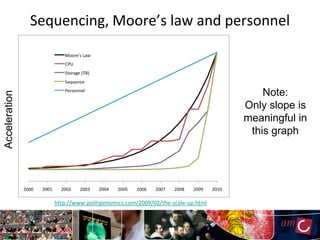
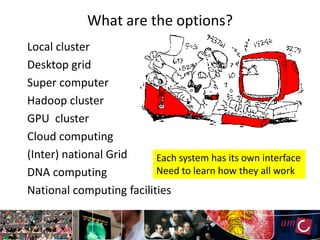
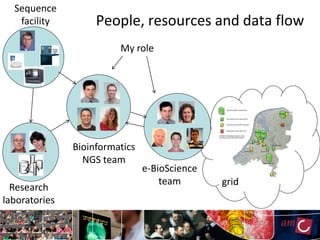
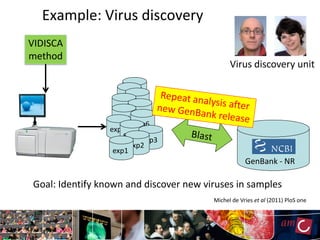
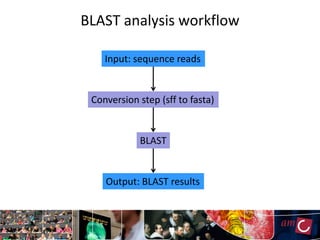
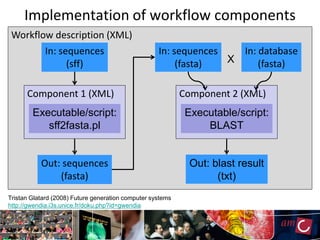
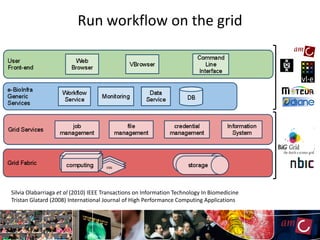
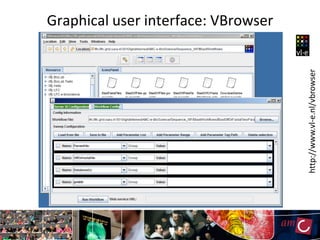
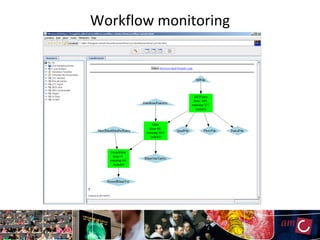
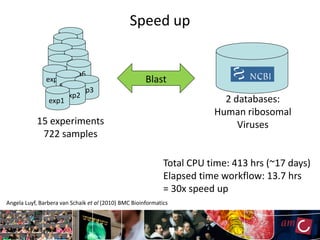
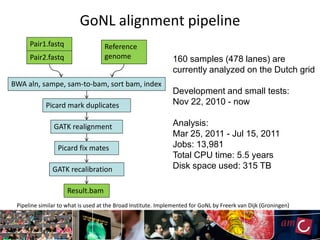
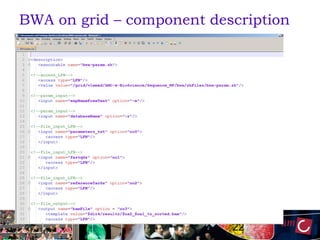
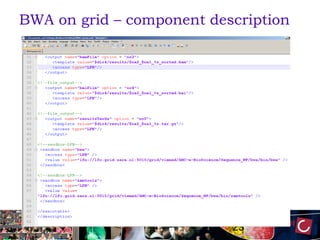
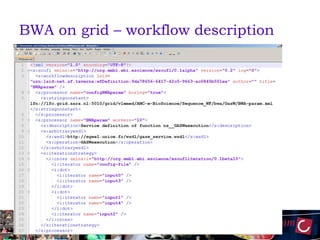
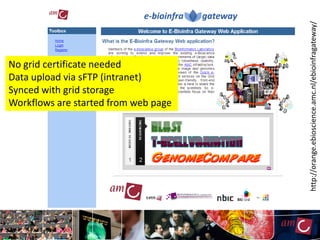
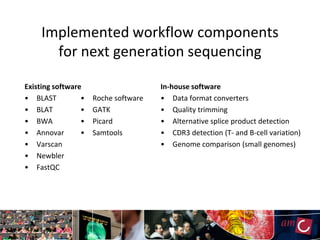
The document outlines the development of a production platform for DNA sequence analysis using grid computing and workflow technology, focusing on various methods like virus discovery and analyzing larger datasets. It highlights the implementation of bioinformatics workflows on the Dutch Grid, detailing the challenges and benefits of using such technology for next-generation sequencing (NGS) data analysis. The document emphasizes the need for collaboration, resource sharing, and agile development to improve bioinformatics research and infrastructure.