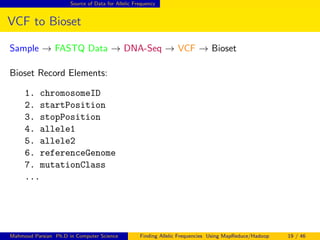
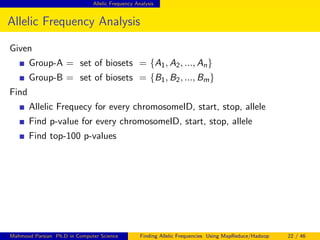
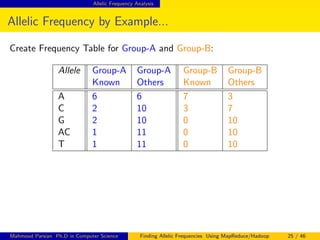
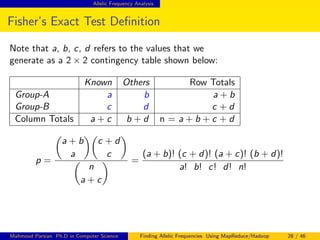
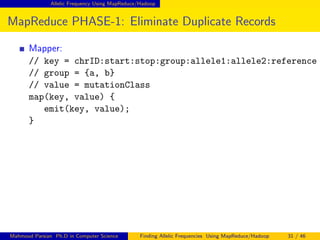
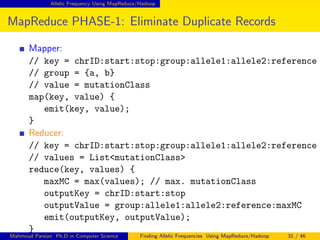
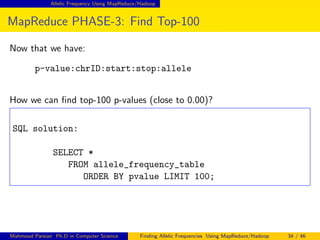
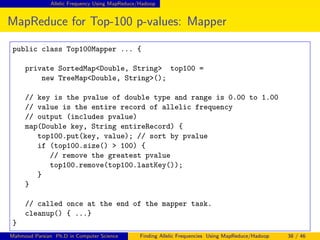
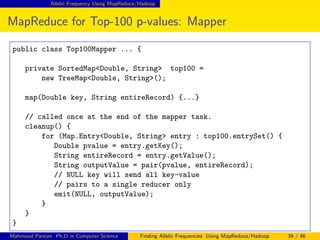
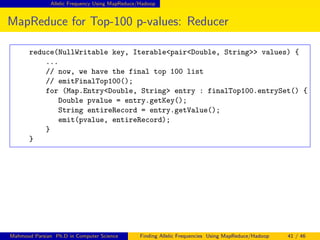
This document discusses finding allelic frequencies using MapReduce/Hadoop. It begins with an introduction of the presenter and an overview of analyzing genetic variants identified through sequencing to estimate allelic frequency differences between patient groups. It then provides definitions for key genetic terms. The document describes the source data in Variant Call Format files and converting to bioset records. It outlines performing allelic frequency analysis on two groups of biosets to find frequencies, p-values, and top differences between the groups.



































![Allelic Frequency Analysis
Fisher’s Exact Test Using R
# R (version 2.15.1)
> mytable = rbind( c(6, 6), c(7, 3) );
> mytable
[,1] [,2]
[1,] 6 6
[2,] 7 3
> fisher.test(mytable)
Fisher’s Exact Test for Count Data
data: mytable
p-value = 0.4149
Mahmoud Parsian Ph.D in Computer Science Finding Allelic Frequencies Using MapReduce/Hadoop 27 / 46](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hadooppaper20140402-160824184117/85/Finding-Allelic-Frequencies-Using-MapReduce-Hadoop-42-320.jpg)











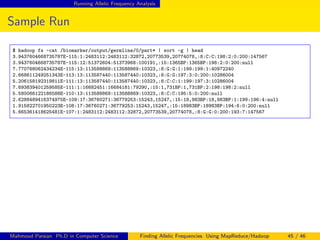
![Running Allelic Frequency Analysis
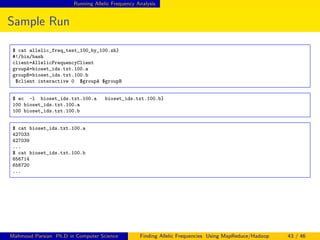
Sample Run
$ ./allelic_freq_test_100_by_100.sh
Wed Feb 12 15:27:10 PST 2014
Feb 12 2014 15:27:10 [INFO ] [AllelicFrequencyClient] - executionType: interactive
Feb 12 2014 15:27:10 [INFO ] [AllelicFrequencyClient] - requestID: 0
Feb 12 2014 15:27:10 [INFO ] [AllelicFrequencyClient] - GroupA: bioset_ids.txt.100.a
Feb 12 2014 15:27:10 [INFO ] [AllelicFrequencyClient] - GroupB: bioset_ids.txt.100.b
...
Feb 12 2014 15:27:12 [main] [INFO ] [JobClient] - Running job: job_201401170112_0644
Feb 12 2014 15:27:13 [main] [INFO ] [JobClient] - map 0% reduce 0%
Feb 12 2014 15:27:32 [main] [INFO ] [JobClient] - map 11% reduce 0%
...
Feb 12 2014 15:28:39 [main] [INFO ] [JobClient] - map 100% reduce 94%
Feb 12 2014 15:28:40 [main] [INFO ] [JobClient] - map 100% reduce 100%
Feb 12 2014 15:28:45 [main] [INFO ] [JobClient] - Job complete: job_201401170112_0644
...
Feb 12 2014 15:28:45 [main] [INFO ] [JobClient] - Map-Reduce Framework
Feb 12 2014 15:28:45 [main] [INFO ] [JobClient] - Map output materialized bytes=134376521
Feb 12 2014 15:28:45 [main] [INFO ] [JobClient] - Map input records=9,352,649
Feb 12 2014 15:28:45 [main] [INFO ] [JobClient] - Reduce input groups=134,894
Feb 12 2014 15:28:45 [main] [INFO ] [JobClient] - Reduce output records=53,557
Feb 12 2014 15:28:45 [main] [INFO ] [AllelicFrequencyDriver] - run(): jobSucceeded=true
Feb 12 2014 15:28:45 [main] [INFO ] [AllelicFrequencyDriver] - run(): Job Finished in 94.423 seconds
Feb 12 2014 15:28:45 [main] [INFO ] [AllelicFrequencyDriver] - submitJob(): runStatus=0
Mahmoud Parsian Ph.D in Computer Science Finding Allelic Frequencies Using MapReduce/Hadoop 44 / 46](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hadooppaper20140402-160824184117/85/Finding-Allelic-Frequencies-Using-MapReduce-Hadoop-62-320.jpg)