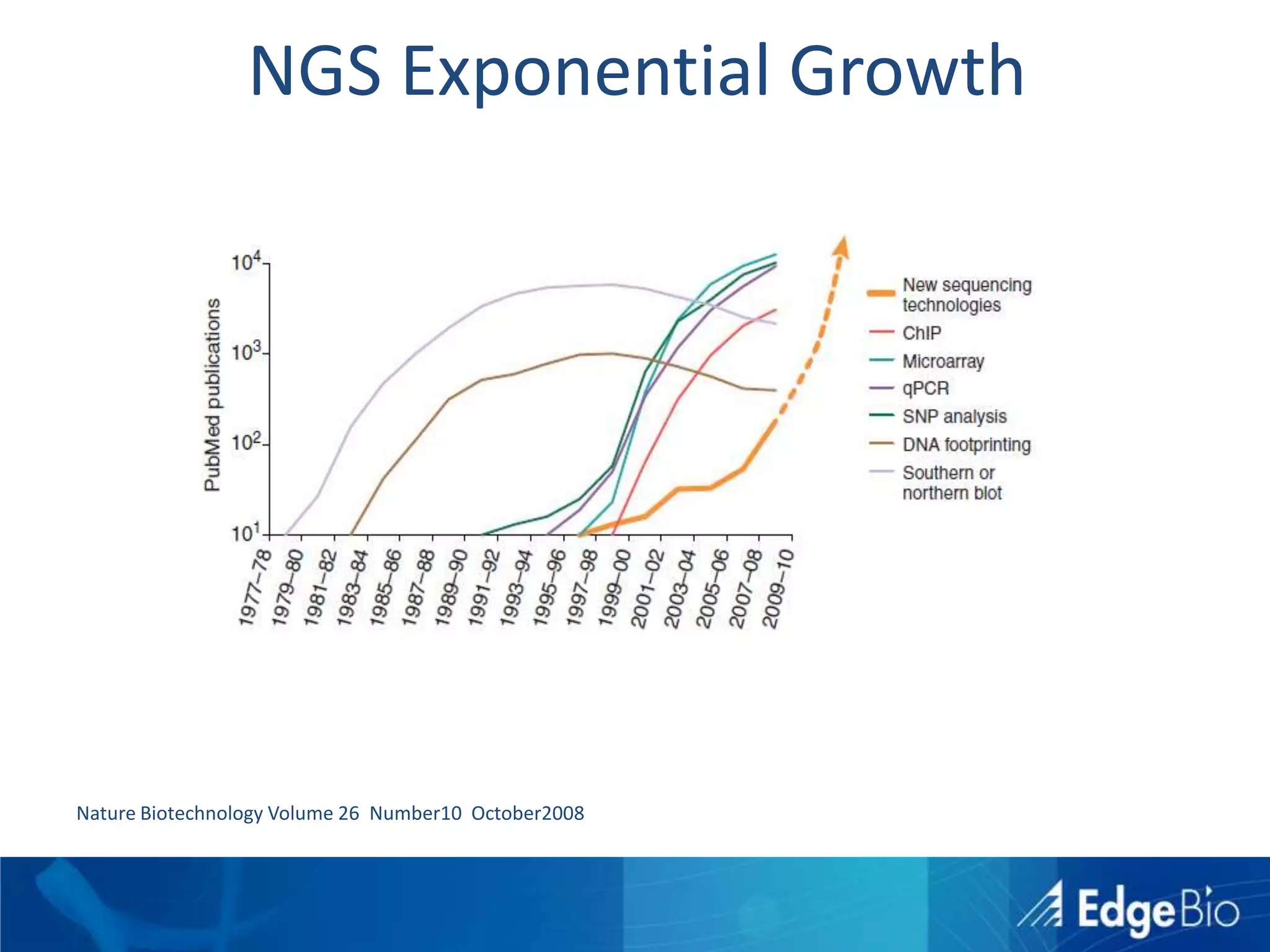
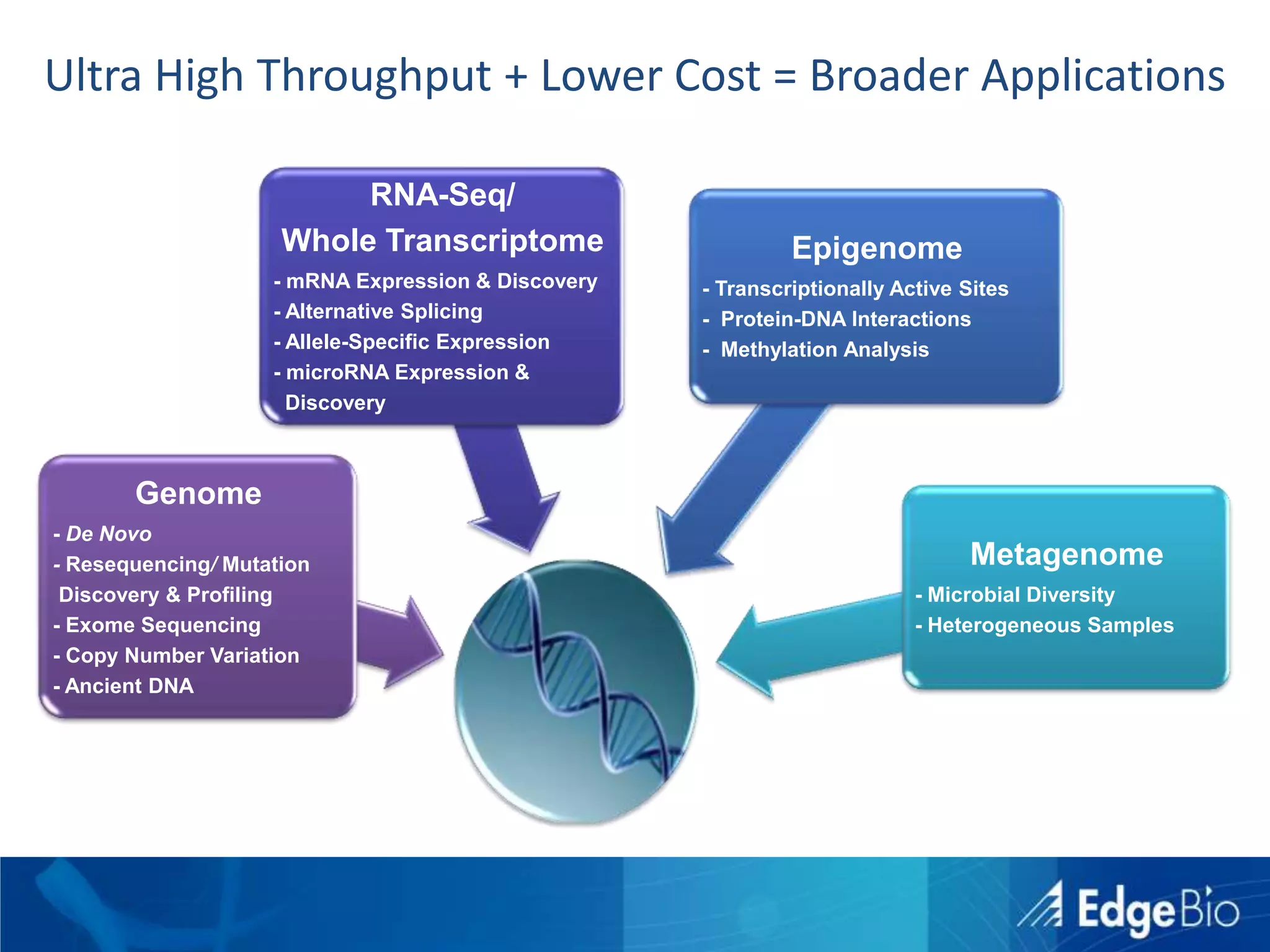
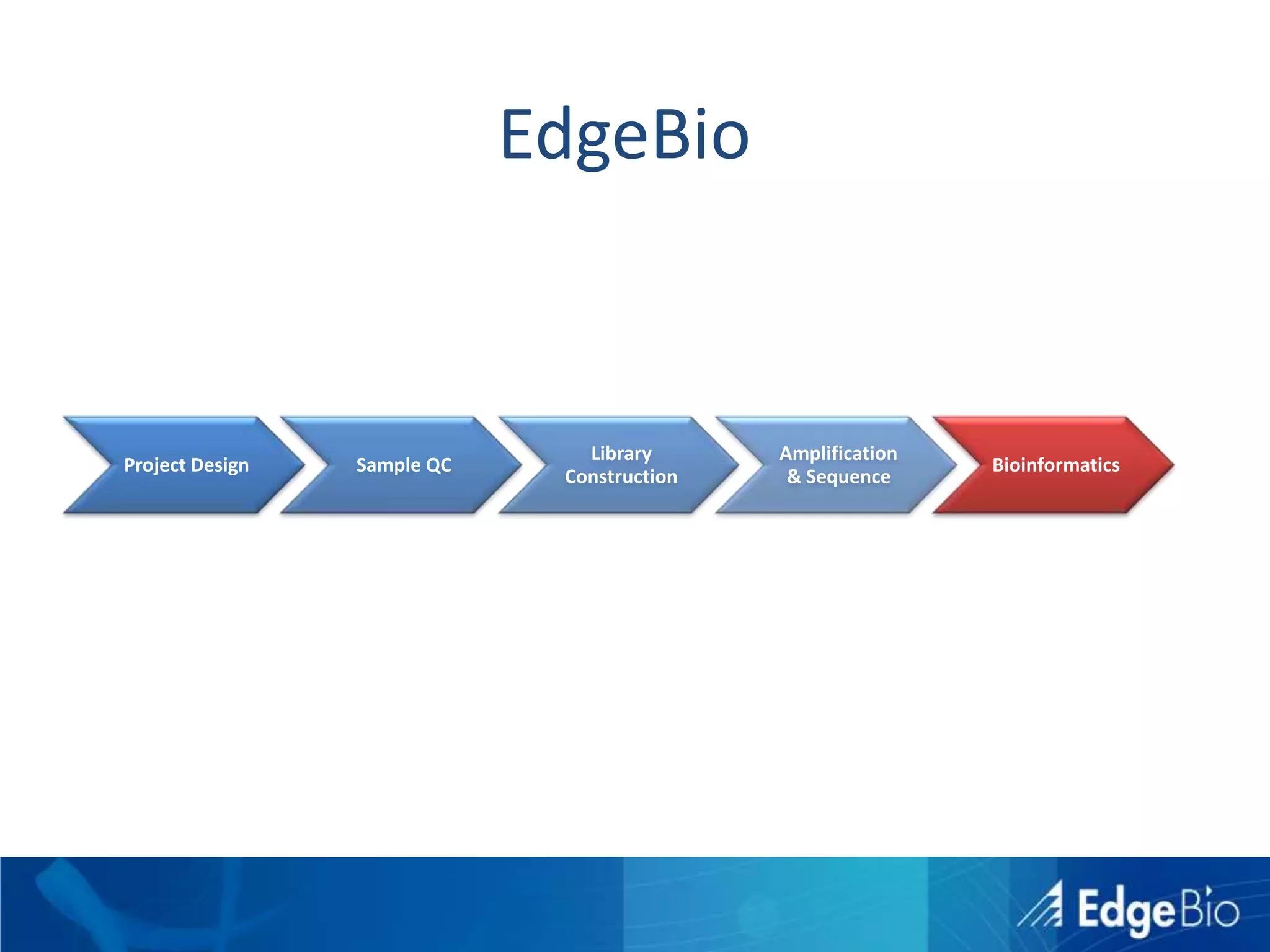
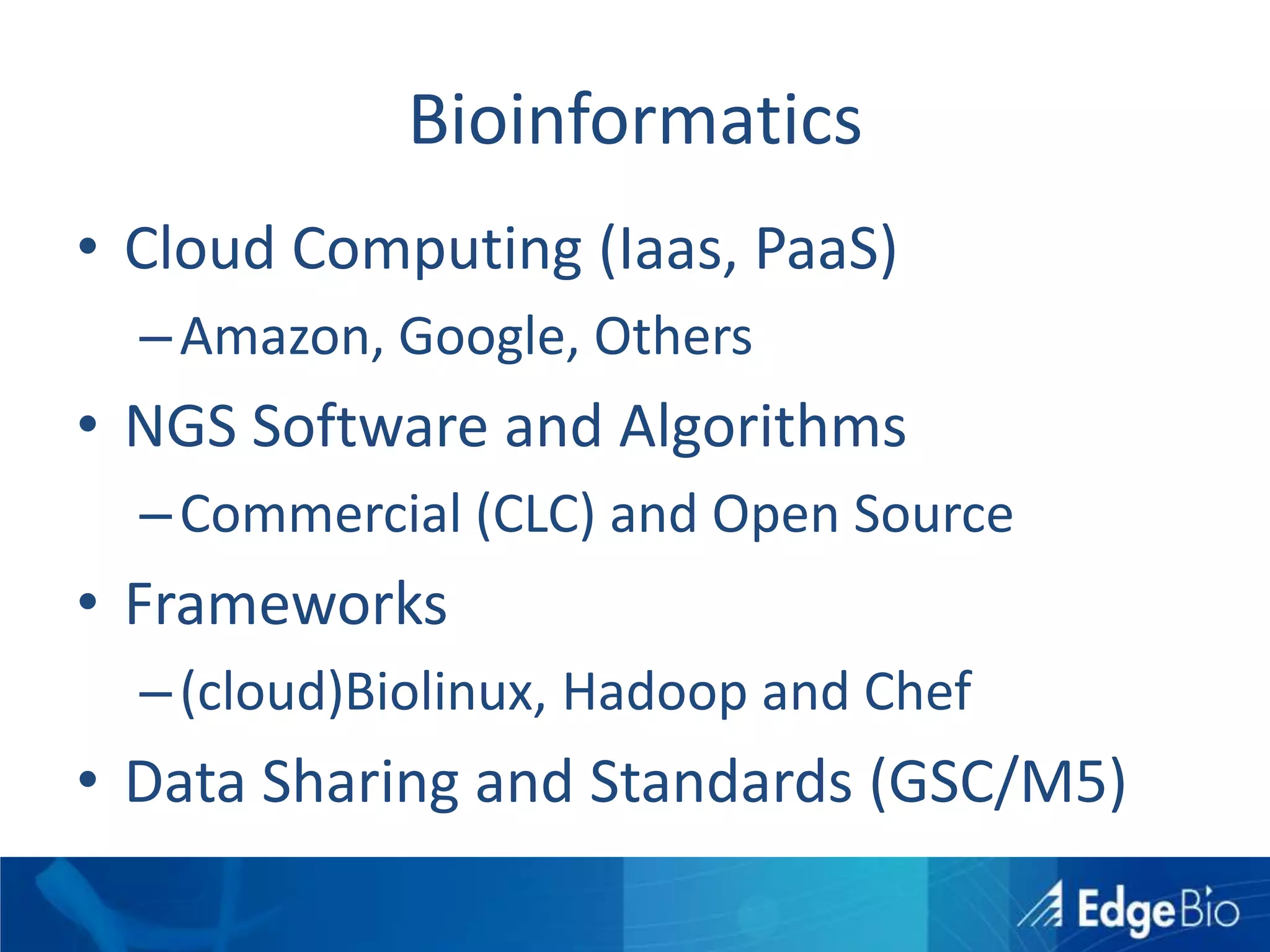
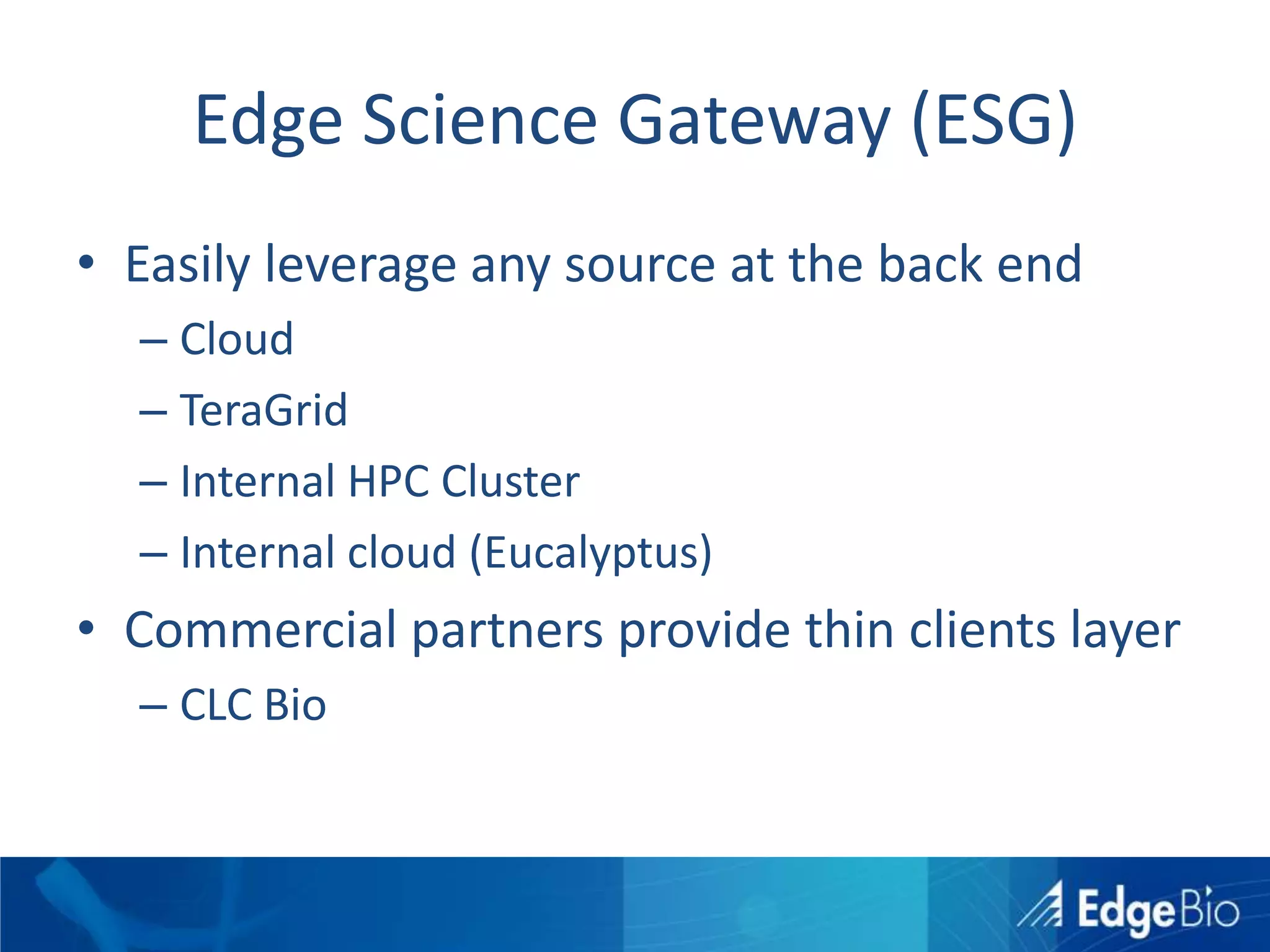
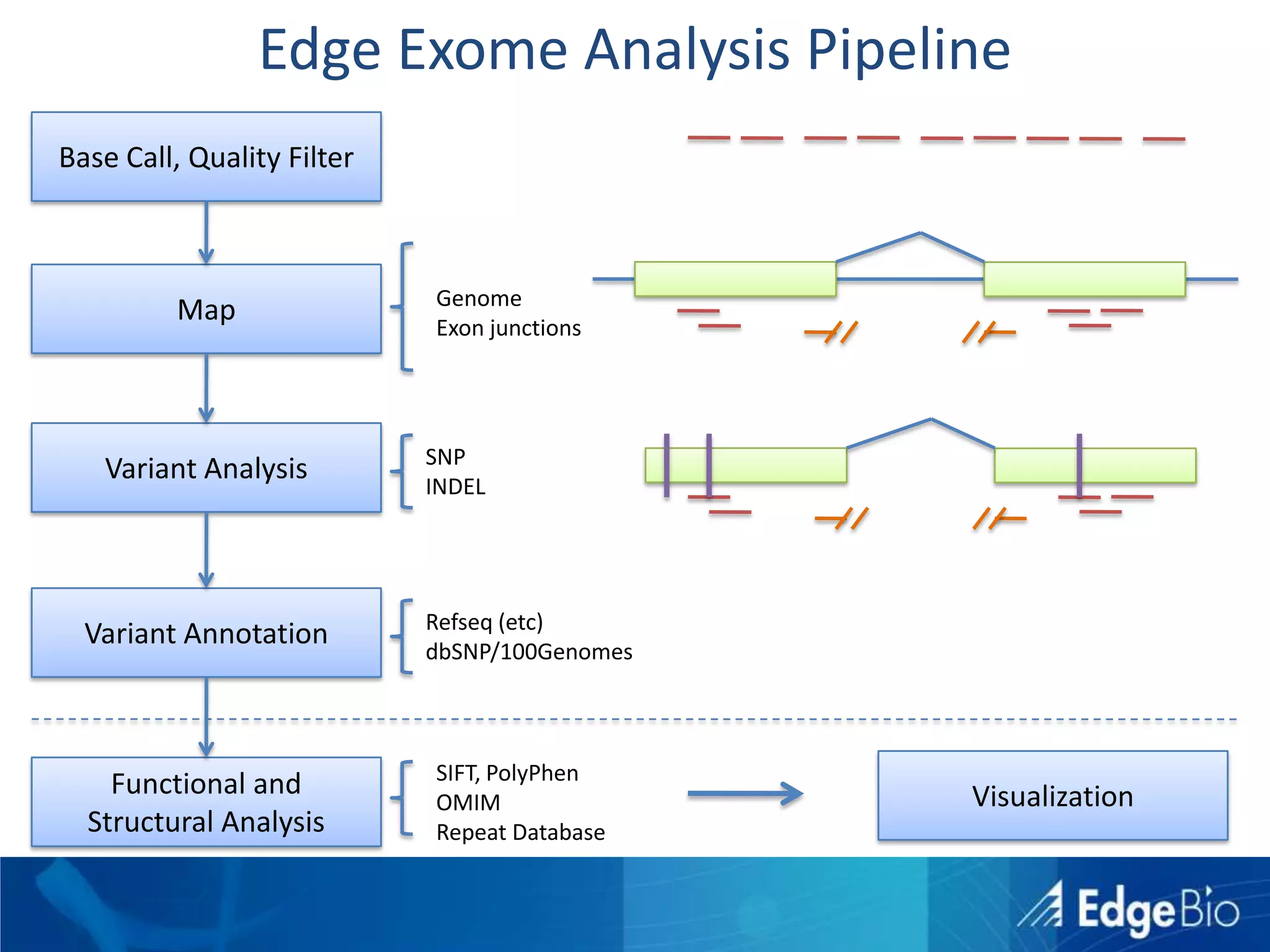
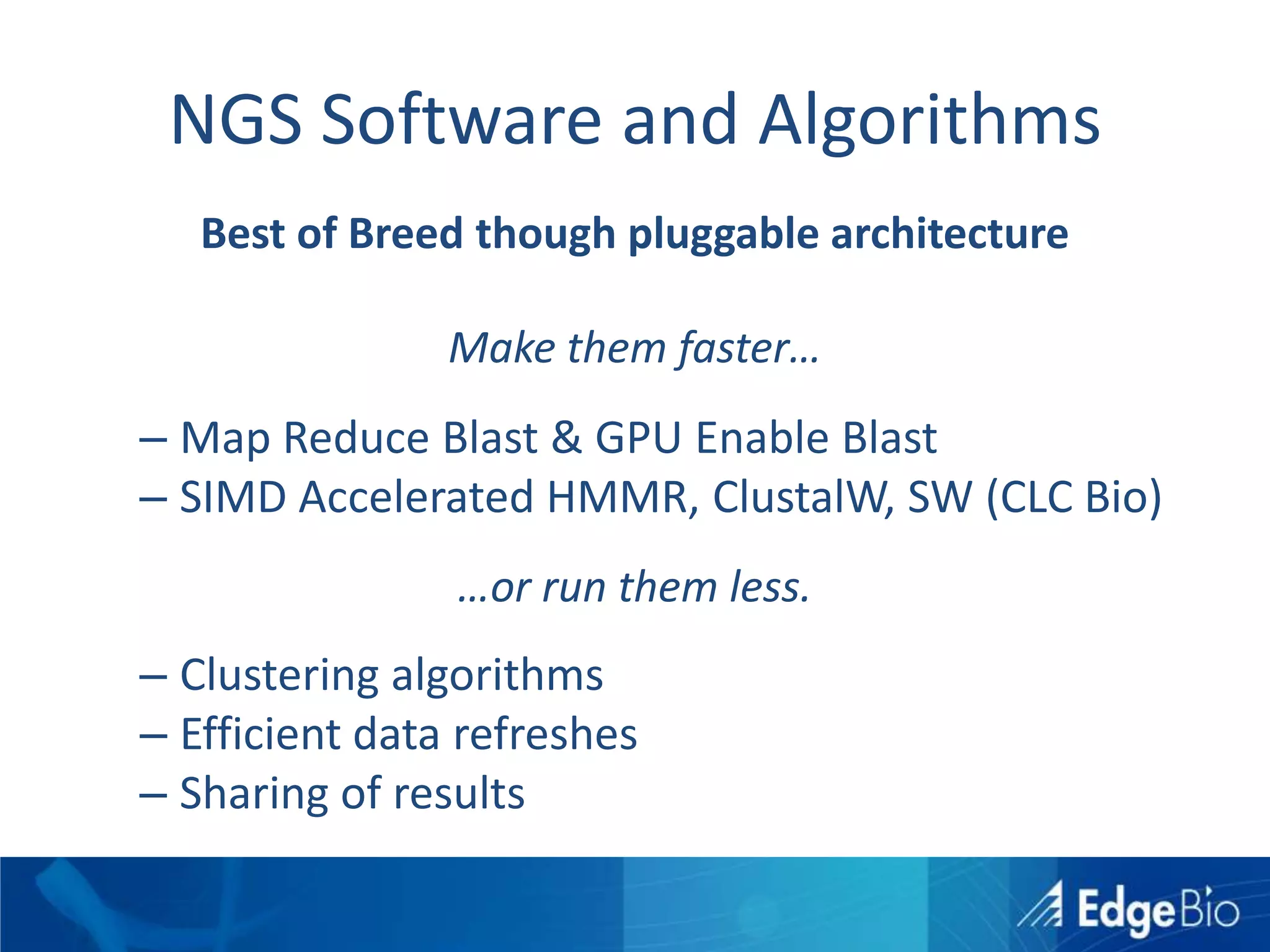
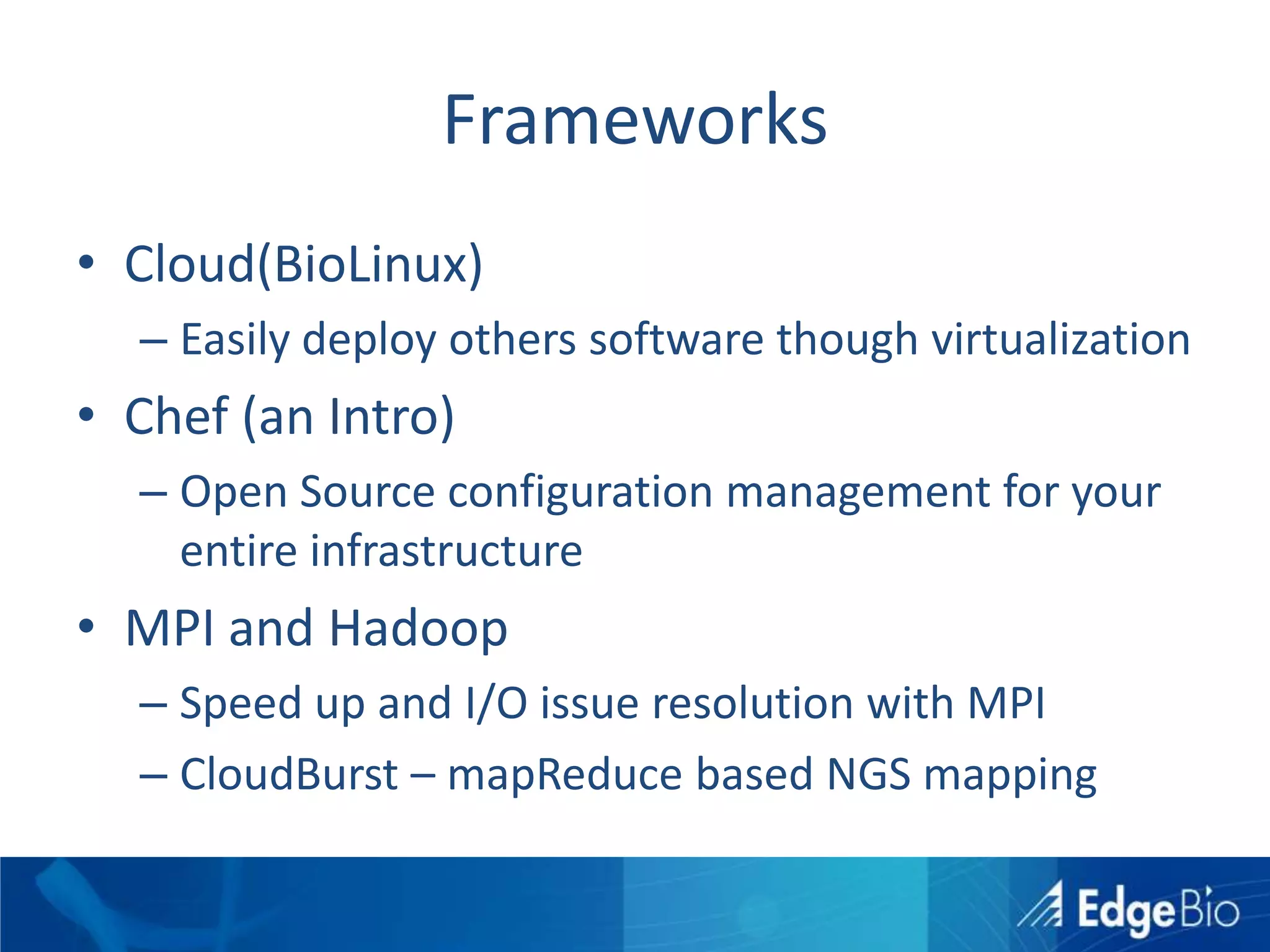
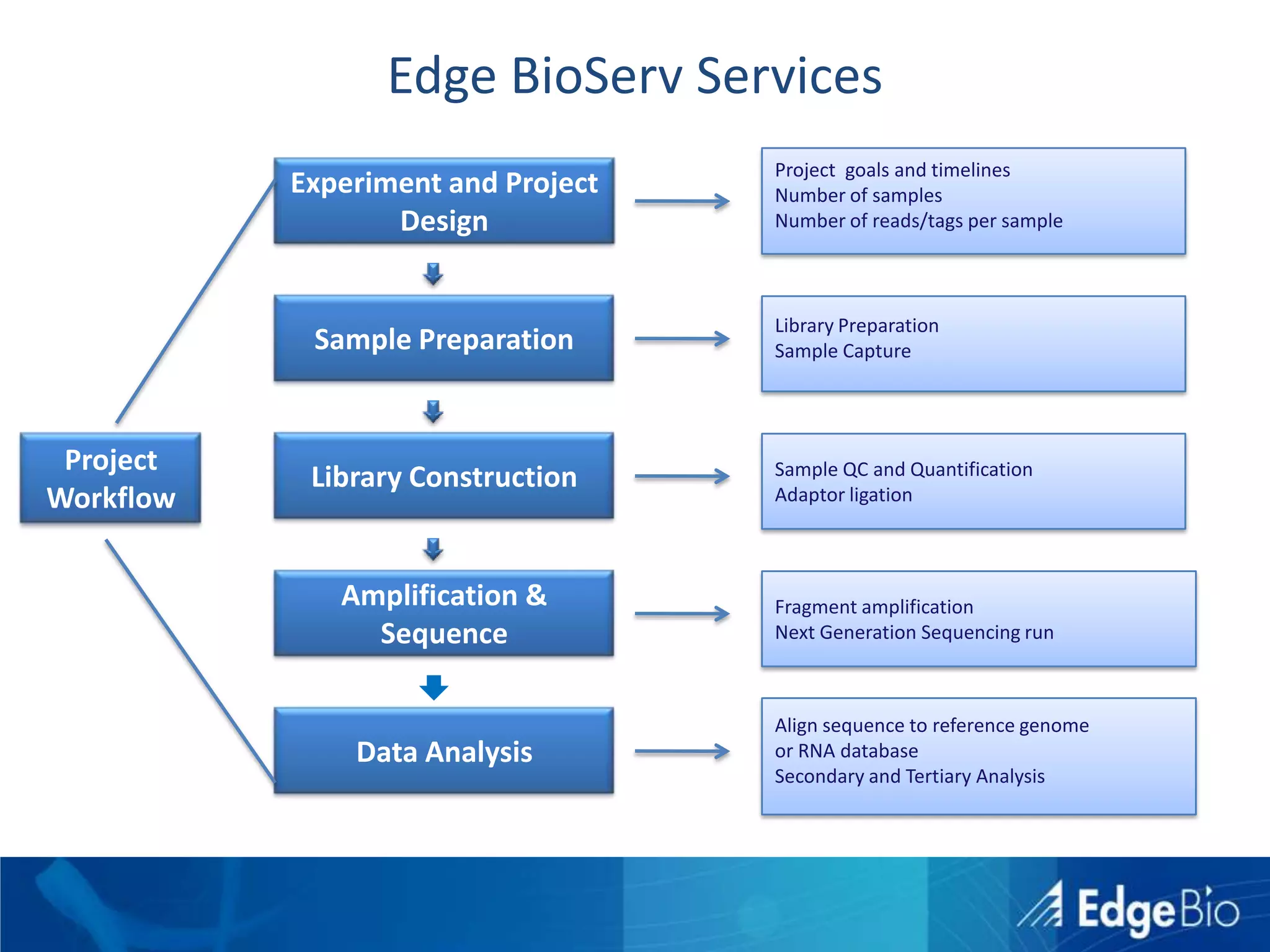
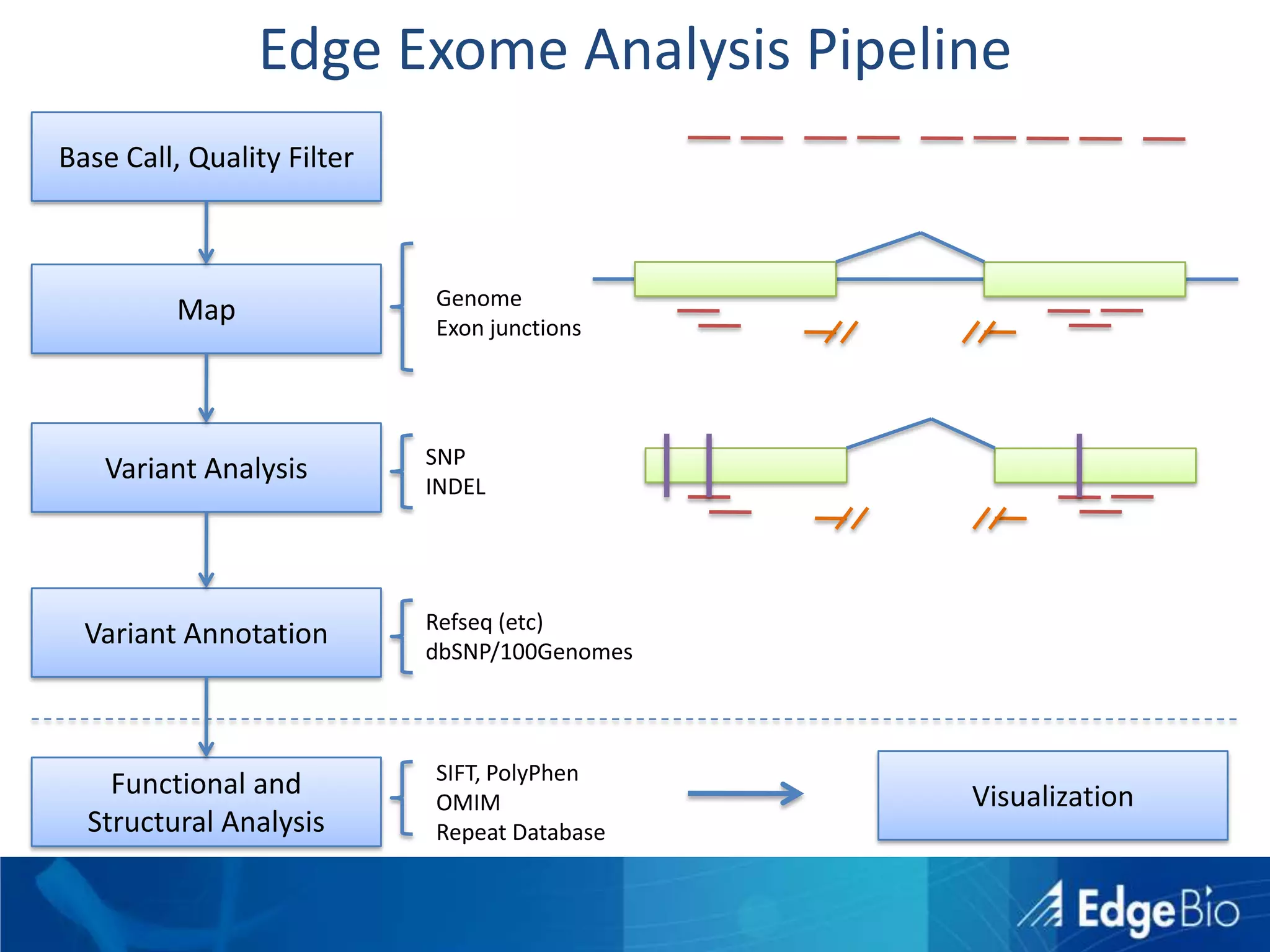
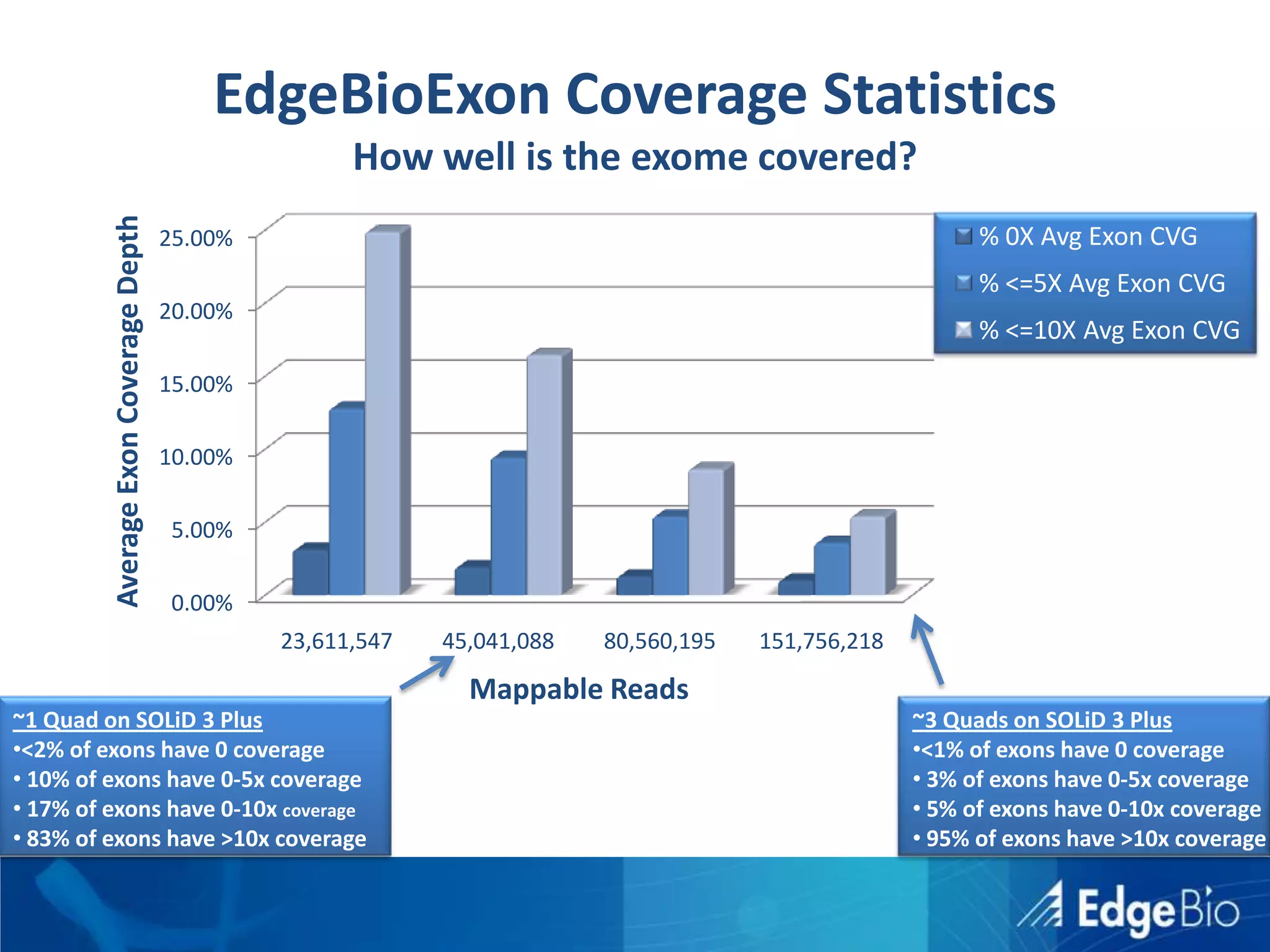
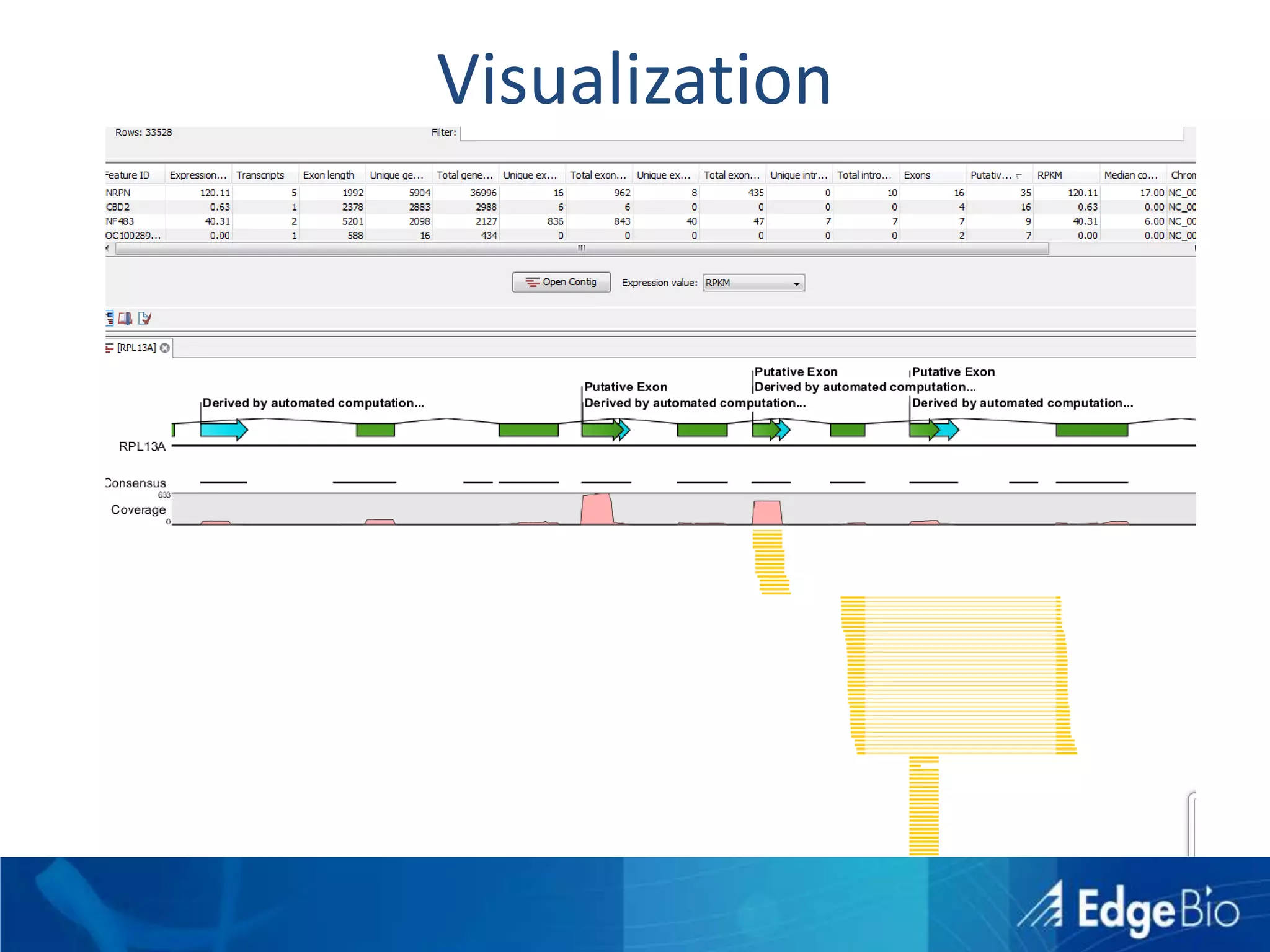
This document discusses science as a service (SaaS) and next-generation sequencing (NGS) data analysis. It summarizes challenges with exponential growth of NGS data, including data management, storage, analysis and sharing. It introduces Edge Bio's approach of distributing computational problems across cloud and HPC resources to avoid bottlenecks. Edge Bio provides full-service NGS analysis pipelines leveraging both commercial and open-source tools.